1. Theodore RF, Broadbent J, Nagin D, et al. Childhood to early-midlife systolic blood pressure trajectories: early-life predictors, effect modifiers, and adult cardiovascular outcomes. Hypertension . 2015;66:1108-1115. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05831
2. Lurbe E, Agabiti-Rosei E, Cruickshank JK, et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J Hypertens . 2016;34:1887-1920. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001039
3. Weaver DJ, Mitsnefes MM. Effects of systemic hypertension on the cardiovascular system. Prog Pediatr Cardiol
4. Ippisch HM, Daniels SR. Hypertension in overweight and obese children. Prog Pediatr Cardiol
5. Urbina EM, Lande MB, Hooper SR, et al. Target organ abnormalities in pediatric hypertension. J Pediatr doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.07.026
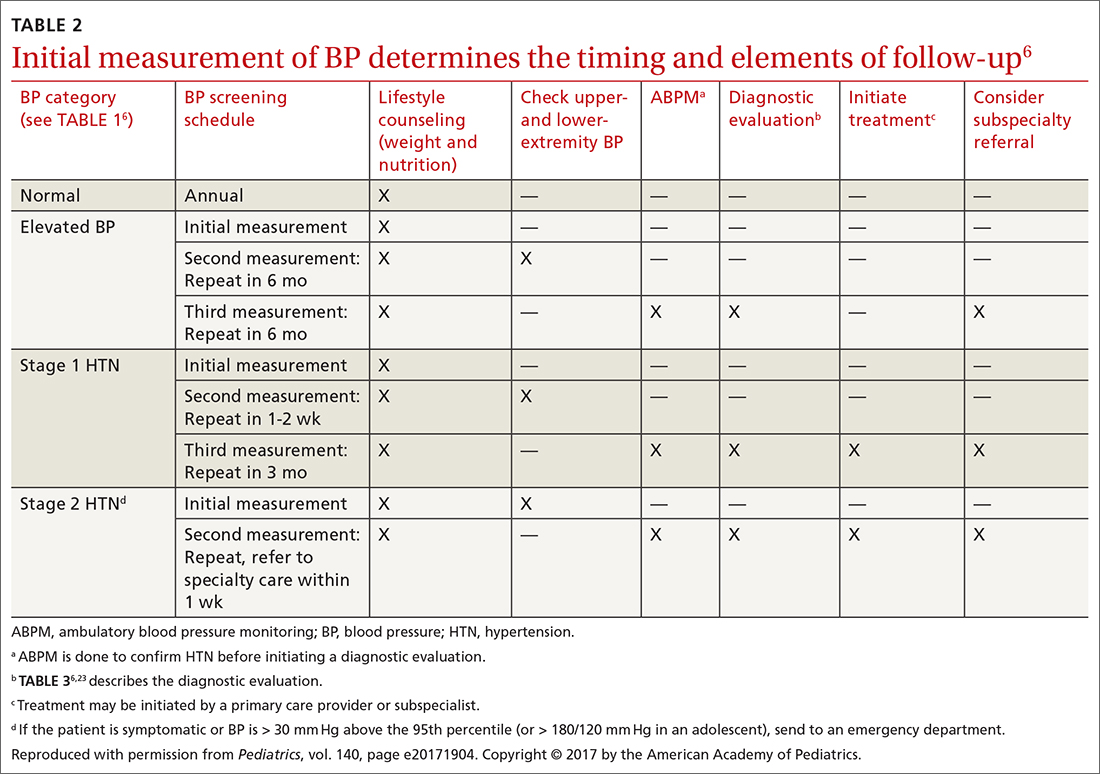
6. Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, et al; Subcommittee on Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children . Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics . 2017;140:e20171904 . doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-1904
7. Khoury M, Khoury PR, Dolan LM, et al. Clinical implications of the revised AAP pediatric hypertension guidelines. Pediatrics . 2018;142:e20180245. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-0245
8. Falkner B, Gidding SS, Ramirez-Garnica G, et al. The relationship of body mass index and blood pressure in primary care pediatric patients. J Pediatr . 2006;148:195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2005.10.030
9. Rodriguez BL, Dabelea D, Liese AD, et al; SEARCH Study Group. Prevalence and correlates of elevated blood pressure in youth with diabetes mellitus: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. J Pediatr . 2010;157:245-251.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.02.021
10. Shay CM, Ning H, Daniels SR, et al. Status of cardiovascular health in US adolescents: prevalence estimates from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) 2005-2010. Circulation . 2013;127:1369-1376. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001559
11. Archbold KH, Vasquez MM, Goodwin JL, et al. Effects of sleep patterns and obesity on increases in blood pressure in a 5-year period: report from the Tucson Children’s Assessment of Sleep Apnea Study. J Pediatr . 2012;161:26-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.12.034
12. Flynn JT, Mitsnefes M, Pierce C, et al; Chronic Kidney Disease in Children Study Group . Blood pressure in children with chronic kidney disease: a report from the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children study. Hypertension . 2008;52:631-637. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.110635
13. Martin RM, Ness AR, Gunnell D, et al; ALSPAC Study Team. Does breast-feeding in infancy lower blood pressure in childhood? The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Circulation . 2004;109:1259-1266. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000118468.76447.CE
14. Brickner ME, Hillis LD, Lange RA. Congenital heart disease in adults. N Engl J Med . 2000;342:256-263. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200001273420407
15. Chen X, Wang Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Circulation . 2008;117:3171-3180. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.730366
16. Sun SS, Grave GD, Siervogel RM, et al. Systolic blood pressure in childhood predicts hypertension and metabolic syndrome later in life. Pediatrics . 2007;119:237-246. doi: 10.1542/peds.2006-2543
17. Parker ED, Sinaiko AR, Kharbanda EO, et al. Change in weight status and development of hypertension. Pediatrics . 2016; 137:e20151662. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-1662
18. Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, et al; Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research . Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: Part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension . 2005;45:142-161. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000150859.47929.8e
19. Staley JR, Bradley J, Silverwood RJ, et al. Associations of blood pressure in pregnancy with offspring blood pressure trajectories during childhood and adolescence: findings from a prospective study. J Am Heart Assoc . 2015;4:e001422. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001422
20. Yang Q, Zhang Z, Zuklina EV, et al. Sodium intake and blood pressure among US children and adolescents. Pediatrics . 2012;130:611-619. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-3870
21. Le-Ha C, Beilin LJ, Burrows S, et al. Oral contraceptive use in girls and alcohol consumption in boys are associated with increased blood pressure in late adolescence. Eur J Prev Cardiol . 2013;20:947-955. doi: 10.1177/2047487312452966
22. Samuels JA, Franco K, Wan F, Sorof JM. Effect of stimulants on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure in children with ADHD: a double-blind, randomized, cross-over trial. Pediatr Nephrol . 2006;21:92-95. doi: 10.1007/s00467-005-2051-1
23. Wiesen J, Adkins M, Fortune S, et al. Evaluation of pediatric patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension: yield of diagnostic testing. Pediatrics . 2008;122:e988-993. doi: 10.1542/peds.2008-0365
24. Kapur G, Ahmed M, Pan C, et al. Secondary hypertension in overweight and stage 1 hypertensive children: a Midwest Pediatric Nephrology Consortium report. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) . 2010;12:34-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2009.00195.x
25. Anyaegbu EI, Dharnidharka VR. Hypertension in the teenager. Pediatr Clin North Am doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2013.09.011
26. Gandhi B, Cheek S, Campo JV. Anxiety in the pediatric medical setting. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2012.05.013
27. Farpour-Lambert NJ, Aggoun Y, Marchand LM, et al. Physical activity reduces systemic blood pressure and improves early markers of atherosclerosis in pre-pubertal obese children. J Am Coll Cardiol doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.030
28. Li JS, Baker-Smith CM, Smith PB, et al. Racial differences in blood pressure response to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in children: a meta-analysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther doi: 10.1038/clpt.2008.113
29. Singer PS. Updates on hypertension and new guidelines. Adv Pediatr doi: 10.1016/j.yapd.2019.03.009
30. Torrance B, McGuire KA, Lewanczuk R, et al. Overweight, physical activity and high blood pressure in children: a review of the literature. Vasc Health Risk Manag
31. DASH eating plan. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Accessed April 26, 2021. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/dash-eating-plan
32. Nutritional goals for age-sex groups based on dietary reference intakes and dietary guidelines recommendations (Appendix 7). In: US Department of Agriculture. Dietary guidelines for Americans, 2015-2020. 8th ed. December 2015;97-98. Accessed April 26, 2021. https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/2015-2020_Dietary_Guidelines.pdf
33. Asghari G, Yuzbashian E, Mirmiran P, et al. Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) dietary pattern is associated with reduced incidence of metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents. J Pediatr doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.03.077
34. Damasceno MMC, de Araújo MFM, de Freitas RWJF, et al. The association between blood pressure in adolescents and the consumption of fruits, vegetables and fruit juice–an exploratory study. J Clin Nurs doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2010.03608.x
35. Anderson KL. A review of the prevention and medical management of childhood obesity. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2017.08.003
36. Kumar S, King EC, Christison, et al; POWER Work Group. Health outcomes of youth in clinical pediatric weight management programs in POWER. J Pediatr . 2019;208:57-65.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.12.049
37. Gregoski MJ, Barnes VA, Tingen MS, et al. Breathing awareness meditation and LifeSkills® Training programs influence upon ambulatory blood pressure and sodium excretion among African American adolescents. J Adolesc Health doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2010.05.019
38. Escape Trial Group; Wühl E, Trivelli A, Picca S, et al. Strict blood-pressure control and progression of renal failure in children. N Engl J Med doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa090206 6