, according to a Vital Signs report published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention based upon a simultaneous MMWR Early Release. The report indicates that many Americans with HIV are not aware of their status or are not receiving effective treatment. Furthermore, the data suggest that few Americans who could benefit from preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP), a daily pill that prevents HIV, are receiving it.
The report “shows that HIV testing, treatment, and prevention have not reached enough Americans, and it emphasizes the continued urgent need to increase these interventions,” said Jay C. Butler, MD, deputy director for infectious diseases at the CDC, at a press conference. “We made a lot of progress in the late ’90s and into the early part of the 21st century in reducing the number of new cases of HIV. But HIV prevention progress has stalled in America since 2013. This stalling underscores the need to increase resources, deploy new technologies, and build expertise, particularly in areas where they’re needed most.”
To achieve these objectives, the CDC has proposed a federal initiative called Ending the HIV Epidemic: A Plan for America. The goal of the initiative is to reduce new HIV infections by 90% by 2030, in part by expanding access to PrEP medications.
Data suggest shortcomings in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention
In its review of data on HIV testing and treatment in 2017, the Vital Signs report found that approximately 154,000 people with HIV (that is, 14% of the total population with HIV) were unaware that they had the virus. These patients consequently could not take advantage of HIV treatment to maintain health, control the virus, and prevent HIV transmission. Young people aged 13-24 years were less likely to know their HIV status than did those aged 25 years and older, according to the report.
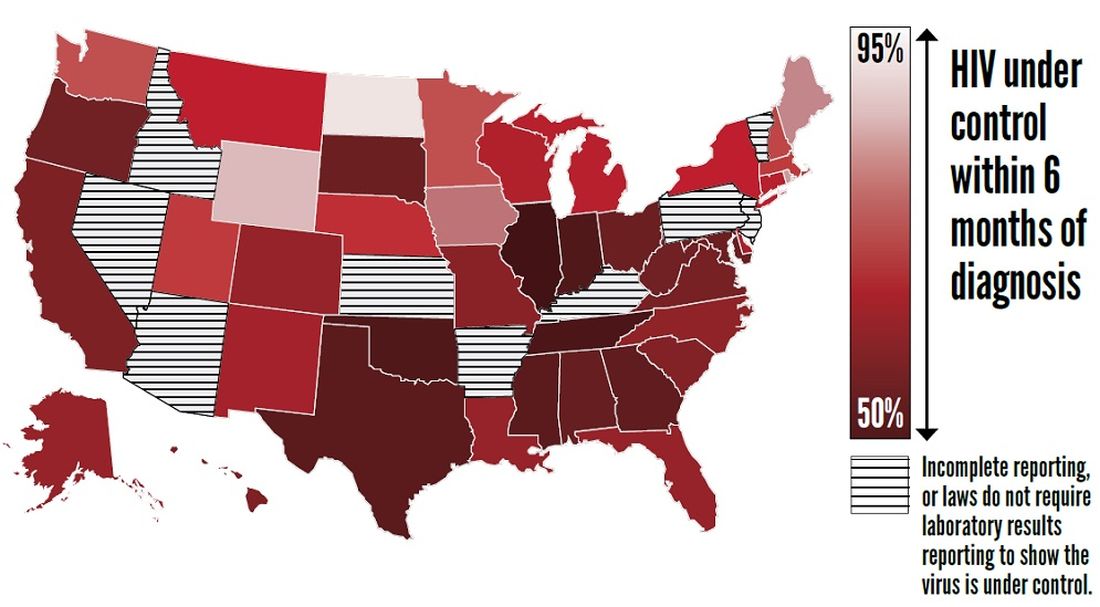
Furthermore, approximately two-thirds (63%) of patients who knew that they had HIV had the virus under control through effective treatment. Young people and African Americans were least likely to have the virus under control, according to the report.
The report also examines data about treatment with PrEP in 2018. About 1.2 million Americans could benefit from PrEP, but only 219,700 (18%) of them had received a prescription for the drug. The eligible groups with the lowest rates of coverage were young people, African Americans, and Latinos.
The report presents a conservative estimate of PrEP coverage, however. Researchers examined data from 92% of prescriptions from retail pharmacies in the United States but did not include prescriptions from closed health care systems such as managed care organizations and military health plans. PrEP coverage in 2018 likely was higher than these estimates indicate, according to the CDC.
“There has been a rapid increase in the number of people taking PrEP over the past 3 years, but there is no doubt that PrEP uptake is too low,” said Eugene McCray, MD, director of CDC’s division of HIV/AIDS prevention. “We are working hard to increase access to PrEP, especially among gay and bisexual men, women, transgender people, young people, African Americans, and Latinos.”
The rate of new HIV infections has not decreased, but remained stable, according to the report. The CDC estimates that there were about 38,000 new infections per year from 2013 to 2017.