WASHINGTON – Red blood cell distribution width provides a novel tool for cardiovascular risk stratification in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Chang H. Kim, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
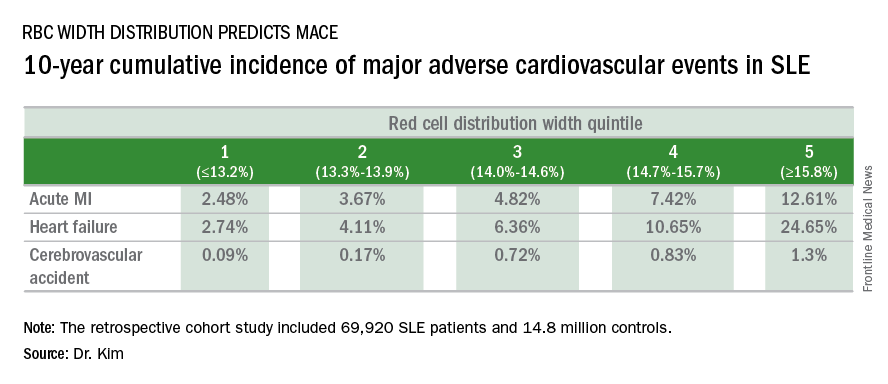
In a retrospective cohort study of nearly 70,000 patients with SLE, the 10-year rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) rose stepwise according to quintile of red cell distribution width (RDW) from 5.3% in patients with an RDW of 13.2% or less to 38.6% in those with an RDW of 15.8% or greater, according to Dr. Kim of Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland.
He utilized the Explorys database to determine the 10-year cumulative incidence of MACE – defined as acute MI, heart failure, or cerebrovascular accident – during 2007-2016 in 69,920 patients with SLE and 14,825,240 controls. Explorys is an 8-year-old Cleveland-based company that maintains a health care database incorporating 26 health care systems across the United States with nearly 50 million patients. It is part of IBM Watson Health.
The MACE rate in patients with SLE displayed a graded increase in association with RDW quintile as measured in a routine CBC. (See table.) MACE rates were significantly higher in male than female SLE patients, but the graded relationship between RDW quintile and 10-year incidence of MACE persisted after adjustment for gender and the presence of anemia.
A graded association between RDW quintile and MACE also was noted in the control group of nearly 15 million individuals, but the absolute incidence of MACE in the non-SLE controls was far lower.
Dr. Kim reported having no financial conflicts regarding this unfunded study.