Photo Challenge
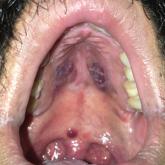
Violaceous Nodules on the Hard Palate
A 30-year-old man presented to our outpatient clinic with rapidly growing, ulcerated, violaceous lesions on the hard palate of 4 months' duration...
Dr. Dearborn is from the University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine, Biddeford, Maine. Drs. Neal, Fillman, and Neiner are from San Antonio Military Medical Center, Texas. Drs. Neal and Neiner are from the Dermatology Department, and Dr. Fillman is from the Pathology Department.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
The views expressed are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy or position of the US Army, US Air Force, the Department of Defense, or the US Government.
Correspondence: Danielle Neal, DO, San Antonio Military Medical Center, Joint Base San Antonio, TX 78234 (danielle.e.neal.mil@mail.mil).

A 61-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic, slowly enlarging, 9-mm, firm, red papule on the left nipple of 2 years' duration. She had no notable medical history, including a BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) mammogram score of 2 that was suggestive of benign findings 2 years prior. A repeat mammogram ordered by radiology and completed before presenting to dermatology had a BI-RADS score of 4, noting a concerning feature in the area of the lesion and prompting a biopsy.
Biopsy of the lesion revealed proliferative sections of glandular epithelium demonstrating apocrine differentiation, connecting to the epidermis and traversing throughout the entire dermis of the specimen (Figure). There were papillary projections of dilated ducts with a retained layer of myoepithelial cells surrounding the epithelial layers. Cytologic atypia was not appreciated. The patient was diagnosed with erosive adenomatosis of the nipple (EAN), also known as nipple adenoma. The lesion subsequently was treated and cleared with Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS). At 8-month follow-up there was no clinical recurrence of the lesion, and the patient was satisfied with the overall cosmetic appearance and conservation of the areola. The patient was followed clinically with annual breast examinations and mammography to monitor future recurrence.
Erosive adenomatosis of the nipple is an uncommon benign proliferative process of the lactiferous ducts of the nipple. Recognizing EAN is important because it resembles malignant breast diseases such as Paget disease of the nipple and invasive breast carcinoma. Due to these similarities, early cases of EAN have resulted in unnecessary mastectomies before the benignity of the condition was established.1 Accurate diagnosis is important to both the patient and the clinician for treatment planning as well as psychosocial consequences associated with the potential removal of this anatomically and cosmetically sensitive area.
Reviewing the literature on EAN is complicated by the variety of terms used to describe this condition, including but not limited to nipple adenoma, nipple duct adenoma, papillary adenoma of the nipple, and florid papillomatosis of the nipple. In 1955, Jones2 described EAN using the term florid papillomatosis of the nipple ducts. In 1962, Handley and Thackray1 argued that adenoma of the nipple was a more descriptive term because it more closely described the appearance of a sweat gland adenoma. They reasoned that adenoma of the nipple is a separate process from ductal papilloma due to the adenomatous proliferation into the nipple stroma rather than the lumen of the nipple ducts.1 The term adenoma of the nipple was further supported in 1965 by Taylor and Robertson.3 In 1959, Le Gal et al4 used the term erosive adenomatosis of the nipple to describe the erosive nature of nipple adenoma. The term nipple adenoma was published in the 2012 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Breast with 4 common histologic subtypes.5,6
Erosive adenomatosis of the nipple is clinically indistinguishable from Paget disease of the nipple, thus biopsy is essential for accurate diagnosis. In contrast to Paget disease, EAN tends to present in younger patients and progresses more slowly, and symptoms may be exacerbated around menstruation.1 Case reports demonstrate that patients may wait years before seeking medical attention for EAN.1,3,7,8 Presenting symptoms may include inflammation, crusting, nipple skin erosion, itching, and pain. Serous or sanguineous discharge from the lesions also is commonly reported. Palpation may reveal a small, hard, or elastic nodule within or underlying the nipple. In addition to Paget disease, EAN may resemble squamous cell carcinoma of the nipple, eczema, psoriasis, or a skin infection.6 Axillary lymphadenopathy is not present in the absence of a concomitant breast malignancy.8 On biopsy, nipple adenoma represents ductal proliferation of glandular structures within the stroma of the nipple that is well circumscribed but without borders. The erosive appearance of the lesion is produced by extensions of the glandular epithelium on the surface of the nipple.1,6 Specific to EAN is the presence of 2 cell types: an inner columnar epithelium and an outer cuboidal myoepithelium. These 2 cell types are present in normal lactiferous ducts; however, normal ducts are highly organized compared to EAN.9
After confirmation of EAN by nipple biopsy, complete surgical excision has been the gold standard for treatment, followed by reconstructive surgery.6 Handley and Thackray1 advocated for total excision of the nipple and areola with an underlying wedge of breast tissue to facilitate wound closure. More recently, successful alternative forms of treatment have been utilized to minimize disfiguring surgery. Alternative treatments include MMS,8 cryotherapy,10 and nipple splitting enucleation.6 Treatment with MMS has resulted in nipple sparing with the least amount of surface area sacrificed (1.1 cm2).9 Our case and prior case reports demonstrate that the tissue sparing potential of MMS is appropriate for the treatment of EAN, though traditionally it has been reserved for more malignant tumors. Preserving this sensitive area is both cosmetically and psychologically advantageous for the patient and thus should be considered when reviewing treatment options for EAN.

A 30-year-old man presented to our outpatient clinic with rapidly growing, ulcerated, violaceous lesions on the hard palate of 4 months' duration...

A frail 85-year-old man presented to the emergency department for treatment of an erythematous tender nodule on the scalp. The area was...

A 57-year-old woman with triple-negative ductal breast cancer presented with a mildly pruritic rash on bilateral mastectomy scars of 3 to 4 months...
