Dermpath Diagnosis
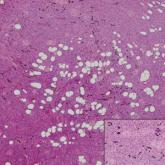
Pigmented Mass on the Shoulder
A 37-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic, indurated, pigmented, subcutaneous nodule on the right shoulder of more than 3 years' duration...
Dr. Wu is from the Department of Dermatology, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China. Dr. Wu also is from and Drs. Skipper and Elston are from the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. Drs. Wu and Elston are from the Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery, and Dr. Skipper is from the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Dirk M. Elston, MD, Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery, Medical University of South Carolina, 135 Rutledge Ave, MSC 578, Charleston, SC 29425 (elstond@musc.edu).

Epithelioid histiocytoma (EH), also known as epithelioid cell histiocytoma or epithelioid fibrous histiocytoma, is a rare benign fibrohistiocytic tumor first described in 1989.1 Epithelioid histiocytoma commonly presents in middle-aged adults with a slight predilection for males.2 The most frequently affected site is the lower extremity. The arms, trunk, head and neck, groin, and tongue also can be involved.3,4 It usually presents as a solitary asymptomatic papule or nodule, though cases with multiple lesions have been reported.5 Anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement and overexpression have been confirmed and suggest that EH is distinct from conventional cutaneous fibrous histiocytoma.5
Histologically, EH appears as an exophytic, symmetric, and well-demarcated dermal nodule with a classic epidermal collarette. Prominent vascularity with perivascular accentuation of the epithelioid tumor cells is common. Older lesions may be hyalinized and sclerotic. Epithelioid cells commonly account for more than 50% of the tumor and are characterized by eosinophilic cytoplasm, vesicular nuclei, and small eosinophilic nucleoli. A small population of lymphocytes and mast cells are variably present (quiz image, bottom).1-3,7 A predominantly spindle cell variant has been reported.8 Other histopathologic variants include granular cell,9 cellular,10 and EH with perineuriomalike growth.11 Immunohistochemical staining shows anaplastic lymphoma kinase positivity in most cases, and more than half of cases stain positive for factor XIIIa and epithelial membrane antigen. Tumor cells consistently are negative for desmin and cytokeratins.6,10,12 Excision is curative.8
Polypoid Spitz nevus (PSN) is a benign nevus with a conspicuous polypoid or papillary exophytic architecture. The term was coined in 2000 by Fabrizi and Massi.13 Spitz nevus is a benign acquired melanocytic tumor that typically presents in children and adolescents and has a wide histologic spectrum.14 There is some debate on this entity, as some authors do not regard PSN as a distinct histologic variant; thus, it seems underreported in the literature.15 In a review of 349 cases of Spitz nevi, the authors found 7 cases of PSN.16 In another review of 74 cases of intradermal Spitz nevi, 14 cases of PSN were identified.14 This polypoid variant is easily mistaken for a polypoid melanoma because it can show cytologic atypia with large nuclei. Polypoid Spitz nevus usually lacks mitoses, notable pleomorphism, and sheetlike growth, unlike melanoma (Figure 1).13,14
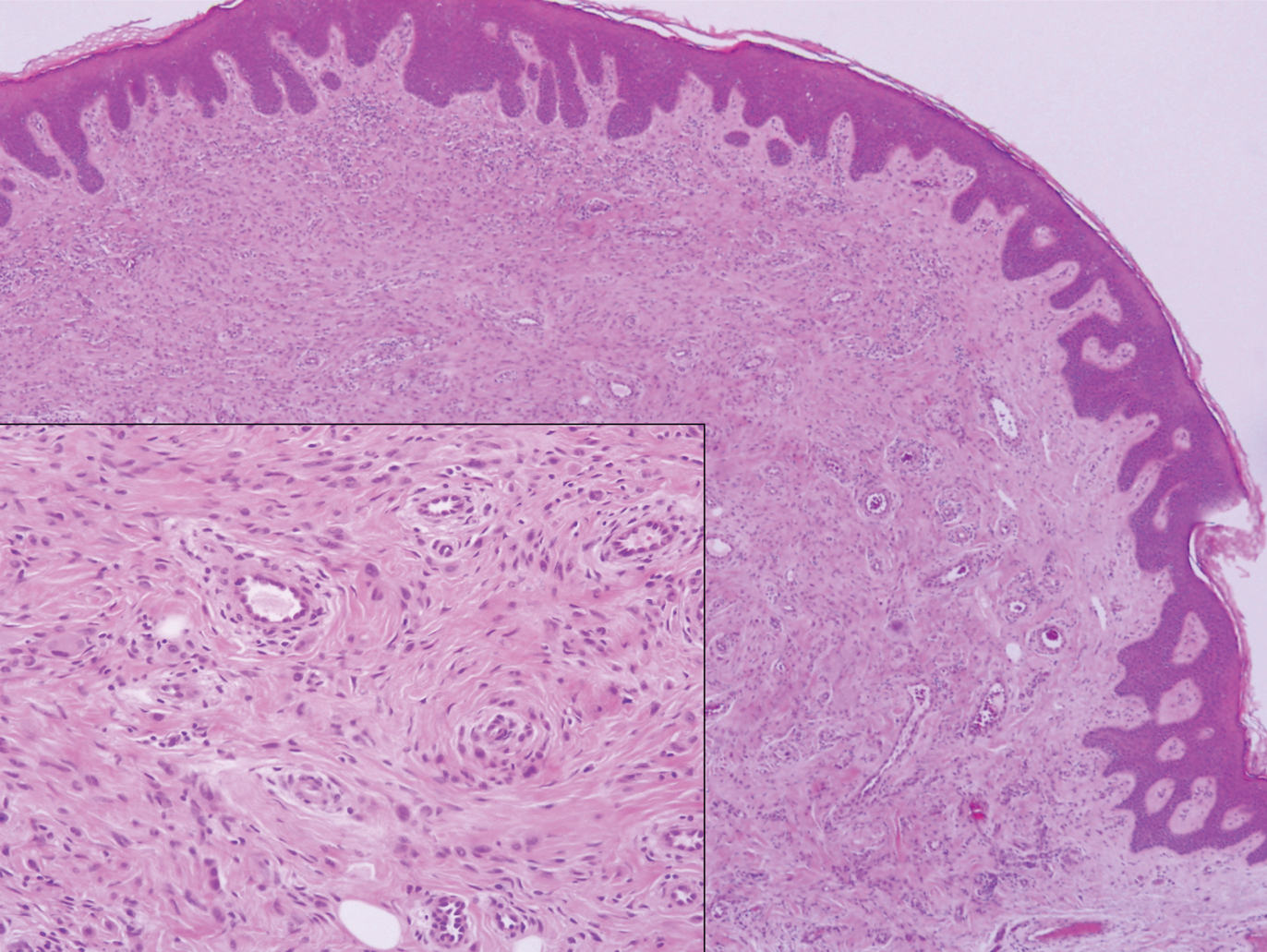
Figure 1. Polypoid Spitz nevus. A polypoid architecture with predominantly intradermal epithelioid and spindled melanocytes arranged as single units splaying between dermal collagen. The thick-walled vascular pattern is characteristic (H&E, original magnification ×40; inset, original magnification ×200).
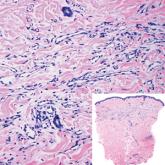
Myopericytoma is an uncommon benign mesenchymal neoplasm that typically presents as a solitary, slowly enlarging and painless nodule with a predilection for the lower extremities, usually in adult males.17-20 Histologically, it consists of a well-circumscribed nodule with numerous thin-walled vessels and a proliferation of ovoid to spindled myopericytes exhibiting a concentric perivascular growth pattern (Figure 2). Myopericytoma usually is positive for smooth muscle actin and h-caldesmon but is negative or only focally positive for desmin. The prognosis is good with rare recurrence, despite incomplete excision.17,18
Solitary reticulohistiocytoma is a rare benign form of non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis.21,22 Unlike its multicentric counterpart, solitary reticulohistiocytoma rarely is associated with systemic disease. It presents as a small, dome-shaped, painless papule or nodule that can affect any part of the body.22,23 Solitary reticulohistiocytoma characteristically demonstrates cells with a ground glass-like appearance and 2-toned cytoplasm. A mixed inflammatory infiltrate including neutrophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes commonly is present (Figure 3). The epithelioid histiocytes are positive for vimentin and histiocytic markers including CD68 and CD163.22
Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is an uncommon mesenchymal fibroblastic neoplasm that can arise at almost any anatomic site.24 Cutaneous SFTs are more common in women, most often involve the head, and appear to behave in an indolent manner.25 Solitary fibrous tumors are translocation-associated neoplasms with a NAB2-STAT6 gene fusion.26 The classic histology of SFT is a spindled fibroblastic proliferation arranged in a "patternless pattern" with interspersed stag horn-like, thin-walled blood vessels (Figure 4). Tumor cells usually are positive for CD34, CD99, and Bcl-2.27 In addition, STAT6 immunoreactivity is useful in diagnosis of SFT.25

A 37-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic, indurated, pigmented, subcutaneous nodule on the right shoulder of more than 3 years' duration...
A 38-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic lesion on the abdomen. On physical examination, there was a 5×2-mm, solitary, ill-defined pink...
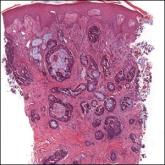
A 68-year-old patient presented with an enlarging flesh-colored nodule on the thigh that was positive for cytokeratin 20 and negative for...
