Methods
Data Collection
A retrospective review of medical records was conducted to investigate the effect of the USF Morsani COM pharmaceutical policy changes on physician prescribing practices within the Department of Dermatology & Cutaneous Surgery. Medical records of patients seen for common dermatology diagnoses before (January 1, 2010, to May 30, 2010) and after (August 1, 2011, to December 31, 2011) the pharmaceutical policy changes were reviewed, and all medications prescribed were recorded. Data were collected from medical records within the USF Health electronic medical record system and included visits with each of the department’s 3 attending dermatologists. The diagnoses included in the study—acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis, onychomycosis, psoriasis, and rosacea—were chosen because in-office samples were available. Prescribing data from the first 100 consecutive medical records were collected from each time period, and a medical record was included only if it contained at least 1 of the following diagnoses: acne vulgaris, atopic dermatitis, onychomycosis, psoriasis, or rosacea. The assessment and plan of each progress note were reviewed, and the exact medication name and associated diagnosis were recorded for each prescription. Subsequently, each medication was reviewed and placed in 1 of 3 categories: brand name, generic, and OTC. The total number of prescriptions for each diagnosis (per visit/note); the specific number of brand, generic, and OTC medications prescribed (per visit/note); and the percentage of brand, generic, and OTC medications prescribed (per visit/note and per diagnosis in total) were calculated. To ensure only intended medications were included, each medication recorded in the medical record note was cross-referenced with the prescribed medication in the electronic medical record. The primary objective of this study was to capture the prescribing physician’s intent as proxied by the pattern of prescription. Thus, changes made in prescriptions after the initial plan—whether insurance related or otherwise—were not relevant to this investigation.
The data were collected to compare the percentage of brand vs generic or OTC prescriptions per diagnosis to see if there was a difference in the prescribing habits before and after the pharmaceutical policy changes. Of note, several other pieces of data were collected from each medical record, including age, race, class of insurance (ie, Medicare, Medicaid, private health maintenance organization, private preferred provider organization), subtype diagnoses, and whether the prescription was new or a refill. The information gathered from the written record on the assessment and plan was verified using prescriptions ordered in the Allscripts electronic record, and any difference was noted. No identifying information that could be used to easily identify study participants was recorded.
Differences in prescribing habits across diagnoses before and after the policy changes were ascertained using a Fisher exact test and were further assessed using a mixed effects ordinal logistic regression model that accounted for within-provider clustering and baseline patient characteristics. An ordinal model was chosen to recognize differences in average cost among brand-name, generic, and OTC medications.
Results
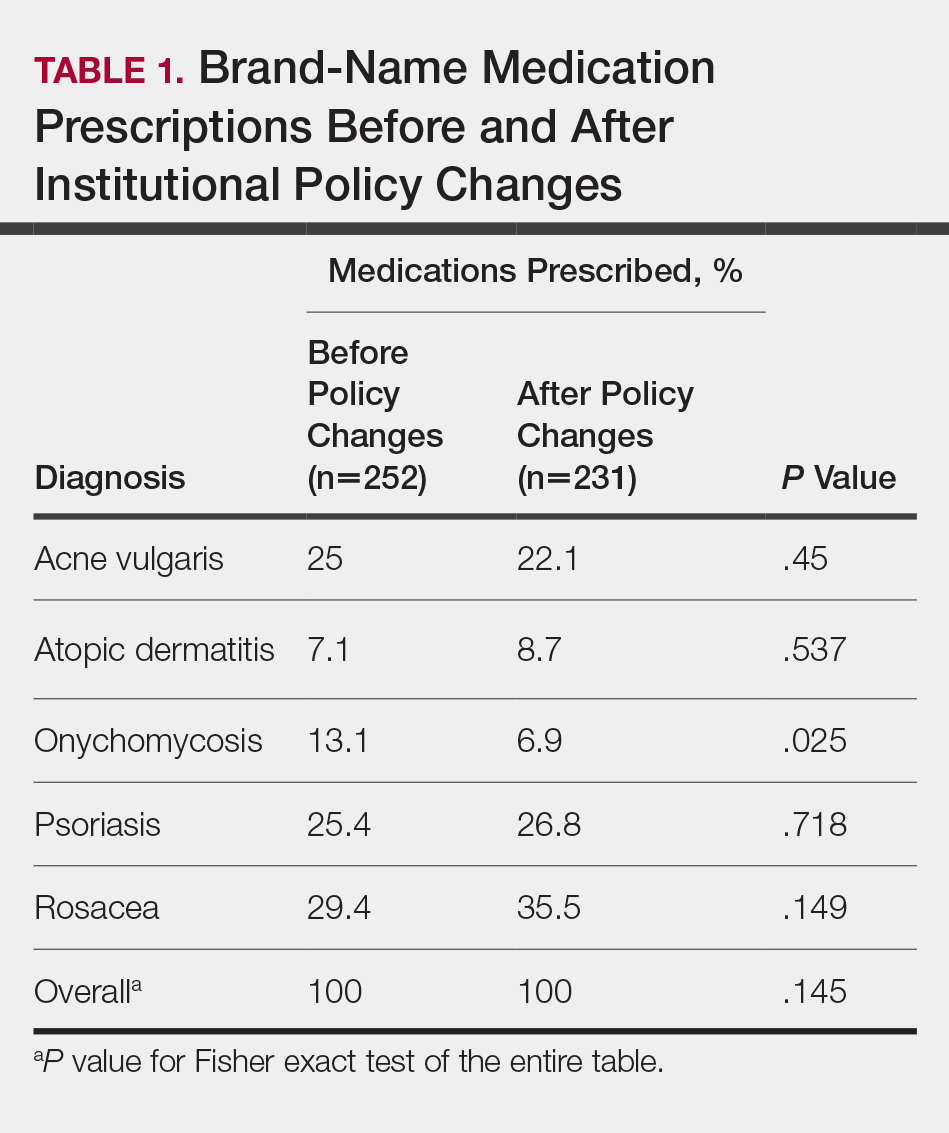
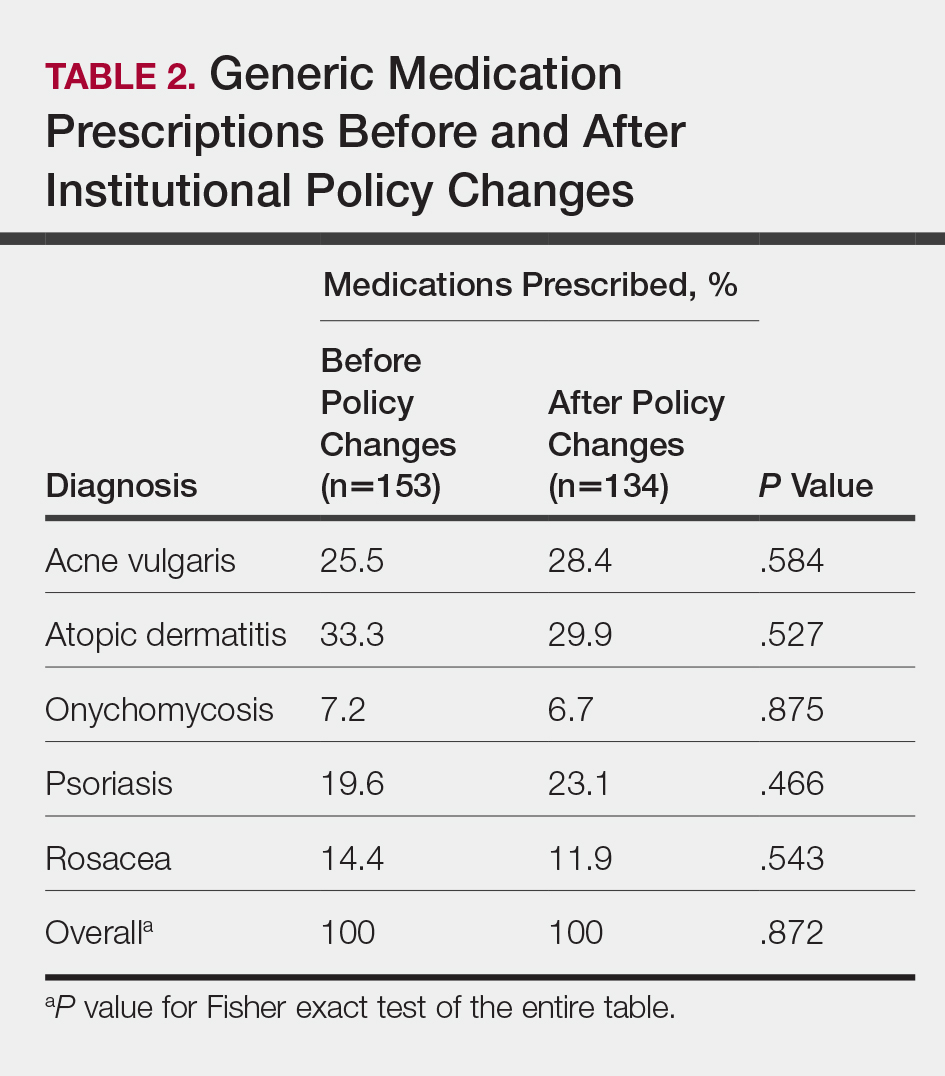
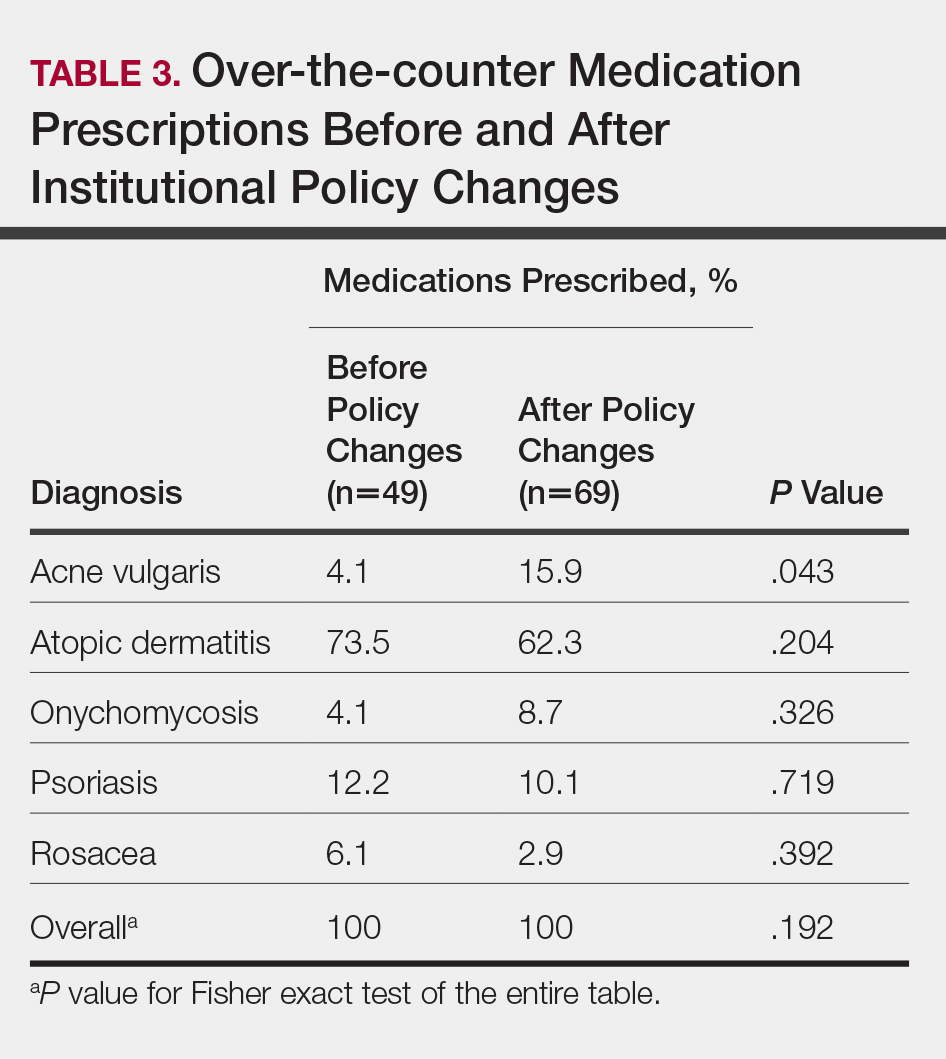
In total, 200 medical records were collected. For the period analyzed before the policy change, 252 brand-name medications were prescribed compared to 231 prescribed for the period analyzed after the policy changes. There was insufficient evidence of an overall difference in brand-name medications prescribed before and after the policy changes (P=.145; Fisher exact test)(Table 1). There also was insufficient evidence of an overall difference in generic prescriptions, which totaled 153 before and 134 after the policy changes (P=.872; Fisher exact test)(Table 2). Over-the-counter prescriptions totaled 49 before and 69 after the policy changes. There was insufficient evidence of an overall difference before and after the policy changes for OTC medications (P=.192; Fisher exact test)(Table 3).