Microscopic Demodex Examination
Demodex count was determined using a standardized skin surface biopsy, which is a noninvasive method. Every patient gave samples from the cheeks. This biopsy was repeated from the same site. A drop of cyanoacrylate was placed on a clean slide, pressed against a skin lesion, held in place for 1 minute, and removed. The obtained samples were evaluated under a light microscope (Nikon E200) with oil immersion. When more than 5 mites were detected per square centimeter, the result was recorded as positive.
Ophthalmologic Examination
A complete ophthalmologic examination including visual acuity assessment, standardized slit lamp examination, and fundus examination was done for all patients. Ocular rosacea was diagnosed on detection of 1 or more of the following: watery or bloodshot appearance, foreign-body sensation, burning or stinging, dryness, itching, light sensitivity, blurred vision, telangiectases of the conjunctiva and eyelid margin, eyelid lid and periocular erythema, anterior blepharitis, meibomian gland dysfunction, or irregularity of eyelid margins. All patients were screened for the signs and symptoms of ocular rosacea and underwent other ophthalmologic examinations, including tear function tests. Tear functions were evaluated with Schirmer tests without anesthesia and fluorescein tear breakup time (TBUT). Tear film breakup time was assessed after instillation of 2% fluorescein staining under a cobalt blue filter. The time interval between the last complete blink and the appearance of the first dry spot was recorded. The mean of 3 consecutive measurements was obtained. The Schirmer test was performed without topical anesthesia using a standardized filter strip (Bio-Tech Vision Care). The amount of wetting was measured after 5 minutes. Meibomian gland expressibility was assessed by applying digital pressure to the eyelid margin.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis of the study was performed with SPSS Statistics Version 22.0 (SPSS Inc). Continuous variables were reported as mean (SD), and categorical variables were reported as percentages and counts. Descriptive statistics for numerical variables were created. An independent sample t test was used for normally distributed continuous variables. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to determine normality. The Schirmer test without anesthesia and TBUT values among groups were compared using one-way analysis of variance. The differences were calculated using the multiple comparison Tukey test. P<.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Demographic Characteristics of Rosacea Patients
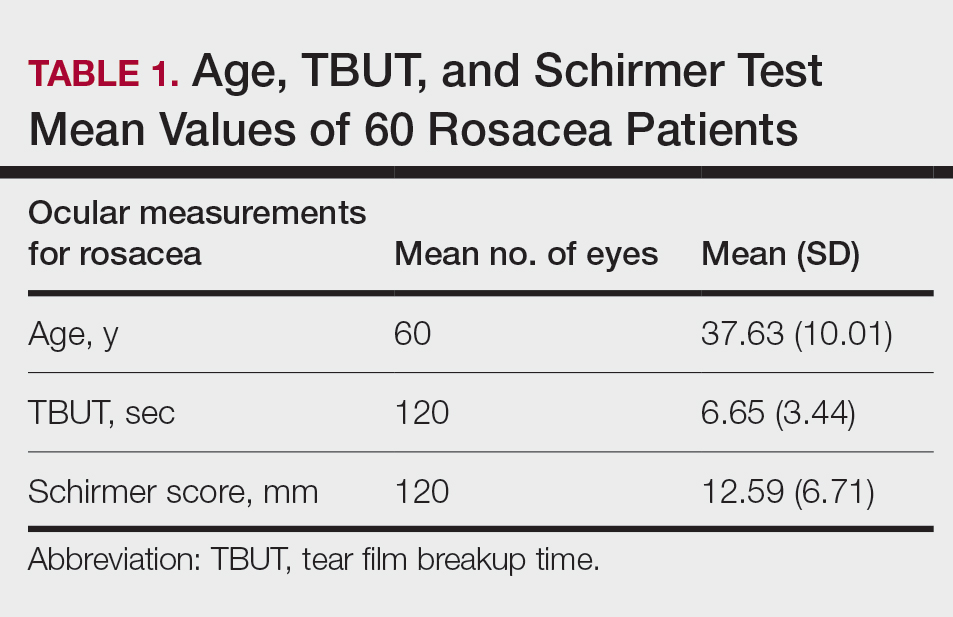
Sixty eyes of 30 newly diagnosed patients with acne rosacea with Demodex infestation and 60 eyes of 30 newly diagnosed patients with acne rosacea without Demodex infestation were enrolled in this study. The mean age (SD) of the 60 patients was 37.63 (10.01) years. The mean TBUT (SD) of the 120 eyes was 6.65 (3.44) seconds, and the mean Schirmer score (SD) was 12.59 (6.71) mm (Table 1).
Meibomian Gland Dysfunction vs Subgroup of Rosacea Patients
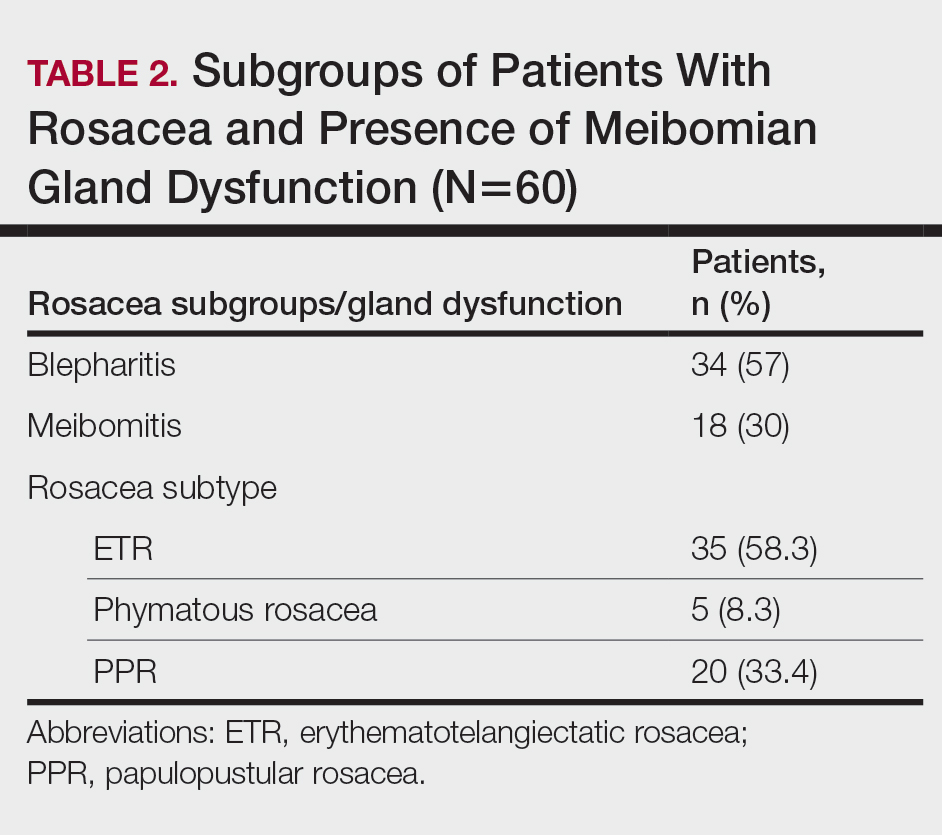
Thirty-four (57%) patients had blepharitis, and 18 (30%) patients had meibomitis. Thirty-five (58.3%) patients had ETR, 5 (8.3%) patients had phymatous rosacea, and 20 (33.4%) patients had PPR (Table 2). Of the Demodex-negative patients, 73.3% (22/30) had ETR, 20% (6/30) had PPR, and 6.7% (2/30) had phymatous rosacea. Of the Demodex-positive patients, 43.3% (13/30) had ETR, 46.7% (14/30) had PPR, and 10% (3/30) had phymatous rosacea (Table 3). Papulopustular rosacea was found to be significantly associated with Demodex positivity (P=.003); neither ETR nor phymatous rosacea was found to be significantly associated with Demodex infestation (P=.66 and P=.13, respectively)(Table 3).
There was no statistically significant difference between the Demodex-negative and Demodex-positive groups for mean age (SD)(37.4 [11.54] years vs 37.87 [8.41] years; P=.85), mean TBUT (SD)(6.73 [3.62] seconds vs 6.57 [3.33] seconds; P=.85), and mean Schirmer score (SD)(13.68 [7.23] mm vs 11.5 [6.08] mm; P=.21)(Table 4).
Fifteen (50%) patients (30 eyes) in the Demodex-negative group and 19 (63.3%) patients (38 eyes) in the Demodex-positive group had blepharitis, with no statistically significant difference between the groups (P=.43). Seven (23.3%) patients (14 eyes) in the Demodex-negative group and 11 (36.7%) patients (22 eyes) in the Demodex-positive group had meibomitis, with no statistically significant difference between the groups (P=.39)(Table 3).