Photo Challenge
Recalcitrant Ulcer on the Lower Leg
An 80-year-old woman with a medical history notable for obesity (body mass index, 31.2), type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and chronic...
From Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut. Drs. Shi, Leventhal, Galan, and Choate are from the Department of Dermatology. Dr. Mensah is from the Department of Internal Medicine, Section of Rheumatology. Drs. Galan and Choate also are from the Department of Pathology. Dr. Choate also is from the Department of Genetics.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Jonathan S. Leventhal, MD, 15 York St, LMP 5040, New Haven, CT 06510 (jonathan.leventhal@yale.edu).

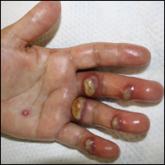
A man in his 50s with a medical history of arterial thrombosis of the right arm, multiple deep vein thromboses (DVTs) of the legs on long-term warfarin, ischemic stroke, atrial fibrillation, and peripheral arterial disease presented with discoloration of the right foot and increasing tenderness of 1 month's duration. There was no history of trauma or recent change in outpatient medications. A family history was notable for an aunt and 2 cousins with DVTs and protein S deficiency. Physical examination revealed livedo reticularis on the sole and lateral aspect of the right foot. There was violaceous discoloration of the volar aspects of all 5 toes and a focal area of ulceration on the fifth toe. Pulses were palpable bilaterally. Initial laboratory evaluation was notable for thrombocytopenia, and preliminary blood cultures revealed no growth of bacterial or fungal organisms. Imaging studies revealed increased arterial stenosis of the right leg as well as DVT of the right great saphenous vein. A punch biopsy of the right medial foot was performed for hematoxylin and eosin stain as well as tissue culture.
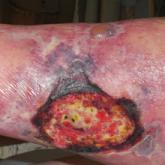
A biopsy demonstrated scattered intravascular thrombi in the dermis and subcutis, intact vascular walls, and scant lymphocytic inflammation in a background of stasis (Figure 1). A periodic acid-Schiff stain was negative for fungal elements and highlighted the intravascular thrombi. Histologic findings were consistent with thrombotic vasculopathy. On further laboratory workup, lupus anticoagulant studies, including a mixing study, diluted Russell viper venom test, and hexagonal phase phospholipid neutralization test, were abnormal. Titers of anticardiolipin and β2-glycoprotein I antibodies were elevated (anticardiolipin IgG, 137.7 calculated units [normal, <15 calculated units]; β2-glycoprotein I IgG, 256.4 calculated units [normal, <20 calculated units]). Tissue cultures showed no growth of microorganisms and studies for cryoglobulinemia were negative.
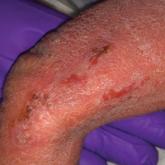
The patient was diagnosed with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). He remained on anticoagulation therapy with fondaparinux as an inpatient and was treated with pulse-dose intravenous (IV) corticosteroids followed by a slow oral taper, daily plasmapheresis for 1 week, IV immunoglobulin (0.5 g/kg) for 3 doses, and 4 weekly doses of rituximab (375 mg/m2). His cutaneous findings slowly improved over the next several weeks (Figure 2).
Antiphospholipid syndrome is an autoimmune disorder characterized by thrombotic events and the presence of autoantibodies. The syndrome is defined by 2 major criteria: (1) the occurrence of at least 1 clinical feature of either an episode of vascular thrombosis or pregnancy morbidity such as unexplained fetal death beyond 10 weeks of gestation or recurrent unexplained pregnancy losses; and (2) the presence of at least 1 type of autoantibody, including lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin, or β2-glycoprotein antibodies, on 2 separate occasions at least 12 weeks apart.1 Antiphospholipid syndrome can either be primary with no identifiable associated rheumatologic disease or secondary to another autoimmune disease such as systemic lupus erythematosus. Cutaneous manifestations are common and frequently are the first sign of disease in 30% to 40% of patients.2 The most common skin finding is persistent livedo reticularis, which can be seen in 20% to 25% of patients. Patients also may develop skin necrosis, ulcerations, digital gangrene, splinter hemorrhages, and livedoid vasculopathy.2 Systemic manifestations of APS include thrombocytopenia, nephropathy, cognitive dysfunction, and cardiac valve abnormalities.
The exact pathogenesis of APS remains unknown. It is thought to be due to the combination of an inflammatory stimulus that has yet to be characterized in conjunction with autoantibodies that affect multiple target cells including monocytes, platelets, and endothelial cells, which results in activation of the complement system and clotting cascade.3 In rare cases, the disorder can progress to catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS), which requires fulfillment of 4 criteria: (1) evidence of involvement of 3 organs, tissues, or systems; (2) development of manifestations simultaneously or in less than 1 week; (3) laboratory confirmation of the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies; and (4) confirmation by histopathology of small vessel occlusion.4 Probable CAPS is diagnosed when 3 of 4 criteria are present. Our patient met criteria for probable CAPS, as his antibody titers remained elevated 15 weeks after initial presentation. Precipitating factors that can lead to CAPS are thought to include infection, surgical procedures, medications, or discontinuation of anticoagulation drugs.2 Although the mainstay of management of APS is anticoagulation therapy with warfarin and antiplatelet agents such as aspirin, first-line treatment of CAPS involves high-dose systemic glucocorticoids and plasma exchange. Intravenous immunoglobulin also may be employed in treatment. Data from the CAPS registry demonstrate a role for rituximab, an anti-CD20 antibody, at 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks (the regimen described in our case) or 1 g every 14 days for 2 sessions.5 A majority of the registry patients treated with rituximab recovered (75% [15/20]) and had no recurrent thrombosis (87% [13/15]) at follow-up.5 Data also are emerging on the role of eculizumab, an anti-C5 antibody that inhibits the terminal complement cascade, as a therapy in difficult-to-treat or refractory CAPS.6-8 The prognosis for CAPS patients without treatment is poor, and mortality has been reported in up to 44% of patients. However, with intervention mortality is reduced by more than 2-fold.9,10
It is important to recognize that acral cyanosis with persistent livedo reticularis and digital gangrene can be a presenting manifestation of APS. These cutaneous manifestations should prompt histologic evaluation for thrombotic vasculopathy in addition to serologic tests for APS autoantibodies. Although APS may be treated with anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, CAPS may require more aggressive therapy with systemic steroids, plasma exchange, IV immunoglobulin, rituximab, and/or eculizumab.

An 80-year-old woman with a medical history notable for obesity (body mass index, 31.2), type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and chronic...
A 1-day-old Hispanic female infant was born via uncomplicated vaginal delivery at 41 weeks' gestation after a normal pregnancy. Linear plaques...