Benign nonmelanocytic lesions
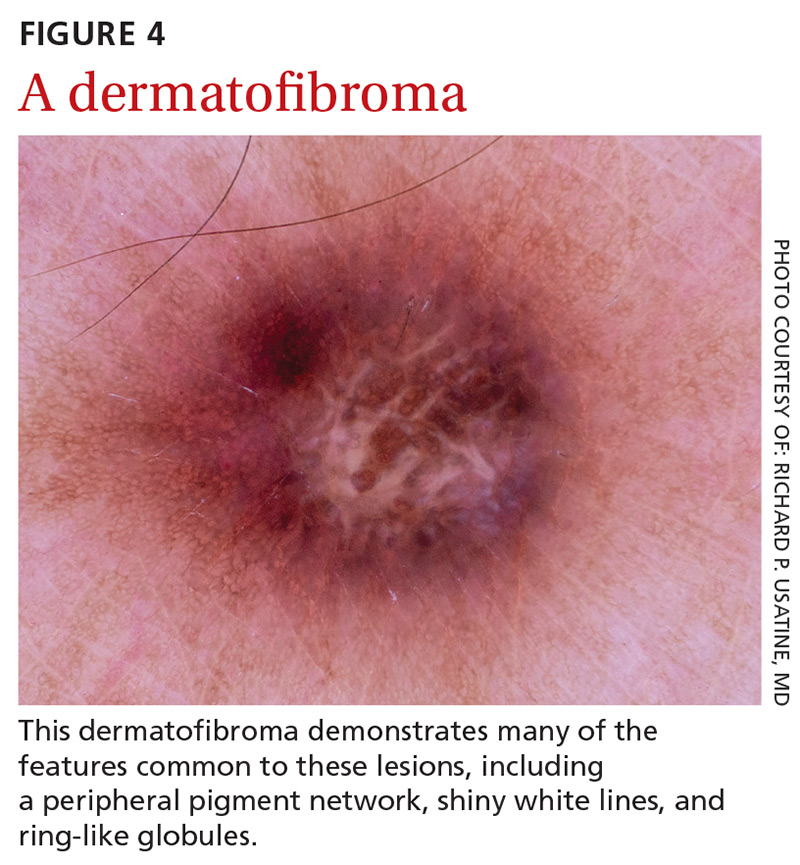
Dermatofibromas are benign symmetric lesions that feel firm and may dimple upon application of lateral pressure. They are fibrotic scar-like lesions that present with 1 or more of the following dermoscopic features (FIGURE 4):
- peripheral pigment network, due to increased melanin in keratinocytes
- homogeneous brown pigmented areas
- central scar-like area
- shiny white lines
- vascular structures (ie, dotted, polymorphous vessels), usually seen within the scar-like area
- ring-like globules, usually seen in the zone between the scar-like depigmentation and the peripheral network. They correspond to widened hyperpigmented rete ridges.
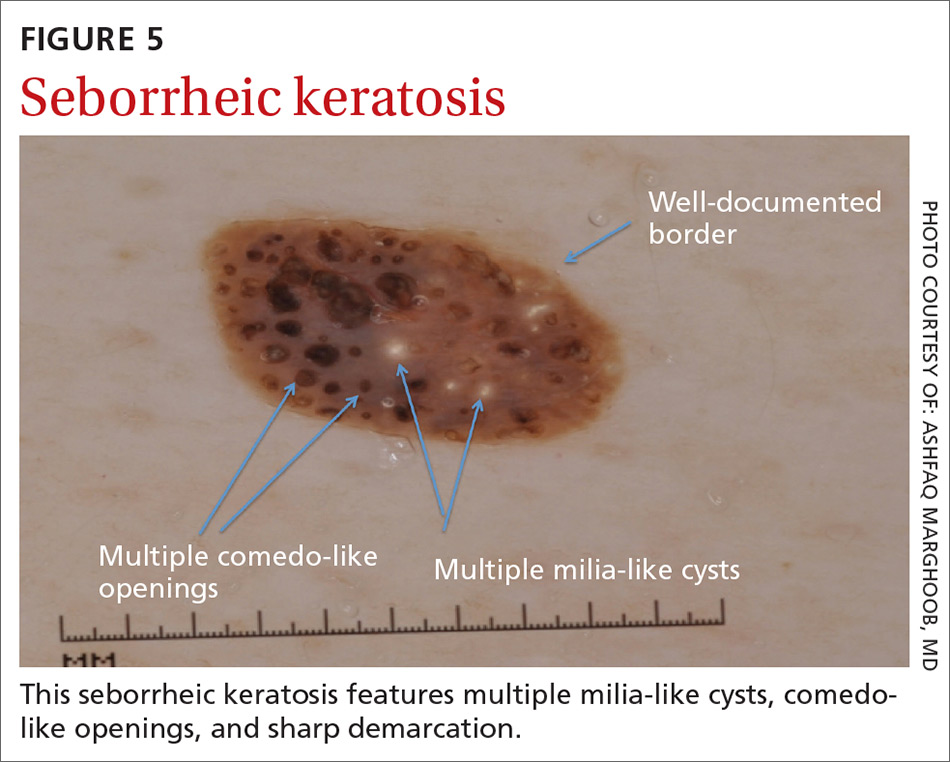
Seborrheic keratosis (SK) is a benign skin growth that often has a stuck-on appearance (FIGURE 5). Features often include:
- multiple (>2) milia-like cysts
- comedo-like openings
- a network-like structure that corresponds to gyri and sulci and which in some cases can create a cerebriform pattern
- fingerprint-like structures
- moth-eaten borders
- jelly sign. This consists of semicircular u-shaped structures that have a smudged appearance and are aligned in the same direction. The appearance resembles jelly as it is spread on a piece of bread.
- hairpin (looped or twisted-looped) vessels surrounded by a white halo.
Other clues include a sharp demarcation and a negative wobble sign (which we’ll describe in a moment). The presence or absence of a wobble sign is determined by using a dermatoscope that touches the skin. Mild vertical pressure is applied to the lesion while moving the scope back and forth horizontally. If the lesion slides across the skin surface, the diagnosis of an epidermal keratinocytic tumor (ie, SK) is favored. If, on the other hand, the lesion wobbles (rolls back and forth), then the diagnosis of a neoplasm with a dermal component (ie, intradermal or compound nevus) is more likely.
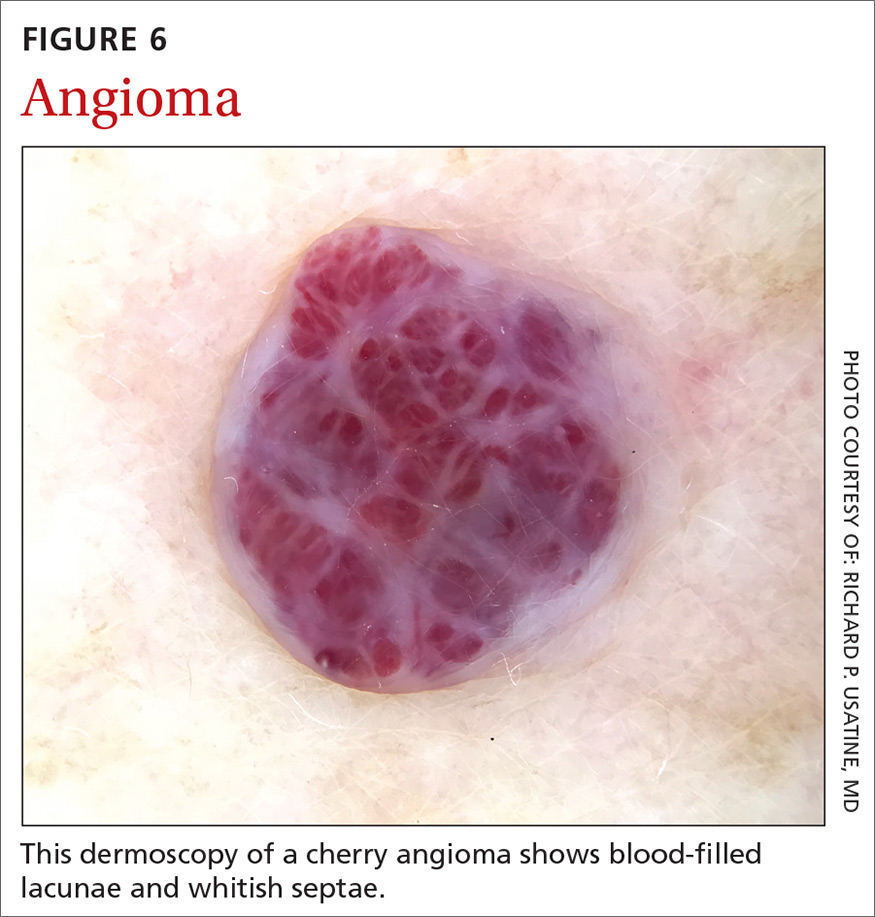
Angiomas and angiokeratomas. Angiomas demonstrate lacunae that are often separated by septae (FIGURE 6). Lacunae can vary in size and color. They can be red, red-white, red-blue, maroon, blue, blue-black, or even black (when thrombosis is present).
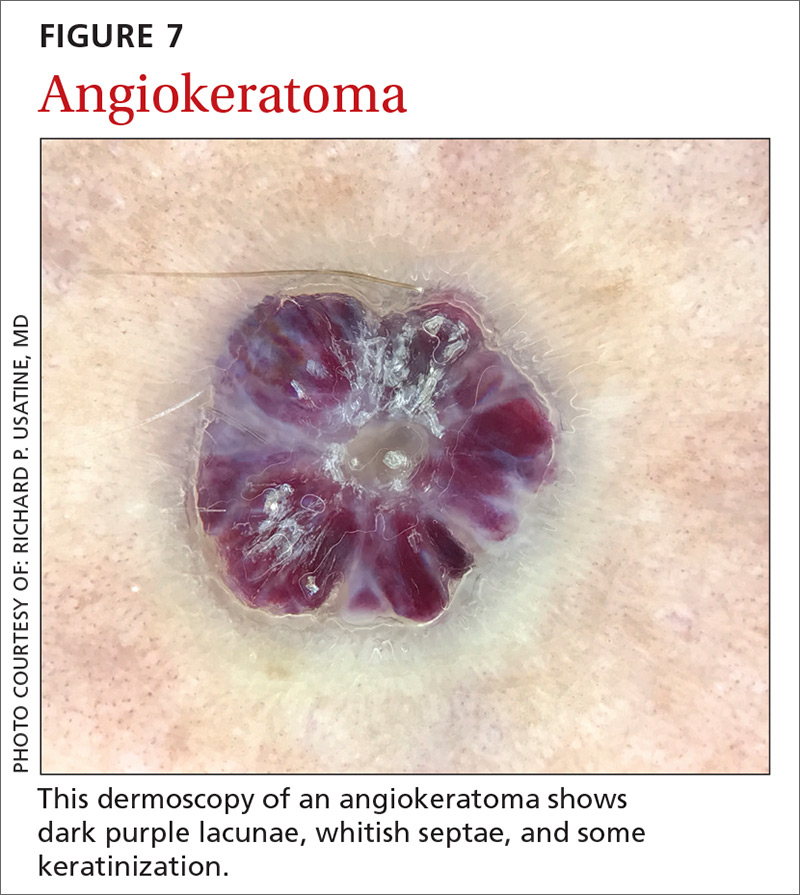
Angiokeratomas (FIGURE 7) can reveal lacunae of varying colors including black, red, purple, and maroon. In addition, a blue-whitish veil, erythema, and hemorrhagic crusts can be present.
Continue to: Sebaceous hyperplasia...