Case Report
A 24-year-old man was referred to the dermatology department for evaluation of pustules, atrophic scars, and alopecia on the scalp of 6 years’ duration. Six years prior, erythema, scaling, and follicular keratotic papules had appeared on the superciliary arches, and he started to lose hair from the eyebrows. Three months later, he developed mildly pruritic and painful scaling and pustules on the scalp. These lesions resolved with atrophic scarring accompanied by alopecia. One year later, follicular keratotic papules developed on the cheeks, chest, abdomen, back, lateral upper arms, thighs, and axillae. Two years later, direct microscopy of the lesions on the scalp and fungal culture were negative. After 2 weeks of treatment with roxithromycin (0.15 g twice daily), the scalp pustules dried out and resolved; however, they recurred when the patient stopped taking the medication. Six months later, he was started on isotretinoin treatment (10 mg once daily) for half a year, but no improvement was seen. His parents were nonconsanguineous, and no other family members were affected.
Dermatologic examination revealed large areas of atrophic scarring and alopecia on the scalp. Only a few solitary hairs remained on the top of the head, with the follicles surrounded by keratotic papules, pustules, and black scabs. There was sparse hair on the forehead and temples and scattered hair clusters in the occipital region near the hairline. These follicles also were associated with keratotic papules (Figure 1A). Erythema, scales, and follicular keratotic papules of the superciliary arches with sparse eyebrows and axillary hairs were noted. Follicular keratotic papules also were observed on the cheeks, axillae, chest, abdomen, back, lateral upper arms, and thighs. Dental examination revealed a large space between the upper anterior teeth and the lower anterior teeth. The upper anterior teeth were anteverted, there was congenital absence of right lower central incisors, and the anterior teeth were in deep overbite and overjet (Figure 1B). There was gingival atrophy and calculus dentalis in the upper and lower teeth. He had a fissured tongue with atrophic filiform papillae (Figure 1C).
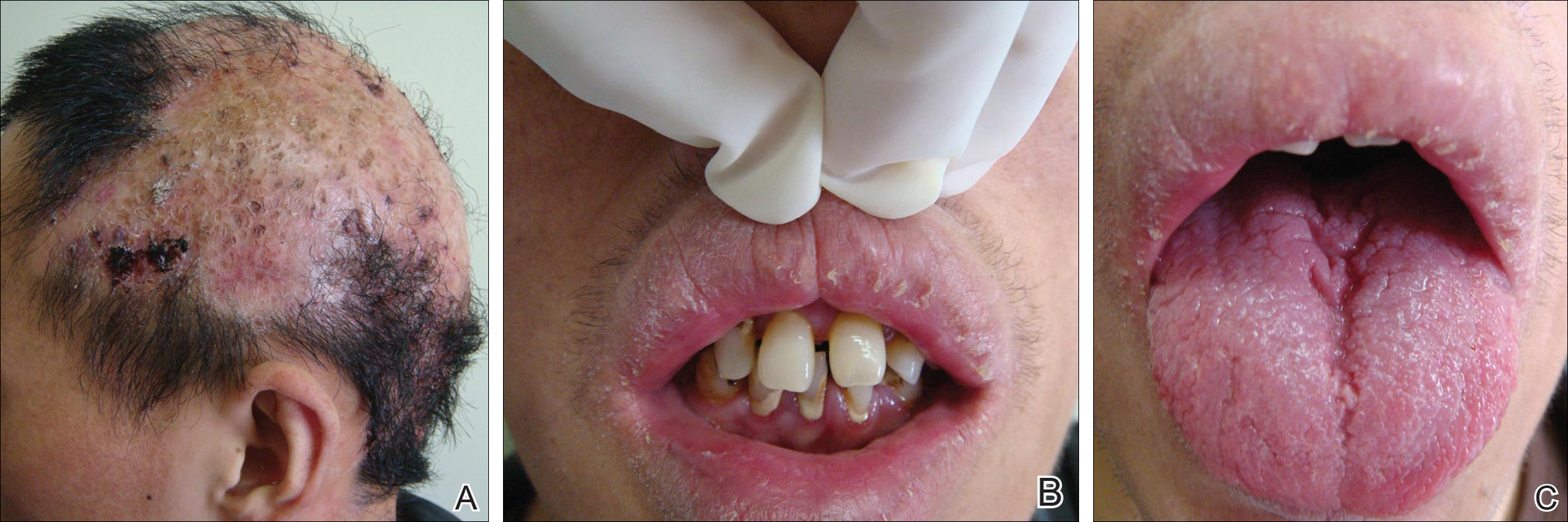
Figure 1. Characteristic lesions of folliculitis spinulosa decalvans on the scalp (A). This patient also presented with a large space between the upper anterior teeth and lower anterior teeth (B). Anteversion of the upper anterior teeth, congenital absence of right lower central incisors, and deep overbite and overjet of the anterior teeth also were seen. A fissured tongue with atrophic filiform papillae also was present (C).
Laboratory testing of the blood, urine, stool, hepatic and renal function, and serum vitamin B2 and B12 levelswere all within reference range. A panoramic radiograph of the occlusal surface showed congenital absence of right lower central incisors (Figure 2), and a lateral projection of a cranial radiograph confirmed that the anterior teeth were in deep overbite and overjet. Direct microscopy and fungal culture of material collected from the dorsal tongue were negative. Direct microscopy and fungal culture of diseased hairs also were negative. A rapid plasma reagin test, Treponema pallidum hemagglutination assay, and human immunodeficiency virus test were negative. Staphylococcus aureus was isolated from the scalp pustules, and in vitro drug susceptibility testing showed that it was sensitive to clarithromycin and moxifloxacin. Pathological examination of a biopsy of the occipital skin lesions showed a thickened epidermal spinous layer and massive infiltration of plasma cells, neutrophils, and multinucleated giant cells around the hair follicles (Figure 3). Pathological examination of the skin lesions on the superciliary arch also showed infiltration of inflammatory cells in the dermis around the hair follicles.
Based on these findings, a diagnosis of folliculitis spinulosa decalvans (FSD) was made and the patient was started on clarithromycin (0.25 g twice daily), metronidazole (0.2 g 3 times daily), viaminate (50 mg 3 times daily), and fusidic acid cream (coating the affected area twice daily). When he returned for follow-up 1 month later, the pustules had disappeared and the black scabs had fallen off, leaving atrophic scars. The long-term efficacy of this regimen is still under observation.
Comment
Folliculitis spinulosa decalvans, along with keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans (KFSD), keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei, and atrophoderma vermiculatum, belongs to a group of diseases that includes keratosis pilaris atrophicans. In 1994, Oranje et al1 suggested the term folliculitis spinulosa decalvans, with signs including persistent pustules, characteristic keratotic papules, and scarring alopecia of the scalp, which may be exacerbated at puberty. Staphylococcus aureus was isolated from the pustules in one study2; however, in another study, repeated cultures were negative.3 Although the main inheritance pattern of KFSD is X-linked, autosomal-dominant inheritance is more common in FSD. Furthermore, there are certain differences in the clinical manifestations of these 2 conditions. Therefore, it remains controversial if FSD is an independent disease or merely a subtype of KFSD.



