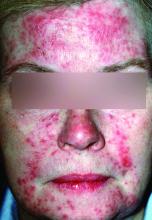
Caffeinated coffee intake is linked to a decreased incidence of rosacea, results of a large, observational study suggest.
Increased levels of caffeinated coffee consumption were associated with progressively lower levels of incident rosacea in a study of more than 82,000 participants representing more than 1.1 million person-years of follow-up.
By contrast, caffeine from other foods was not associated with rosacea incidence, reported Wen-Qing Li, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and his coinvestigators. Those findings may have implications for the “causes and clinical approach” to rosacea.
“Our findings do not support limiting caffeine intake as a preventive strategy for rosacea,” they concluded in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
This is not the first study looking for potential links between rosacea and caffeine or coffee intake. However, previous studies didn’t distinguish between caffeinated coffee versus other beverages, and only one previous study made a distinction between the amounts of caffeine and coffee consumed, according to the authors.
Their research was based on data from the Nurses’ Health Study II, a prospective cohort study started in 1989. They looked specifically at 82,737 women who, in 2005, responded to the question about whether they had been diagnosed with rosacea. They identified 4,945 incident rosacea cases over the 1,120,051 person-years of follow-up.
A significant inverse association was found between caffeinated coffee intake and rosacea: Individuals who consumed four or more servings a day had a significantly lower risk of rosacea, compared with those who consumed one or fewer servings per month (hazard ratio, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.69-0.87; P less than .001). They also found a dose-dependent effect, with the absolute risk of rosacea decreased by 131 per 100,000 person-years with at least four daily servings of caffeinated coffee, compared with under one serving a month.
By contrast, decaffeinated coffee was not associated with a reduced risk of rosacea, and in further analysis, the investigators found that there was no significant inverse association when they looked just at caffeine intake from sources other than coffee, such as chocolate, tea, and soda.
Caffeine could influence rosacea incidence by one of several mechanisms, including its effect on vascular contractility, the investigators hypothesized. “Increased caffeine intake may decrease vasodilation and consequently lead to diminution of rosacea symptoms.”
However, caffeine also has documented immunosuppressant effects that could possibly decrease rosacea-associated inflammation and has been shown to modulate hormone levels. “Hormonal factors have been implicated in the development of rosacea, and caffeine can modulate hormone levels,” they wrote.
Two study authors reported disclosures related to AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas Pharma, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer, among others. Funding for the study came from several sources, including National Institutes of Health grants for the Nurses’ Health Study II.
SOURCE: Li W-Q et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2018 Oct 17. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3301.