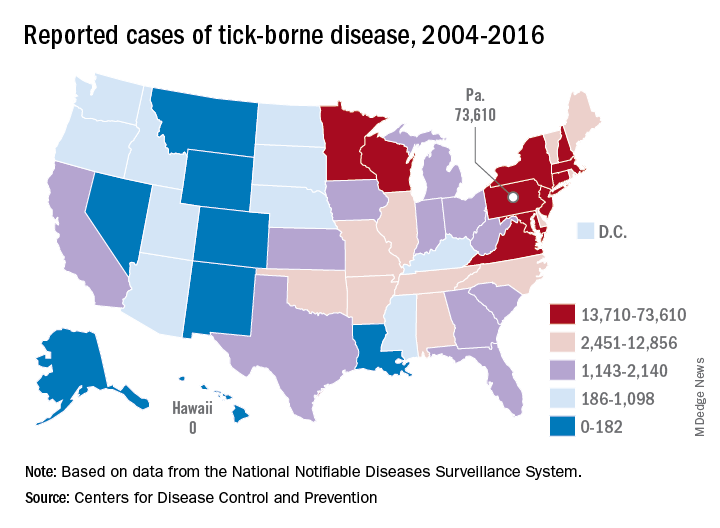
Pennsylvania had more reported cases of tick-borne disease from 2004 to 2016 than any other state, but these diseases are becoming a national threat, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were 73,000 cases reported in Pennsylvania over that period, and tick-borne diseases, including Lyme disease, anaplasmosis/ehrlichiosis, spotted fever rickettsiosis, babesiosis, tularemia, and Powassan virus, among others, affected almost 492,000 people nationwide, with Lyme disease representing the majority of cases, the CDC said in a Vital Signs report.
Although it’s no surprise that Pennsylvania, New York, and Connecticut were tick-borne disease hot spots, non-Northeastern states like Virginia, Wisconsin, and Minnesota also were among the top 10 in cases. States even further away from the Northeast can be found in the next 10: Arkansas had more than 7,000 cases in 13 years, and Oklahoma had over 4,600 cases, data from the National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System show.
Nationally, the number of cases more than doubled from 23,000 in 2004 to 49,000 in 2016, and tick-borne disease hit every state except Hawaii. Over that same time, seven new tick-borne pathogens were discovered or introduced into the United States, the CDC reported.
“Local and state health departments and vector control organizations face increasing demands to respond to these threats,” the CDC said, but “more than 80% of vector control organizations report needing improvement in one or more of five core competencies, such as testing for pesticide resistance [and using] data to drive local decisions about vector control.”