The prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) appears to be much lower than previously believed and may pose “a potential risk to research funding for the disease,” according to results of a meta-analysis involving a network of population-based registries.
“When we started this study, a widely cited lupus statistic was that approximately 1.5 million Americans were affected. Our meta-analysis found the actual prevalence to be slightly more than 200,000: a number that approaches the [Food and Drug Administration’s] definition of a rare disease,” Emily Somers, PhD, ScM, senior author and associate professor of rheumatology and environmental health sciences at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in a written statement.
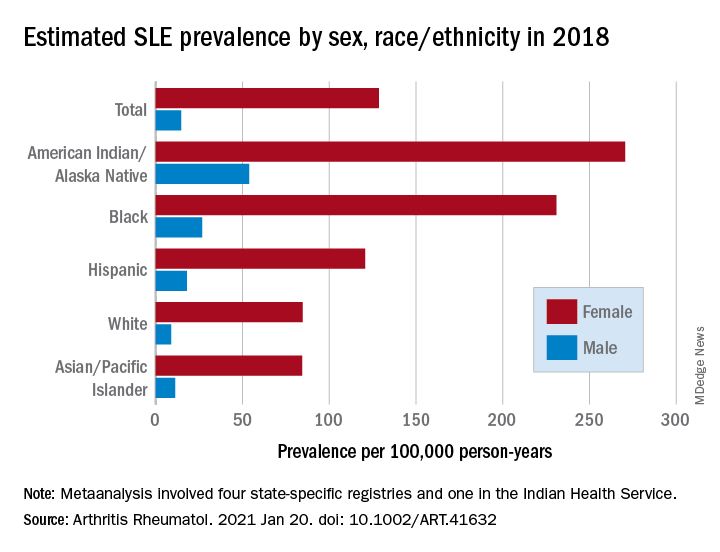
Their estimates, published online in Arthritis & Rheumatology, put the overall SLE prevalence in the United States at 72.8 per 100,000 person-years in 2018, with nearly nine times more females affected (128.7 cases per 100,000) than males (14.6 per 100,000). Race and ethnicity also play a role, as prevalence was highest among American Indian/Alaska Native and Black females, with Hispanic females lower but still higher than White and Asian/Pacific Islander females, Peter M. Izmirly, MD, MSc, of New York University, the lead author, and associates said.
SLE prevalence was distributed similarly in men, although there was a greater relative margin between American Indians/Alaska Natives (53.8 cases per 100,000 person-years) and Blacks (26.7 per 100,000), and Asians/Pacific Islanders were higher than Whites (11.2 vs. 8.9), the investigators reported.
The meta-analysis leveraged data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s national lupus registries, which include four state-specific SLE registries and a fifth in the Indian Health Service. All cases of SLE occurred in 2002-2009, and the data were age adjusted to the 2000 U.S. population and separately extrapolated to the 2018 U.S. Census population, they explained.
The analysis was funded by cooperative agreements between the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene and New York University, and the CDC and National Institute of Health.