Photo Challenge
From Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut. Dr. Khurana is from the Department of Internal Medicine, and Drs. Leventhal, Levy, McNiff, and Antaya are from the Department of Dermatology.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Jonathan S. Leventhal, MD, 15 York St, LMP 5040, New Haven, CT 06510 (jonathan.leventhal@yale.edu).

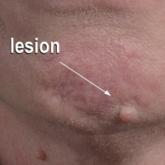
A 7-month-old boy admitted to the hospital with new-onset respiratory stridor was found to have a rash of the scalp, axillae, and groin of 1 month's duration that was unresponsive to treatment with mineral oil. Bronchoscopy revealed tracheal compression, and urgent magnetic resonance imaging of the chest demonstrated an anterior mediastinal mass. Prior to presentation, the patient was otherwise healthy with normal growth and development. On physical examination, scattered red-brown and purpuric papules with hemorrhagic crust were noted on the scalp. There were well-defined pink erosive patches and purpuric papules in the inguinal folds bilaterally and similar erosive patches in the axillae. Numerous punched out ulcerations were noted on the lower gingiva. There was no palpable lymphadenopathy. The hands, feet, penis, scrotum, and perianal area were spared. Biopsies of the skin and mediastinal mass were performed.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a clonal proliferative disorder of Langerhans cells that can affect any organ, most commonly the skin and bones. It typically develops in children aged 1 to 3 years, with a male to female ratio of 2 to 1.1 Skin manifestations include purpuric papules, pustules, vesicles, erosions, and fissuring distributed predominantly on the scalp and flexural sites. Mucosal sites, particularly the oral mucosa, may be involved and usually present as erosions associated with underlying bone lesions.1 Langerhans cell histiocytosis should be considered in the differential diagnosis of recalcitrant diaper dermatitis in an infant, especially when there is purpura and erosions, as seen in our patient. Common conditions in infants such as cutaneous candidiasis (intense erythema with superficial erosions, peripheral scale and satellite pustules on flexural areas, potassium hydroxide microscopy revealing yeast forms and pseudohyphae) and seborrheic dermatitis (well-defined pink to red, moist, and often scaly patches favoring the folds) may be distinguished clinically from Hailey-Hailey disease (malodorous plaques with fissures and erosions favoring the folds), which is rare in infancy, and acrodermatitis enteropathica (erythema and erosions with scale-crust and desquamation on periorificial, acral, and intertriginous skin).
Histopathologic evaluation is instrumental in diagnosing the skin lesions of LCH. Further evaluation for systemic involvement is necessary once the diagnosis is made. Skin biopsy of the scalp and right inguinal fold revealed a wedge-shaped infiltrate of histiocytes with slightly folded nuclear contours in our patient (Figure 1). CD1a (Figure 2) and S-100 stains were markedly positive, which is characteristic of LCH. Complete blood cell count, renal function, liver function, urinalysis, and flow cytometry results were within reference range. A skeletal survey and echocardiogram were unremarkable; however, mild hepatosplenomegaly was noted on abdominal ultrasonography.
Treatment of LCH varies based on the extent of organ involvement. For isolated cutaneous disease, topical steroids, topical nitrogen mustard, phototherapy, and thalidomide may be employed.2 Multisystem disease requires chemotherapeutic agents including vinblastine and prednisone.2,3 Because more than half of patients with LCH have oncogenic BRAF V600E mutations,4 vemurafenib may have a therapeutic role in treatment. Rare case reports have documented disease response in patients with LCH and Erdheim-Chester disease.5,6
Prognosis varies based on age and extent of systemic involvement. Children younger than 2 years with multiorgan involvement have a poor prognosis (35%-55% mortality rate) compared to older children without hematopoietic, hepatosplenic, or lung involvement (100% survival rate). Additionally, response to treatment affects prognosis, as there is a 66% mortality rate in those who do not respond to treatment after 6 weeks.3 Long-term sequelae of LCH include endocrine dysfunction (ie, diabetes insipidus, growth hormone deficiencies), hearing impairment, orthopedic impairment, and neuropsychological disease; thus, multidisciplinary care often is neccessary.7
Given the multisystem involvement in our patient, he was treated with vinblastine, 6-mercaptopurine, and prednisolone with only partial and transient disease response. He was then treated with clofarabine with dramatic resolution of the mediastinal mass on follow-up positron emission tomography. The cutaneous lesions persisted and were managed with topical corticosteroids.