Results
Patients
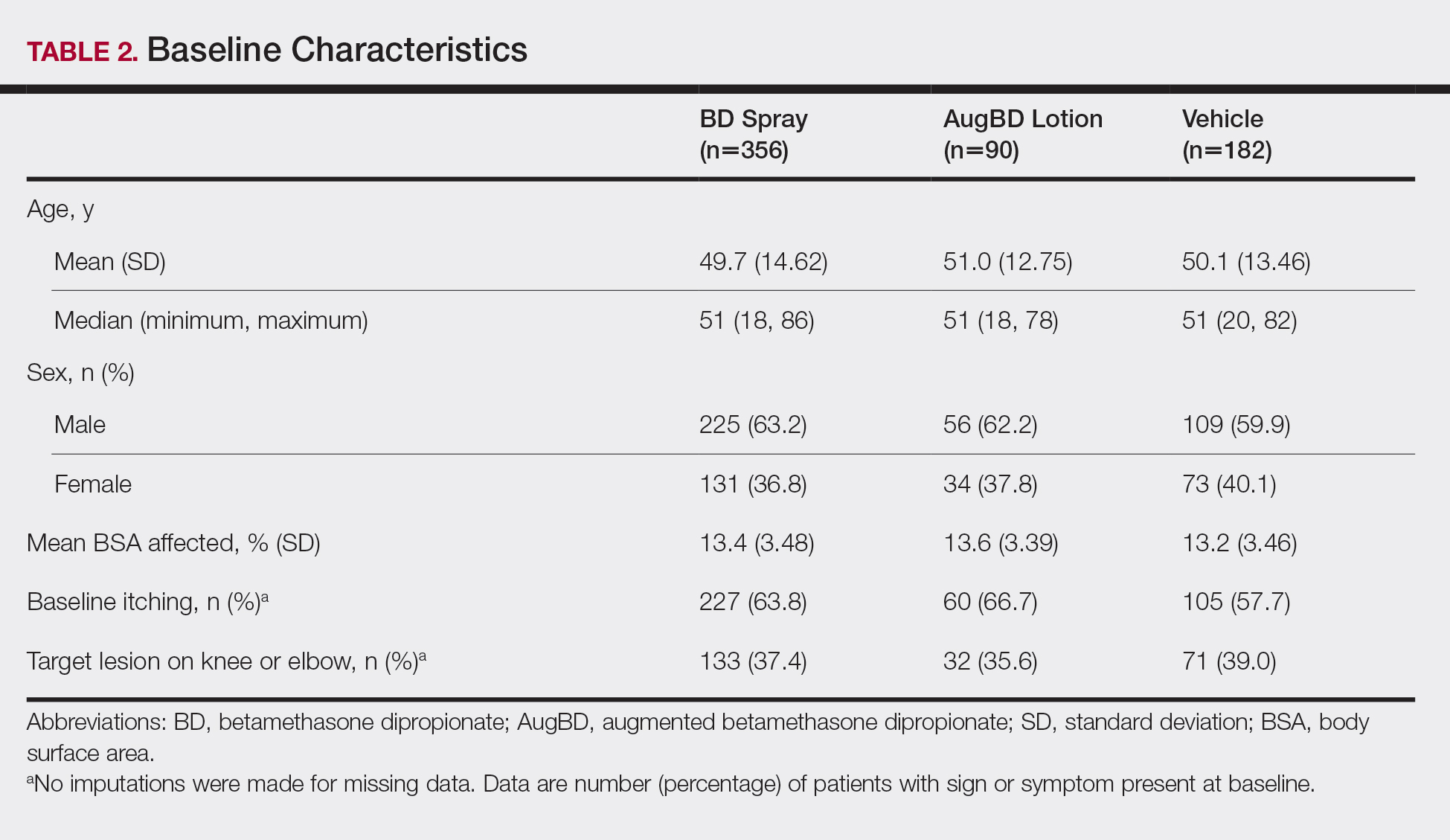
These analyses included data from the 628 patients enrolled in the 2 phase 3 trials. Patients had similar baseline characteristics across treatment groups (Table 2). Itching was the most common cutaneous symptom at baseline, reported by almost two-thirds (n=392, 62.4%) of patients. Of the 628 patients, 236 (37.6%) had a target lesion located on the elbow or knee selected for assessment. The mean baseline body surface area was 13% to 14% across groups.
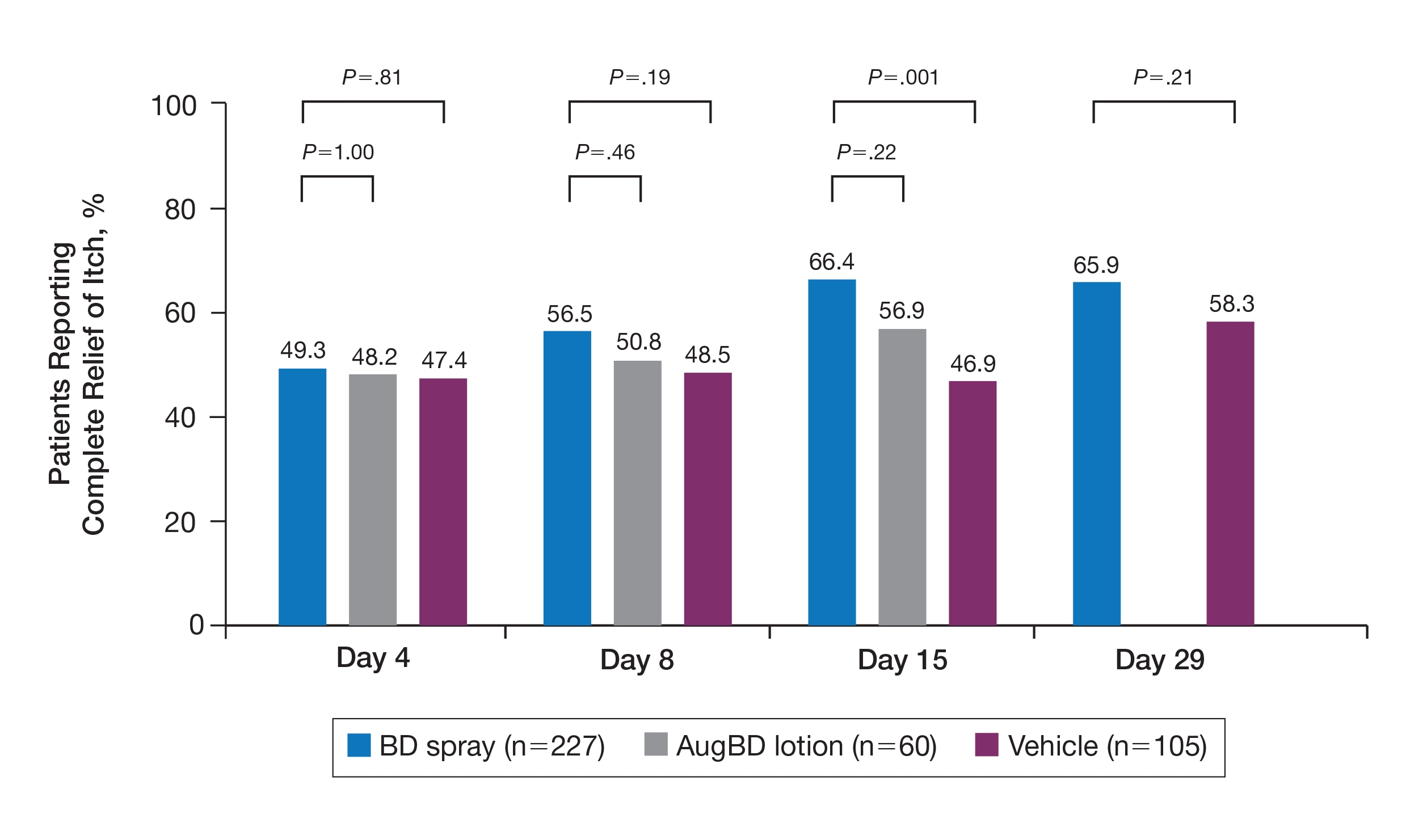
A post hoc analysis was performed on the subgroup of patients who reported itching at baseline (N=392)(eFigure 1). For these patients, almost half were itch free by day 4 across all groups (49.3% BD spray, 48.2% AugBD lotion, and 47.4% vehicle). By the end of treatment, 65.9% of patients using BD spray and 58.3% of patients using vehicle were itch free at day 29, with 56.9% of AugBD lotion patients itch free at day 15.
Application-site pruritus recorded as a treatment-emergent adverse event was seen in low numbers and was similar in proportion between the 2 steroid treatments (7.7% BD spray, 6.7% AugBD lotion, and 14.4% vehicle).
Psoriasis Individual Sign Scores for Knee and Elbow Plaques
Target lesions located on the knee or elbow represented 37.6% of all target lesions assessed. Efficacy analysis of the pooled data on knee and elbow lesions revealed that BD spray was similar to AugBD lotion in reducing sign scores to 0 or 1 (Figures 1 and 2).
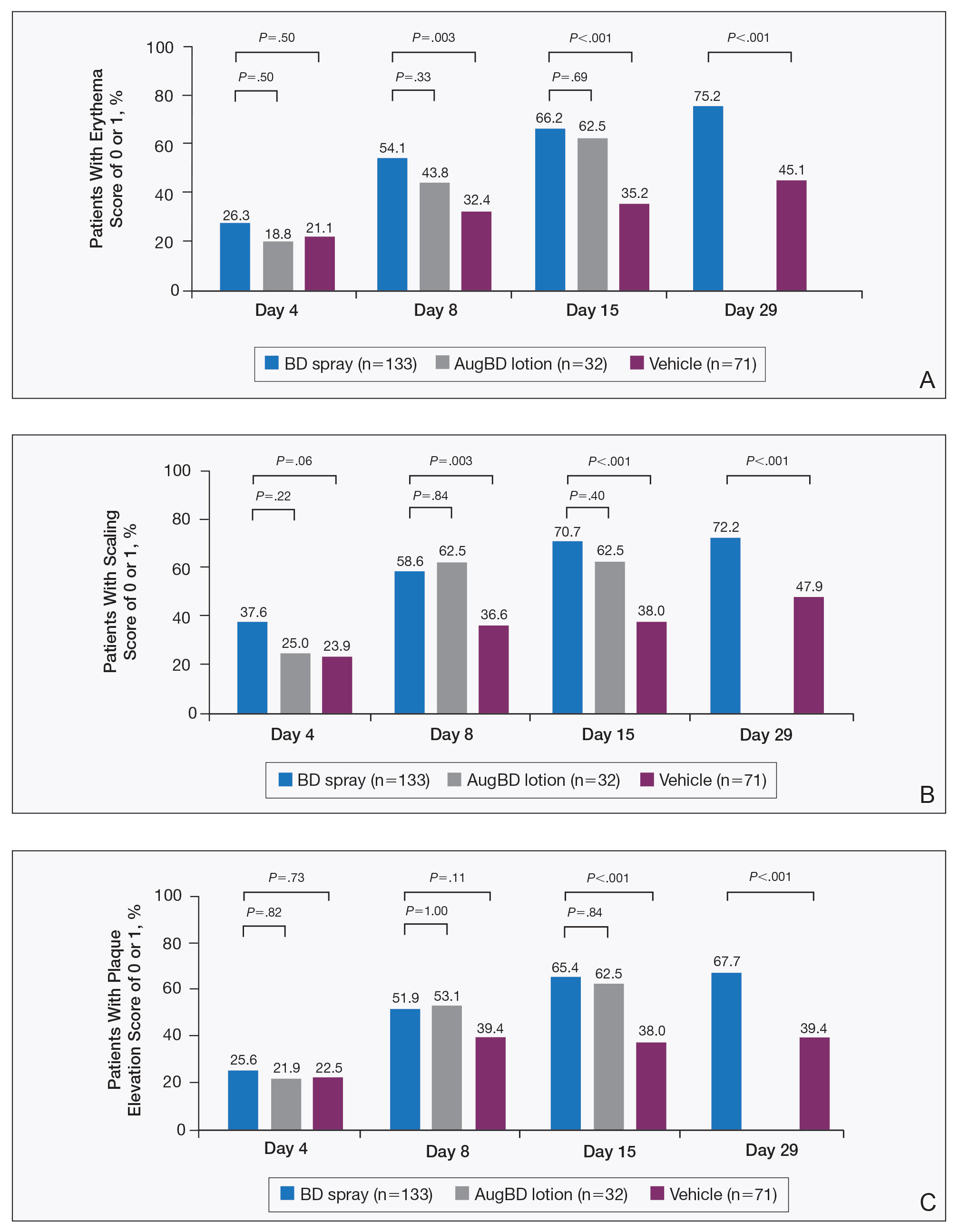
Figure 1. Sign scores of psoriatic target lesions located on the knees and elbows. Mean percentage of patients treated with betamethasone dipropionate (BD) spray 0.05%, augmented betamethasone dipropionate (AugBD) lotion, or vehicle with a score of 0 (clear) or 1 (mild) for individual signs: A, erythema; B, scaling; and C, plaque elevation.
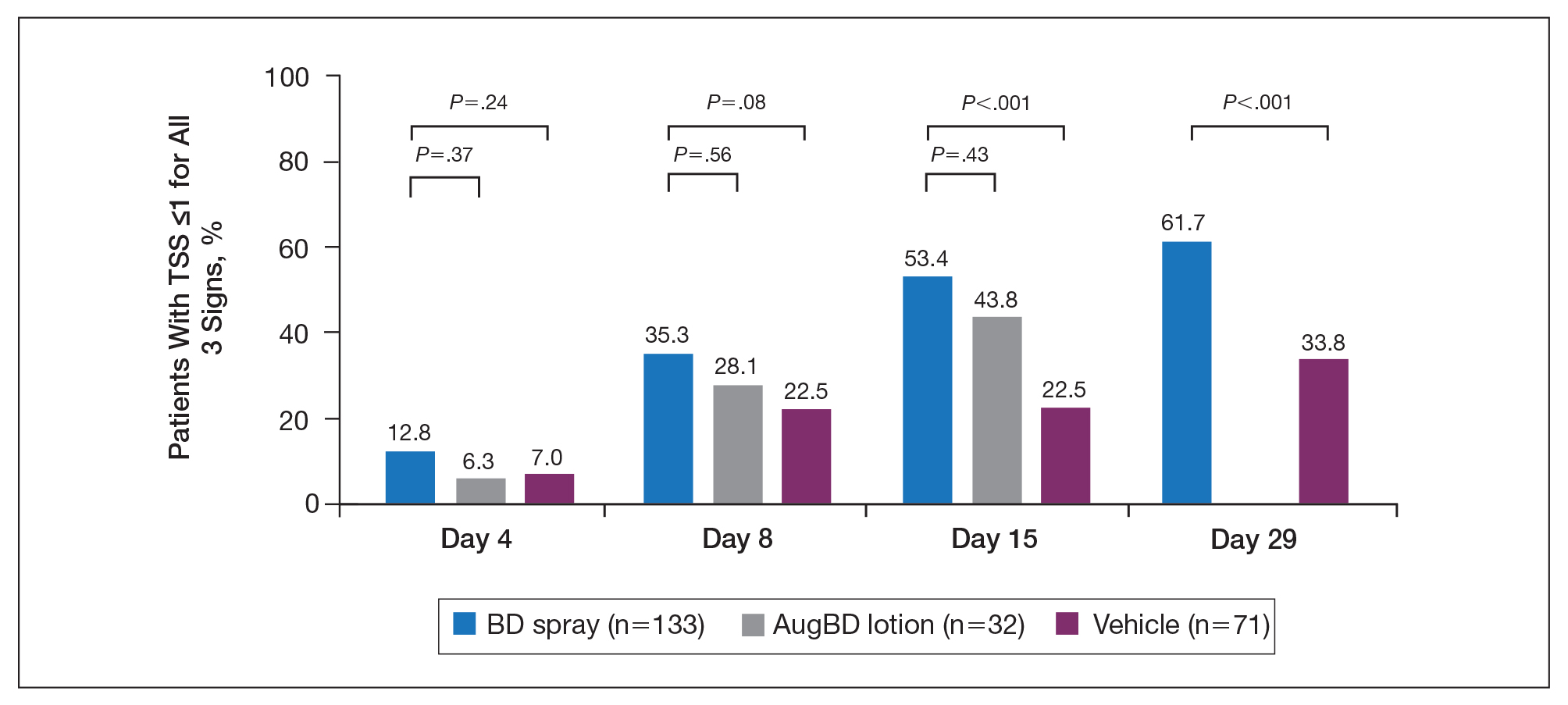
Figure 2. Total sign score (TSS) for lesions on the elbows and knees (≤1 for each sign). Percentage of patients treated with betamethasone dipropionate (BD) spray 0.05%, augmented betamethasone dipropionate (AugBD) lotion, or vehicle with a sign score of 0 or 1 for each of the individual signs of erythema, scaling, and plaque elevation.
The percentage of patients reporting improvements in erythema, scaling, and plaque elevation scores at day 4 were numerically but not statistically significantly greater with BD spray vs AugBD lotion (eFigure 2).
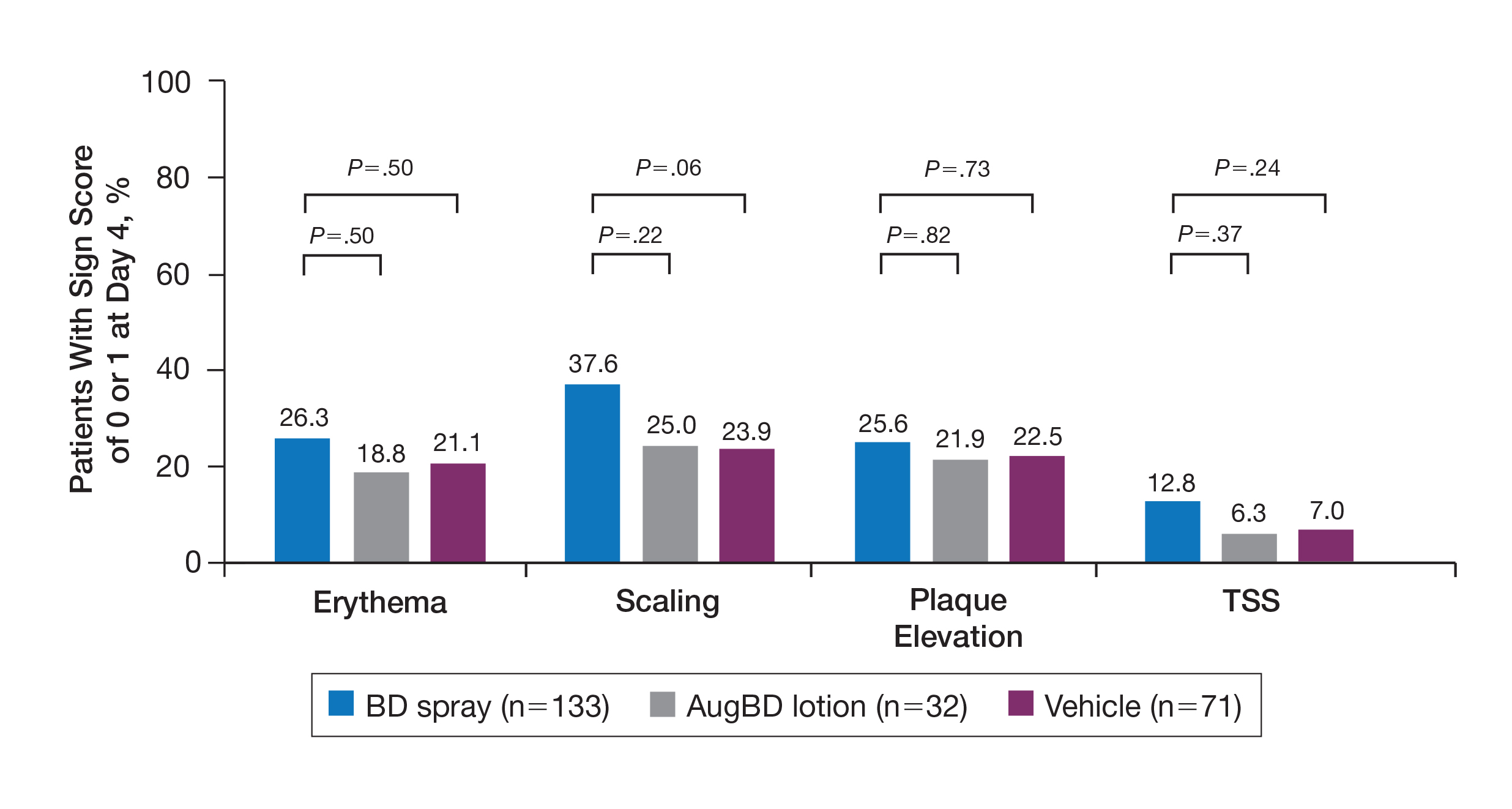
eFigure 2. Sign scores of 0 or 1 for psoriatic target lesions located on the knees and elbows at day 4. Mean percentage of patients treated with betamethasone dipropionate (BD) spray 0.05%, augmented betamethasone dipropionate (AugBD) lotion, or vehicle with a score of 0 (clear) or 1 (mild) for erythema, scaling, and plaque elevation and total sign score (TSS) of 0 or 1 for all 3 signs.
The proportion of patients achieving treatment success (defined as a score of 0 or 1) was comparable for the2 products on day 15 for erythema (66.2% BD spray vs 62.5% AugBD lotion), scaling (70.7% BD spray vs 62.5% AugBD lotion), and plaque elevation (65.4% BD spray vs 62.5% AugBD lotion)(Figure 1). From day 8, BD spray reduced erythema and scaling in significantly more patients than vehicle (P=.003 for both), and BD spray reduced erythema, scaling, and plaque elevation in more patients than vehicle from day 15 (P<.001 for all). No statistically significant difference was found between BD spray and AugBD lotion on erythema, scaling, and plaque elevation scores.
Total Sign Score
Total sign score results showed that the mean percentage of patients achieving a TSS of 0 or 1 for all signs for lesions located on the knees or elbows was numerically higher for BD spray vs AugBD lotion at day 4, but this difference was not statistically significant (Figure 2). Day 15 outcomes for TSS also showed a numerically greater success rate for BD spray, but again this difference was not statistically significant (53.4% BD spray vs 43.8% AugBD lotion). At days 15 and 29, significantly more patients treated with BD spray achieved TSS of 0 or 1 for all 3 signs compared to those treated with vehicle (P<.001). Improvement in TSS with BD spray continued through to day 29 of the study.