NEW ORLEANS – The incidence of acute otitis media has decreased by 25% to 35% in the past decade, thanks largely to the widespread and near universal use of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, according to Ellen R. Wald, MD.
“To a smaller degree, it is also attributable to the use of influenza vaccine, and to the use of more stringent diagnostic criteria,” Dr. Wald, who chairs the department of pediatrics at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. “The fact that we are decreasing the number of episodes of otitis media in children in the first year of life means that we’re going to have fewer otitis-prone children and therefore less of a need for tympanostomy tubes, either as a solution to the problem of recurrence of acute otitis media (AOM) or for the problem of persistent effusion.”
said Dr. Wald, pediatrician-in-chief at the American Family Children’s Hospital in Madison. She noted that OME is a nonbacterial inflammatory state that usually resolves spontaneously. It tends to occur before or after AOM, and often without ever progressing to AOM. “Its principal importance is as a cause of hearing loss and as a confounder in the diagnosis AOM,” she explained. “Because it is a nonbacterial process, antibiotics are not indicated in the management of OME. In contrast, children with AOM have a bacterial infection that will benefit from the use of antimicrobials.”*
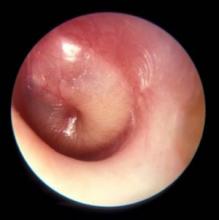
Middle ear effusion is common to both OME and AOM, she continued. To discriminate between the two conditions, clinicians must look for signs of acute inflammation of the tympanic membrane, “which we expect to see in AOM,” she said. “The most powerful sign of inflammation of the tympanic membrane is distinct fullness or bulging of the tympanic membrane on exam.”
Dr. Wald advises clinicians to be as systematic as possible when conducting the otoscopic exam, by looking at color and classifying it as pink, gray, white, yellow, red, amber, or blue, and by documenting the position as neutral, retracted, full, or bulging. “When we gauge how light passes through the tympanic membrane, we judge it as translucent, opaque, or partially opaque, and mobility as normal, decreased, or absent,” she added. “When we find decreased or absent mobility of the tympanic membrane, it tells us that we have fluid in the middle ear, but it does not discriminate between AOM and OME.”
Advances in digital otoscopy are helping pediatricians to improve their diagnostic skills. An early device, the iPhone otoscope by CellScope, uses an iOS smartphone to capture images and videos of the external ear canal and eardrum. “The image is pretty much the same as that seen through the eye of a hand-held otoscope,” Dr. Wald said. “The problem with this particular design is that the speculum is kind of large. It does still require the removal of cerumen, and the smartphone is kind of awkward to use as a handle during an otoscopic exam.”
A new digital otoscope called Wispr was unveiled at the AAP meeting. First developed at the University of Wisconsin and now marketed by WiscMed, Wispr delivers high-resolution views of the eardrum in even small or partially obstructed ear canals with one-button image and video capture. WiscMed was founded by Jim Berbee, MD, MBA, an engineer turned emergency medicine physician.
“One of the advantages of this particular model is that it handles a lot more like a usual otoscope and can be attached to the rechargeable handles that are commercially available,” Dr. Wald said. “It has an extremely tiny speculum. Within the head, there is even a smaller camera that allows the photographs to be taken. Because the speculum is so tiny, it allows the device to sometimes avoid the presence of cerumen, or sometimes go through it and still obtain an image.”
Priced at $1,500, the Wispr also features a built-in USB port for computer download of captures images and video. “This way, multiple observers can look at the uploaded image and have an opportunity to view it at greater length,” she said. “Our hope is that the availability of digital otoscopy in the office setting may improve our diagnostic skills and therefore lead to more judicious use of antimicrobials. This remains to be seen. Prospective studies need to be done, but it’s an exciting development,” Dr. Wald said.
She reported having no financial disclosures.
*This article was updated 12/13/2019