Conclusion
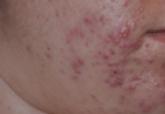
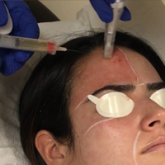
Both salicylic acid 30% peel and PBBL procedures are effective, safe, and well tolerated in treating acne. Although there was no significant difference in the efficacy between both treatments in this study, the small sample size and short follow-up intervals warrant further studies to support the observed outstanding outcomes and should be considered in combination with other medical treatment options. These procedures may be beneficial in holding the patient compliant until their medical therapies have an opportunity to work.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Joyce Okawa, RN (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), for her assistance in the submission to the institutional review board of the University of Pennsylvania.