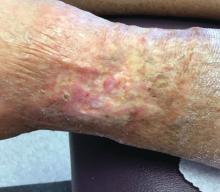
It is a vasculopathy rather than a vasculitis as the former is caused by occlusion of blood vessels and the latter results from inflammation of the vessels. Middle-aged women tend to be affected more frequently. Although the exact cause is unclear, systemic diseases, such as hypercoagulable states, may predispose vessels to develop occlusion. Associated disorders include antiphospholipid syndrome, protein C deficiency, factor V mutation, arteriosclerosis, hyperhomocysteinemia, and hepatitis C.
Typically, lesions begin as painful purpura or reticulated macules on the lower extremities that ulcerate and heal very slowly. Ankles, particularly malleoli, are more frequently affected. When they heal, they form painless white stellate scars typical of atrophie blanche. Surrounding erythema, telangiectasias, and sclerosis may be present; livedo reticularis may be seen as well.
Histologically, the epidermis may be atrophic or necrotic. Hyaline thickening of the blood vessel walls is seen. Thrombi may be present. Direct immunofluorescence of perilesional skin may be positive for complement C3 and immunoglobulin (IgM) in dermal blood vessels.
Livedoid vasculopathy can be difficult to treat. Treatment is aimed at reducing clotting and improving blood flow and includes antiplatelet drugs (low-dose aspirin, dipyridamole), anticoagulants, and vasodilating agents (nifedipine). Pentoxifylline two or three times daily may help by altering blood viscosity. A recent literature search reports success in topical dapsone applied to lesions twice daily under occlusion. Leg elevation and compression stockings help healing. Livedoid vasculopathy may have periods of activity and remission.
The case and photo were submitted by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/edermatologynews.com. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com