Cosmetic Dermatology
Facial Rejuvenation: Combining Cosmeceuticals With Cosmetic Procedures
Cosmetic patients are looking for a more youthful appearance without spending a lot of money, feeling any pain, or experiencing any postprocedure...
Yasaman Mansouri, MD, MRCP; Gary Goldenberg, MD
From the Department of Dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York.
Dr. Mansouri reports no conflict of interest, but her contribution was supported by the Geoffrey Dowling Fellowship, a grant from the British Association of Dermatologists (United Kingdom). Dr. Goldenberg reports no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Gary Goldenberg, MD, 5 E 98th St, 5th Floor, New York, NY 10029-6574 (garygoldenbergmd@gmail.com).

Juvéderm Family
The first Juvéderm product was approved by the FDA in 2006. Juvéderm is a bacterium-derived NASHA. Injectable gel formulations of Juvéderm, including Juvéderm Ultra and Juvéderm Ultra Plus, are FDA approved for the correction of moderate to severe facial wrinkles and folds. The first products in the Juvéderm line were produced using a technology called Hylacross technology, with cohesive molecules of cross-linked HA. In contrast to the sizing technology used by Restylane and Perlane, the Hylacross technology does not break up the cross-linked HA by passing the product through sizing screens via sieves, but instead produces monophasic gels. These Juvéderm products have a high concentration of cross-linked HAs, which accounts for their longevity, and they are soft and easy to use.
Juvéderm Voluma XC was FDA approved in 2013. It is a 20-mg/mL, smooth, highly cohesive, viscous HA, gel that is manufactured using Vycross technology, a combination of low- and high-molecular-weight HA, and it is the only HA filler that is indicated for deep injection for cheek augmentation,10 as it creates a lift due to its higher G′ and a low swelling capacity, with results lasting up to 2 years. The mean volume administered over the initial 4-week period of one study was 5.1 mL.11
Belotero Balance
Belotero Balance was approved by the FDA in 2011 for the correction of moderate to severe facial wrinkles and folds (eg, nasolabial folds).12 Belotero Balance is an HA filler with a cohesive polydensified matrix technology and low elasticity and viscosity. It has the lowest G′ of the currently available dermal fillers12 and therefore is associated with increased injection precision. Belotero Balance is ideal for superficial injections,13 such as forehead lines, vermilion border, tear trough, atrophic scars, and neck lines (off label). Some clinicians reconstitute Belotero Balance with lidocaine (off label) to provide a more pain-free procedure. In our experience, results typically last at least 6 to 8 months.
Complications
Hyaluronic acid fillers share the same adverse events across the product lines. The most common reactions include erythema, swelling, and bruising, which often are unavoidable and may be considered expected effects. Less-frequent events include contour irregularities; product migration; bluish discoloration known as the Tyndall effect, which is more likely to occur with superficial injections; nodules; infection at the injection site; scarring; and vascular occlusion, potentially leading to blindness.14 These more severe complications often can be avoided. Appropriate skin preparation and a sterile technique are critical in preventing infections, while deep placement of filler material reduces the risk for Tyndall effect, nodules, and scarring. Skin necrosis occurs by external compression of the blood supply by the product or occlusion via direct injection into a vessel. Aspirating prior to injection, administering lower volumes, and tenting the skin to inject more superficially can reduce the risk for skin necrosis. Every clinician needs to be able to rapidly recognize the signs of necrosis and to administer urgent therapy, such as the application of warm gauze and nitroglycerin paste, tapping the area to facilitate vasodilatation, and injecting hyaluronidase when required.
On the Horizon
Other dermal fillers that may gain FDA approval in the next few years include Teosyal (Laboratories Teoxane Geneva),6 a new range of monophasic NASHA products that provide high viscosity and elasticity with results lasting 6 to 9 months, and potentially Juvéderm Volbella, a smooth, nonparticle, viscous HA gel developed specifically for the lip area with results lasting up to 1 year.15
Conclusion
Over the last decade, the popularity of dermal fillers has steadily increased, and fillers have become a cornerstone of aesthetic medicine. The increased number of available products necessitates thorough knowledge by the treating physician to ensure optimal outcomes. There is no universal filler that can achieve ideal outcomes in all anatomic sites or in all patients. Often a combination approach may be ideal, such as the use of a product with a higher G′ for re-volumization, followed by a filler with a lower G′ for superficial injection. Some patients may also benefit from a combination of both dermal fillers and neurotoxin injections, either on the same day or at separate visits, which may increase the longevity of the filler.

Cosmetic patients are looking for a more youthful appearance without spending a lot of money, feeling any pain, or experiencing any postprocedure...
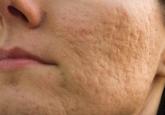
Acne vulgaris is one of the most commonly encountered skin conditions and frequently is seen in both adolescent and adult populations. Scarring is...
Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–...
