The 2008 World Health Organization and European Organization for Treatment of Cancer joint classification has distinguished 3 categories of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma (PCFCL), primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma.1-3 Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma is the most common type of cutaneous B-cell lymphoma, accounting for approximately 60% of cases worldwide.4 The median age at diagnosis is 60 years, and most lesions are located on the scalp, forehead, neck, and trunk.5 Histologically, PCFCL is characterized by dermal proliferation of centrocytes and centroblasts derived from germinal center B cells that are arranged in either a follicular, diffuse, or mixed growth pattern.1 The cutaneous manifestations of PCFCL include solitary erythematous or violaceous plaques, nodules, or tumors of varying sizes.4 Grouped lesions also may be observed, but multifocal disease is rare.1 We report a rare presentation of PCFCL mimicking folliculitis with multiple multifocal papules on the back.
Case Report
A 54-year-old woman presented with fever and leukocytosis of 4 days’ duration and was admitted to the hospital for presumed sepsis. She had a history of mastectomy for treatment of ductal carcinoma in situ of the right breast 5 years prior to the current presentation and endocrine therapy with tamoxifen. Her symptoms were thought to be a complication from a surgery for implantation of a tissue expander in the right breast 5 years prior to presentation.
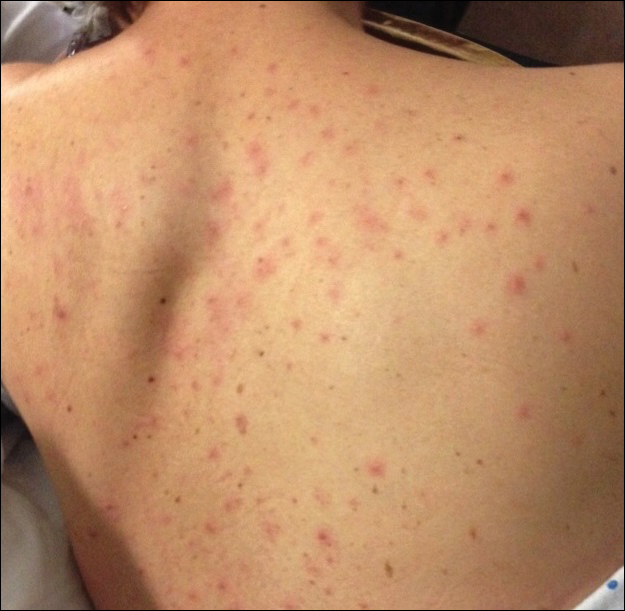
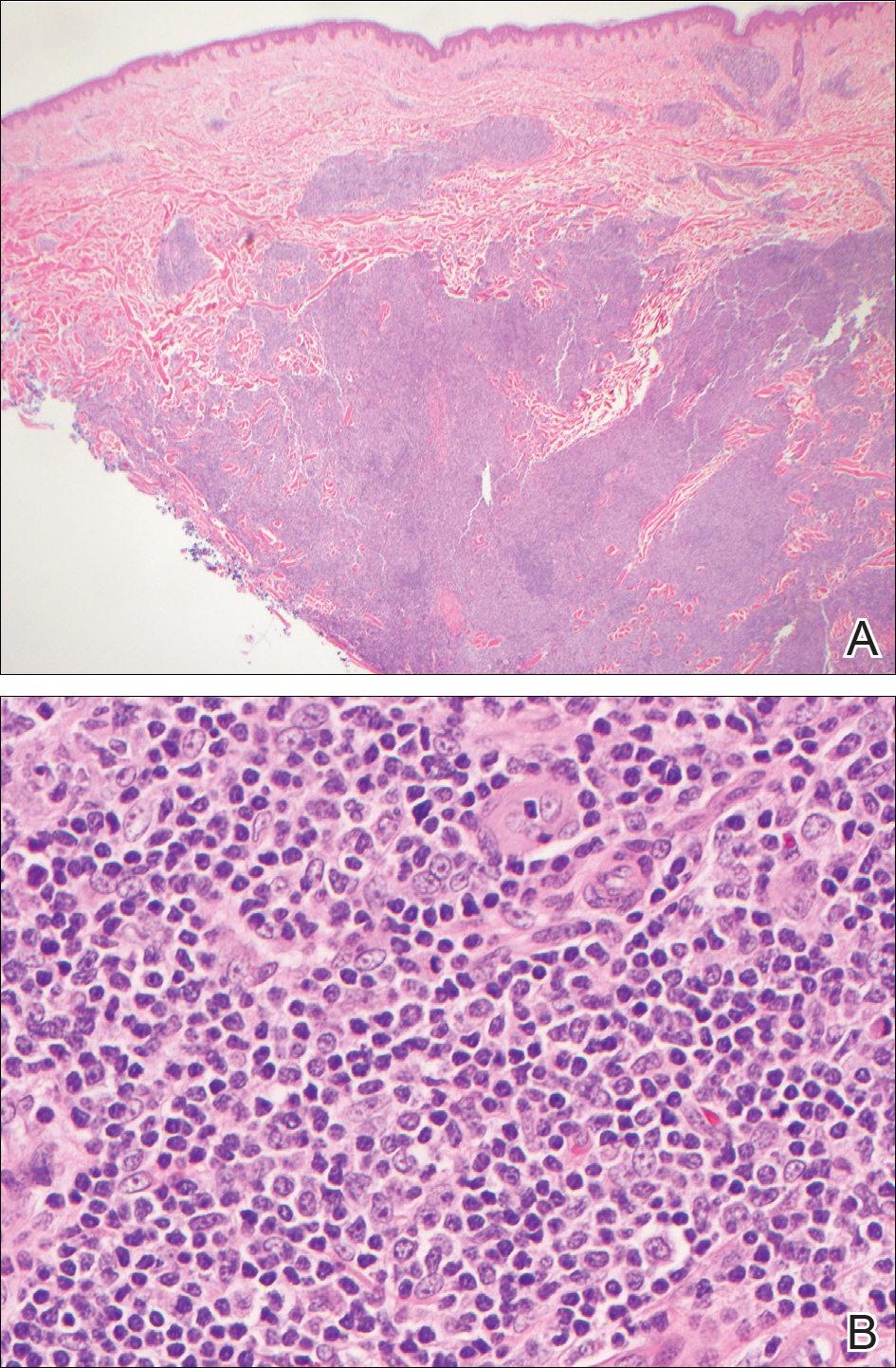
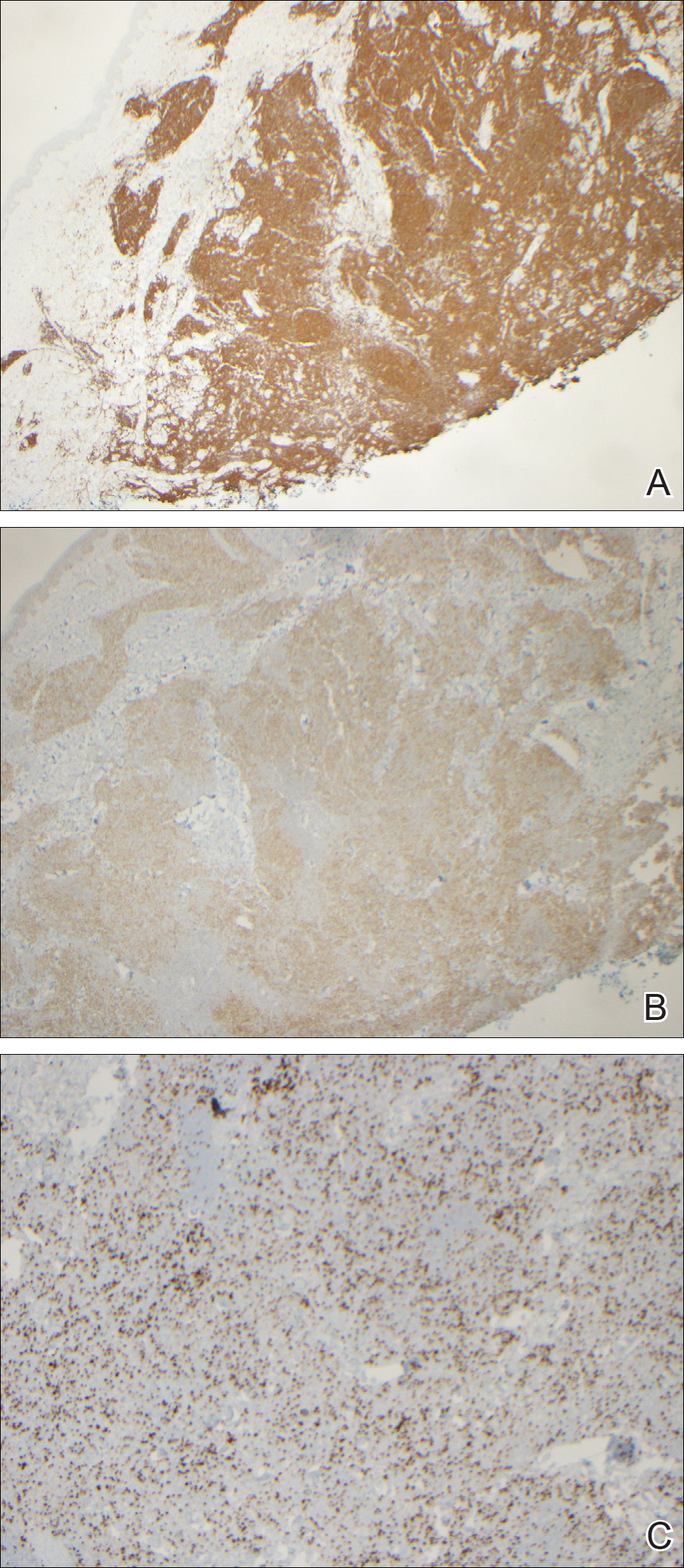
During her hospital admission, she developed a papular and cystic eruption on the back that was clinically suggestive of folliculitis, transient acantholytic dermatosis (Grover disease), or miliaria rubra (Figure 1). This papular and cystic eruption initially was managed conservatively with observation as she recovered from an occult infection. Due to the persistent nature of the eruption on the back, an excisional biopsy of the cystic component was performed 2 months after her discharge from the hospital. Histologic studies showed a dense infiltrate of lymphocytes, which expanded into the deep dermis in a nodular and diffuse growth pattern that was accentuated in the periadnexal areas. The B lymphocytes were small and hyperchromatic with few scattered centroblasts (Figure 2). Further immunohistochemical studies demonstrated that the neoplastic cells were positive for CD20, CD79a, BCL-2, and BCL-6; CD3, CD5, and cyclin D1 were negative. Staining for antigen Ki-67 revealed a proliferation index of 15% to 20% among the neoplastic cells (Figure 3). These findings were consistent with either PCFCL or secondary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma.
Further evaluation for systemic disease was unremarkable. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography revealed no evidence of nodal lymphoma, and a bone marrow biopsy was negative. Other laboratory studies including lactate dehydrogenase were within reference range, which conferred a diagnosis of PCFCL. The patient was treated with localized electron beam radiation therapy to the skin of the mid back for a total dose of 24 Gy in 12 fractions at 2 Gy per fraction once daily over a 12-day period. She tolerated the treatment well and has remained clinically and radiographically without evidence of disease for more than 3 years.