Case Report
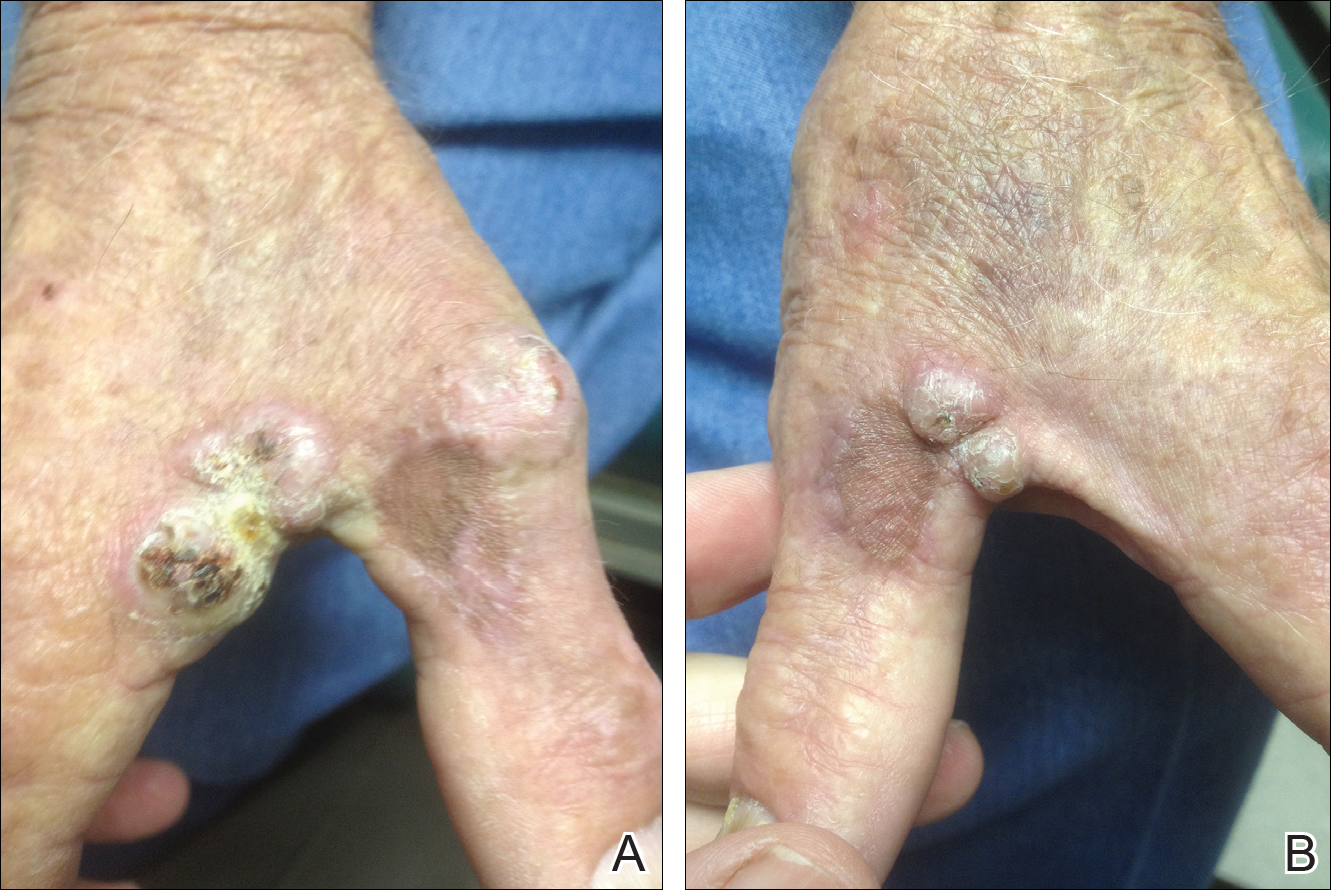
A 78-year-old man presented for evaluation of 4 painful keratotic nodules that had appeared on the dorsal aspect of the right thumb, the first web space of the right hand, and the first web space of the left hand. The nodules developed in pericicatricial skin following Mohs micrographic surgery to the affected areas for treatment of invasive squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) 2 months prior. The patient had worked in lawn maintenance for decades and continued to garden on an avocational basis. He denied exposure to angling or aquariums.
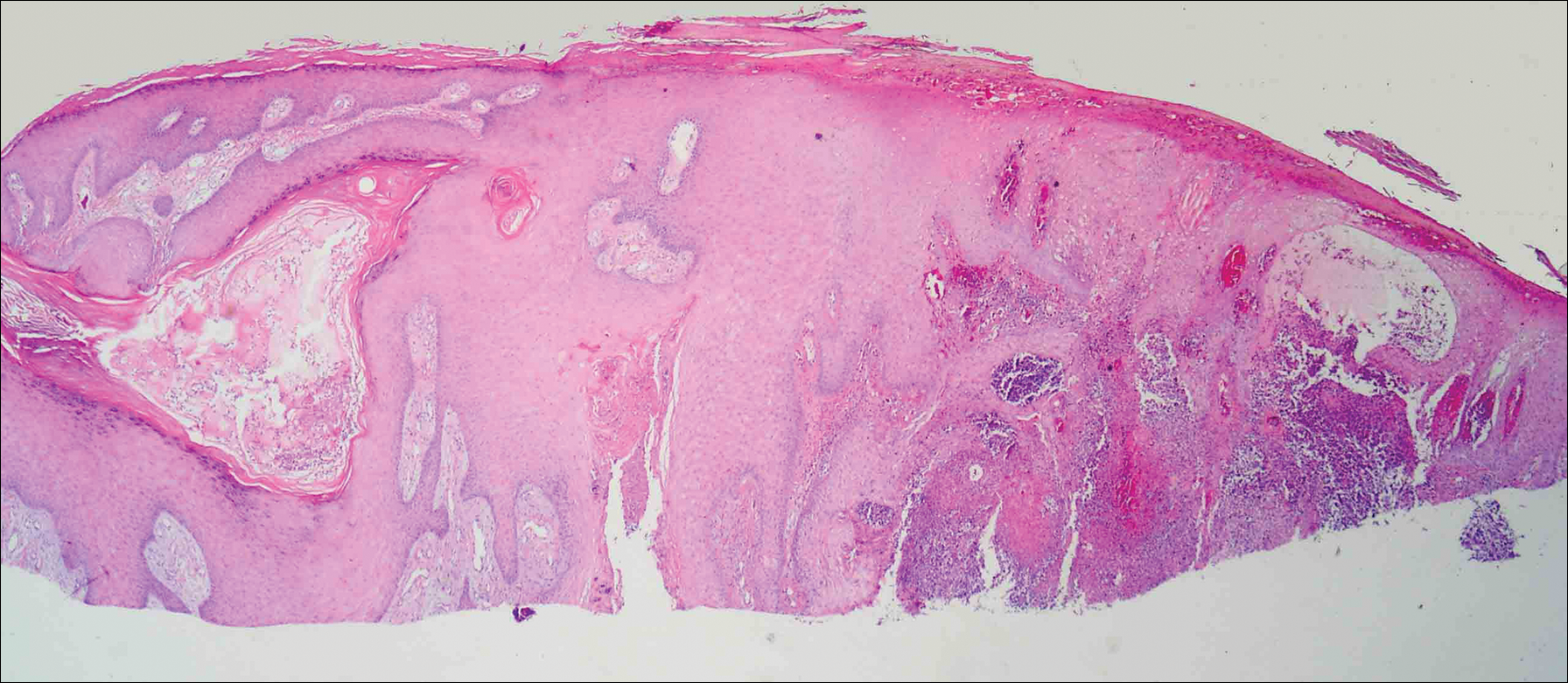
On physical examination the lesions appeared as firm, dusky-violaceous, crusted nodules (Figure 1). Brown patches of hyperpigmentation or characteristic cornlike elevations of the palm were not present to implicate arsenic exposure. Extensive sun damage to the face, neck, forearms, and dorsal aspect of the hands was noted. Epitrochlear lymphadenopathy or lymphangitic streaking were not appreciated. Routine hematologic parameters including leukocyte count were normal, except for chronic thrombocytopenia. Computerized tomography of the abdomen demonstrated no hepatosplenomegaly or enlarged lymph nodes. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of biopsy specimens from the right thumb showed irregular squamous epithelial hyperplasia with an impetiginized scale crust and pustular tissue reaction, including suppurative abscess formation in the dermis (Figure 2). Initial acid-fast staining performed on the biopsy from the right thumb was negative for microorganisms. Given the concerning histologic features indicating infection, a tissue culture was performed. Subsequent growth on Lowenstein-Jensen culture medium confirmed infection with Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). The patient was started on clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily in accordance with laboratory susceptibilities, and the cutaneous nodules improved. Unfortunately, the patient died 6 months later secondary to cardiac arrest.
Comment
The genus Mycobacterium comprises more than 130 described bacteria, including the precipitants of tuberculosis and leprosy. Mycobacterium avium complex--an umbrella term for M avium, Mycobacterium intracellulare, and other close relatives--is a member of the genus that maintains a low pathogenicity for healthy individuals.1,2 Nonetheless, MAC accounts for more than 70% of cases of nontuberculous mycobacterial disease in the United States.3 Mycobacterium avium complex typically acts as a respiratory pathogen, but infection may manifest with lymphadenitis, osteomyelitis, hepatosplenomegaly, or skin involvement. Disseminated MAC infection can occur in patients with defective immune systems, including those with conditions such as AIDS or hairy cell leukemia and those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy.1,4 Although uncommon, cutaneous infection with MAC occurs via 3 possible mechanisms: (1) primary inoculation, (2) lymphogenous extension, or (3) hematologic dissemination.4 According to a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms primary cutaneous Mycobacterium avium complex and MAC skin infection, only 11 known cases of primary cutaneous MAC infection have been reported in the English-language literature,4-14 the most recent being a report by Landriscina et al.11