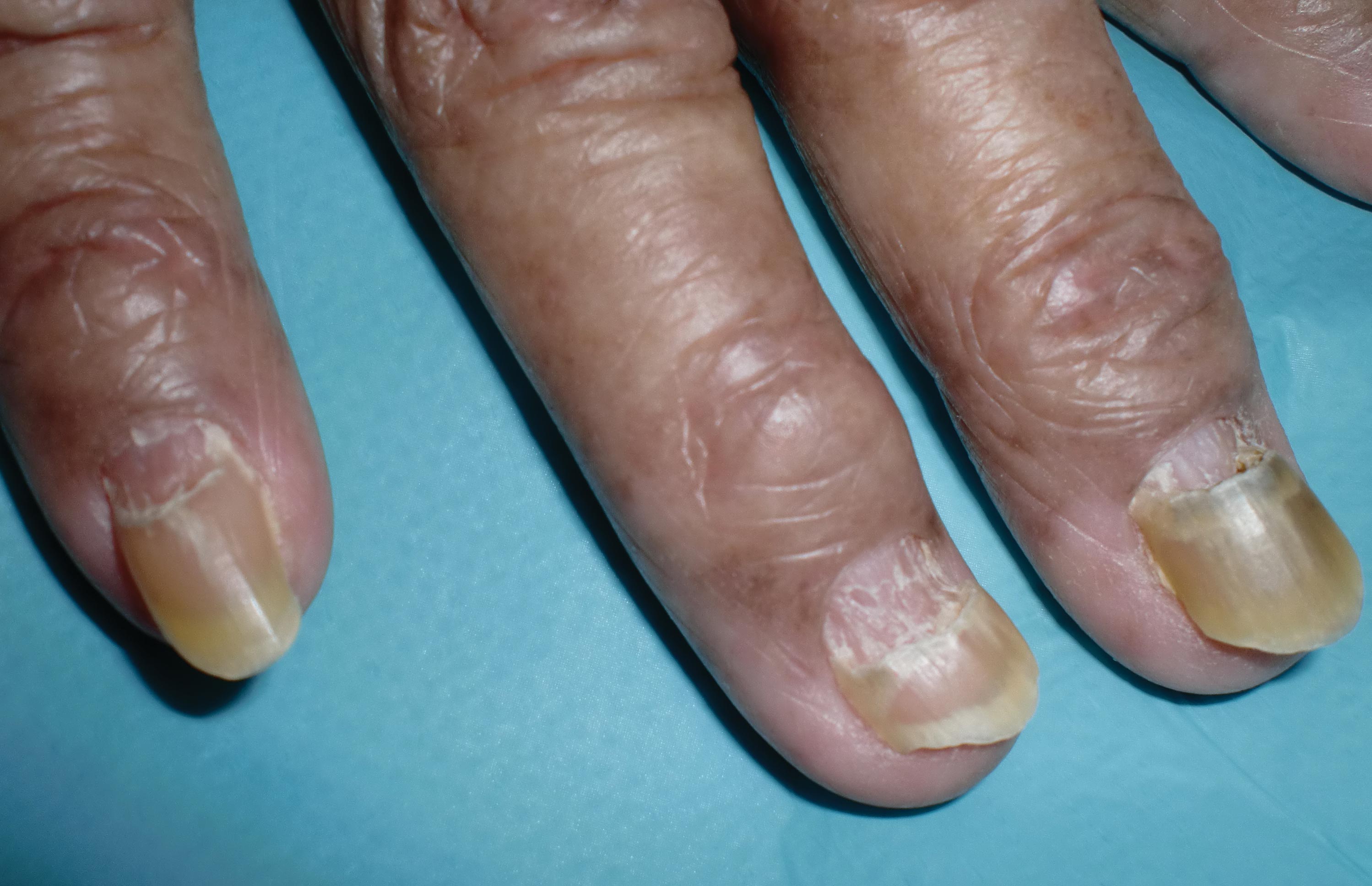
The Diagnosis: Onychomadesis
The nail changes were characteristic of onychomadesis. Systemic illness in this patient most likely resulted in temporary arrest of nail matrix activity, leading to separation of the proximal nail plate from the proximal nail fold, which gave rise to a deep transverse sulcus.1 Conversely, Beau lines are characterized by transverse grooves that move distally as the nail grows. Onychomadesis also is seen in pemphigus vulgaris, which could be due to an autoimmune disease inhibiting normal nail plate growth and development of blisters beneath the nail causing detachment of the nail plate.2 Drug-induced Beau lines or onychomadesis are most frequently caused by chemotherapeutic agents (taxanes) and retinoids, which reflect an arrest in epithelial proliferation.3 Familial cases also have been described.4 Management of the nail abnormality should focus on the underlying medical problem or triggering factor. In our patient, hypertension and kidney disease were managed by a low-salt diet, oral antihypertensives, and iron replacement.