GOTHENBURG, SWEDEN - Legius syndrome, first described only 3 years ago, can be easily misdiagnosed as neurofibromatosis type 1.
The diagnostic confusion has important consequences for the peace of mind of patients and their families. While Legius syndrome and neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) share several phenotypic features, Legius syndrome, unlike NF1, does not carry an increased cancer risk. Nor do patients with Legius syndrome develop clusters of benign cutaneous neurofibromas, Dr. Sirkku Peltonen said at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
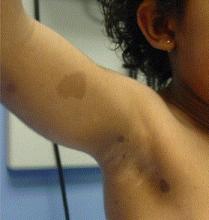
As first described by Dr. Eric Legius and coworkers (Nat. Genet. 2007;39:1120-6) at the Catholic University of Leuven (Belgium), the hallmarks of Legius syndrome include multiple café au lait macules, axillary freckling, and autosomal dominant transmission, all of which are also among the NF1 diagnostic criteria established by the National Institutes of Health (JAMA 1997;278:51-7). But patients with Legius syndrome do not develop any other characteristic findings of NF1, such as bone lesions, plexiform or cutaneous neurofibromas, Lisch nodules in the iris, and nervous system tumors.
Legius syndrome is caused by mutations in the SPRED1 gene, while NF1 is caused by mutations in the gene encoding neurofibromin. Consider the possibility of Legius syndrome, which can be confirmed by molecular genetic analysis, in patients with six or more café au lait macules and axillary freckling but none of the other classic features of NF1, urged Dr. Peltonen of the University of Turku (Finland).
How often is Legius syndrome mistaken for NF1? A report by Dr. Legius and coworkers concluded half a cohort of 40 patients with Legius syndrome confirmed by genetic analysis fulfilled the NIH diagnostic criteria for NF1 based upon the presence of the requisite number of café au lait spots, axillary freckling, and/or a family history compatible with NF1. In the same report, the international group of investigators determined that 1.9% of a series of 1,318 patients with the clinical diagnosis of NF1 based upon the NIH criteria actually had Legius syndrome (JAMA 2009;302:2111-8).
Dr. Peltonen declared having no relevant financial interests.