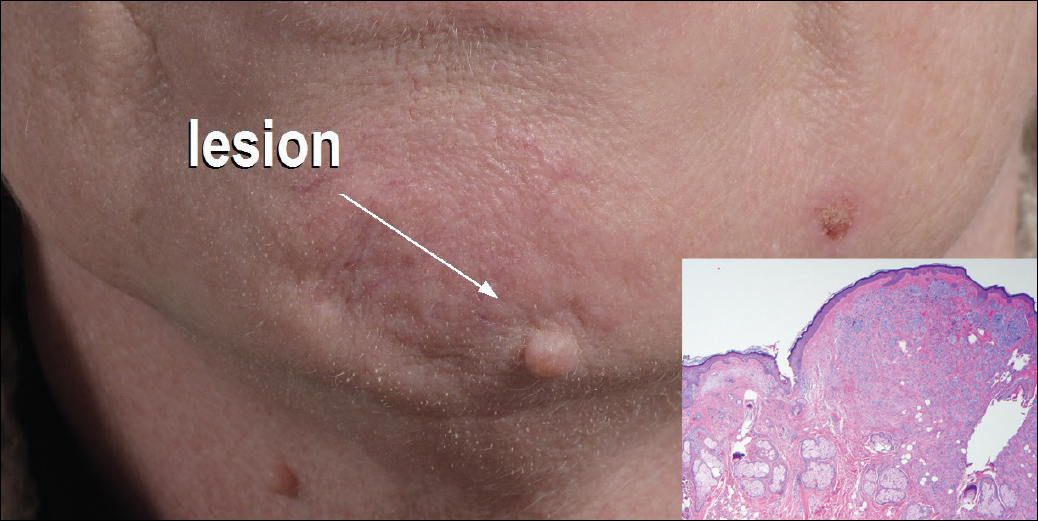
The Diagnosis: Collision Tumor
Excisional biopsy and histopathological examination demonstrated a collision tumor composed of a benign intradermal melanocytic nevus, tumor of follicular infundibulum, and an underlying sclerosing epithelial neoplasm, with a differential diagnosis of desmoplastic trichoepithelioma, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma, and microcystic adnexal carcinoma (Figure).
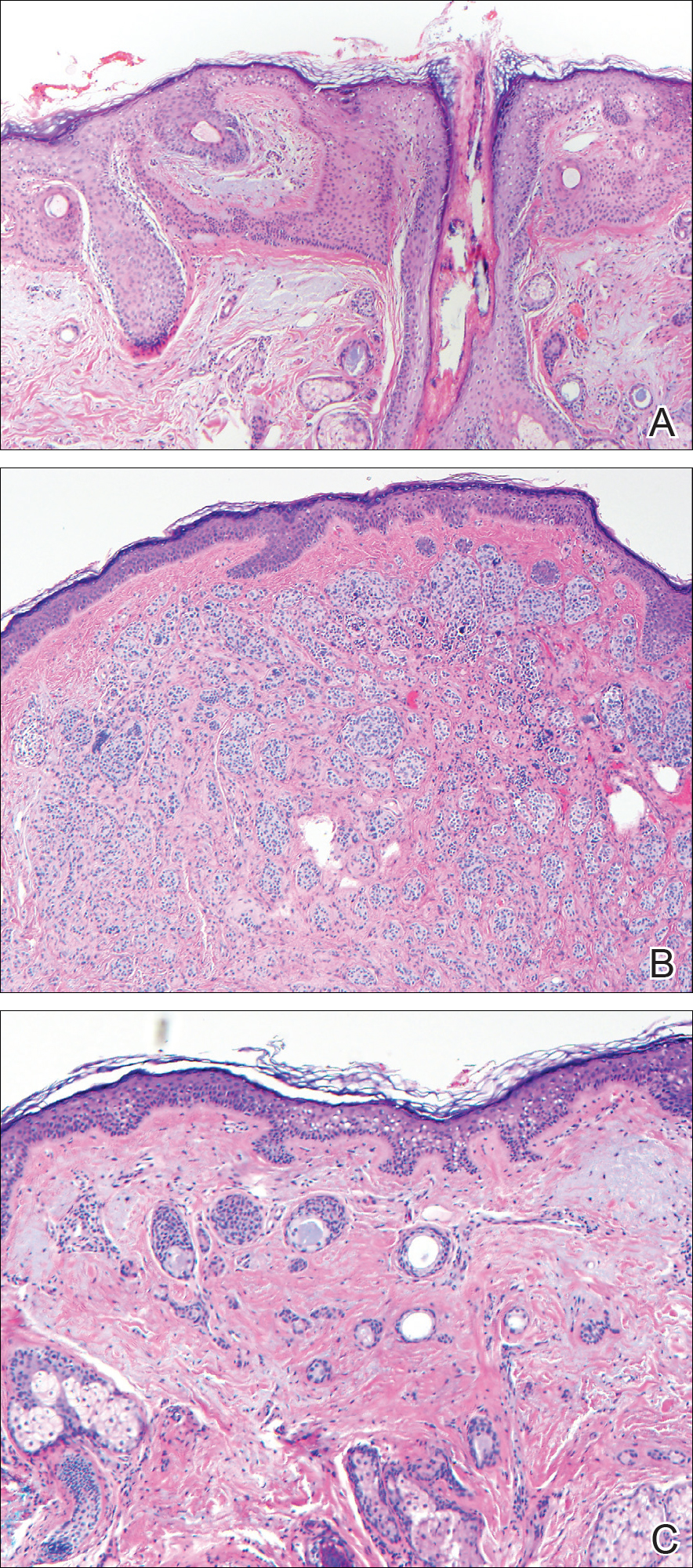
Tumor of follicular infundibulum, with the section showing a platelike subepidermal tumor extending horizontally under the epidermis and tadpolelike structures observed underneath the tumor (A)(H&E, original magnification ×200). Intradermal melanocytic nevus with nests of melanocytes showing maturation and dispersion with descent (B)(H&E, original magnification ×200). Epithelial cells forming strands and tadpolelike morphology with surrounding sclerotic stroma (C)(H&E, original magnification ×200).
Common acquired melanocytic nevus presents clinically as a macule, papule, or nodule with smooth regular borders. The pigmented variant displays an evenly distributed pigment on the lesion. Intradermal melanocytic nevus often presents as a flesh-colored nodule, as in our case. Histopathologically, benign intradermal nevus typically is composed of a proliferation of melanocytes that exhibit dispersion as they go deeper in the dermis and maturation that manifests as melanocytes becoming smaller and more spindled in the deeper portions of the lesion.1 These 2 characteristics plus the bland cytology seen in the present case confirm the benign characteristic of this lesion (Figure, B).
In addition to the benign intradermal melanocytic nevus, an adjacent tumor of follicular infundibulum was noted. Tumor of follicular infundibulum is a rare adnexal tumor. It occurs frequently on the head and neck and shows some female predominance.2,3 Multiple lesions and eruptive lesions are rare forms that also have been reported.4 Histopathologically, the tumor demonstrates an epithelial plate that is present in the papillary dermis and is connected to the epidermis at multiple points with attachment to the follicular outer root sheath. Peripheral palisading is characteristically present above an eosinophilic basement membrane (Figure, A). Rare reports have documented sebaceous and eccrine differentiation.5,6
Tumor of follicular infundibulum has been reported to be associated with other tumors. Organoid nevus (nevus sebaceous), trichilemmal tumor, and fibroma have been reported to occur as a collision tumor with tumor of follicular infundibulum. An association with Cowden disease also has been described.7 Biopsies that represent partial samples should be interpreted cautiously, as step sections can reveal basal cell carcinoma.
The term sclerosing epithelial neoplasm describes tumors that share a paisley tielike epithelial pattern and sclerotic stroma. Small specimens often require clinicopathologic correlation (Figure, C). The differential diagnosis includes morpheaform basal cell carcinoma, desmoplastic trichoepithelioma, and microcystic adnexal carcinoma. A panel of stains using Ber-EP4, PHLDA1, cytokeratin 15, and cytokeratin 19 has been proposed to help differentiate these entities.8 CD34 and cytokeratin 20 also have been used with varying success in small specimens.9,10