STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Statistical analyses were conducted using Stata version 13.1 (StataCorp, LP). All analyses took into account the complex survey design of the NIS. Discharge weights, strata, and cluster variables were included to correctly estimate variance and to produce national estimates from the stratified sample. Pearson’s chi-squared test was used to compare age, sex, ECI, and insurance status between RA and non-RA patients undergoing shoulder arthroplasty.
Bivariate and multivariate logistic regressions were subsequently used to compare the rates of adverse events between RA and non-RA patients undergoing shoulder arthroplasty (non-RA cases were used as the reference). Multivariate linear regressions were used to compare hospital length of stay and hospitalization costs between RA and non-RA patients undergoing shoulder arthroplasty. The multivariate regressions were adjusted for baseline differences in age, sex, ECI, and insurance status. Cochran-Armitage tests for trend were used to assess trends over time. All tests were 2-tailed, and the statistical difference was established at a 2-sided α level of 0.05 (P < .05).
RESULTS
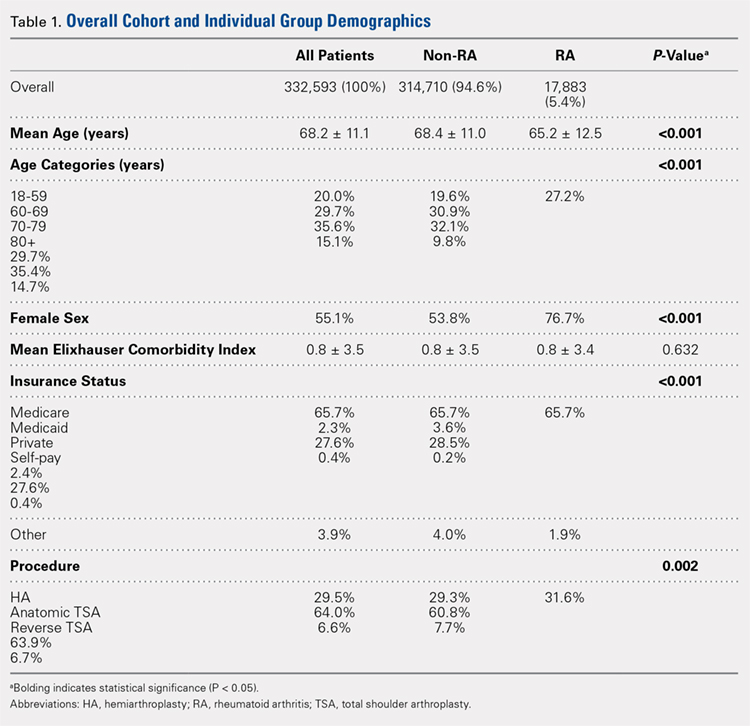
Overall, we identified 332,593 patients who underwent shoulder arthroplasty in the US between 2002 and 2011, of which 17,883 patients (5.4%) had a diagnosis of RA. In comparison with non-RA patients undergoing shoulder arthroplasty, patients with RA at the time of shoulder arthroplasty were significantly younger (65.2 ± 12.5 years vs 68.4 ± 11.0 years, P < .001), included a significantly greater proportion of female patients (76.7% vs 53.8%, P < .001), and included a significantly higher proportion of patients with Medicaid insurance (3.6% vs 2.3%, P < .001). There were no significant differences in the mean ECI between patients with and without a diagnosis of RA (Table 1). As depicted in Table 1, there were significant differences in the utilization of specific shoulder arthroplasty types between patients with and without RA, whereby a significantly greater proportion of RA patients underwent hemiarthroplasty (HA) (31.6% vs 29.3%, P = .002) and reverse TSA (7.7% vs 6.6%, P = .002), whereas a significantly greater proportion of non-RA patients underwent anatomic SA (64.0% vs 60.8%, P = .002).
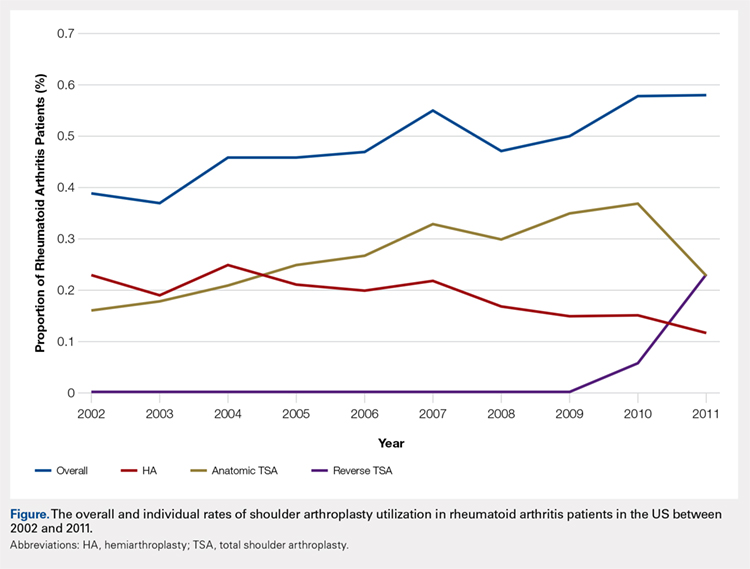
Over the study period from 2002 to 2011, there was a significant increase in the overall utilization of shoulder arthroplasty in RA patients, as indicated by both the absolute number and the proportion of patients with a diagnosis of RA (P < .001) (Table 2, Figure). More specifically, 0.39% of RA patients underwent shoulder arthroplasty in 2002, as compared with 0.58% of RA patients in 2011 (P < .001) (Table 2). With respect to specific arthroplasty types, there was an exponential rise in the utilization of reverse TSA beginning in 2010 and a corresponding decrease in the rates of both HA and anatomic TSA (Table 2, Figure). In addition to changes in shoulder arthroplasty utilization over time among RA patients, we also observed a significant increase in the number of RA patients undergoing shoulder arthroplasty with a corresponding diagnosis of rotator cuff disease (9.7% in 2002 to 15.2% in 2011, P < .001).
Table 2. The Annual Utilization of Shoulder Arthroplasty Among Patients with a Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Proportion of RA patients | |||||
Year | Overall Rate of Shoulder Arthroplastya | HA | Anatomic TSA | Reverse TSA | |
2002 | 0.39 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0 | |
2003 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0 | |
2004 | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0 | |
2005 | 0.46 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0 | |
2006 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0 | |
2007 | 0.55 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0 | |
2008 | 0.47 | 0.17 | 0.30 | 0 | |
2009 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.35 | 0 | |
2010 | 0.58 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 0.06 | |
2011 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.23 | |
Absolute number of RA patients | |||||
2002 | 1295 | 768 | 527 | 0 | |
2003 | 1247 | 650 | 597 | 0 | |
2004 | 1667 | 906 | 761 | 0 | |
2005 | 1722 | 776 | 946 | 0 | |
2006 | 1847 | 794 | 1053 | 0 | |
2007 | 2249 | 910 | 1339 | 0 | |
2008 | 2194 | 799 | 1395 | 0 | |
2009 | 2407 | 724 | 1683 | 0 | |
2010 | 2869 | 722 | 1857 | 290 | |
2011 | 3193 | 649 | 1261 | 1283 | |
aRate determined as number of RA patients undergoing shoulder arthroplasty compared to the number of patients with an RA diagnosis in the stated calendar year.
Abbreviations: HA, hemiarthroplasty; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; TSA, total shoulder arthroplasty.
Continue to: Among patients with RA...