COVID-19 infection is associated with a high risk for mortality in heart transplant (HT) recipients, a new case series suggests.
Investigators looked at data on 28 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 who received a HT between March 1, 2020, and April 24, 2020 and found a case-fatality rate of 25%.
“The high case fatality in our case series should alert physicians to the vulnerability of heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic,” senior author Nir Uriel, MD, MSc, professor of medicine at Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“These patients require extra precautions to prevent the development of infection,” said Dr. Uriel, who is also a cardiologist at New York Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
The study was published online May 13 in JAMA Cardiology.
Similar presentation
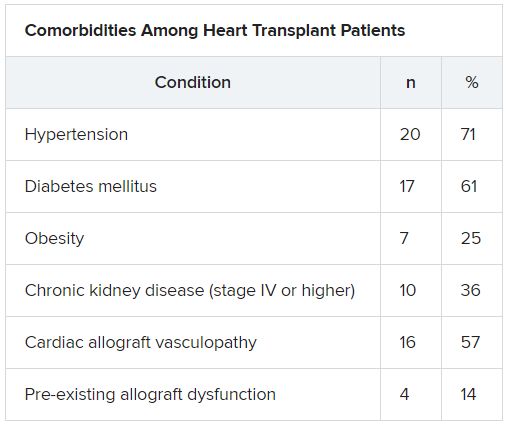
HT recipients can have several comorbidities after the procedure, including hypertension, diabetes, cardiac allograft vasculopathy, and ongoing immunosuppression, all of which can place them at risk for infection and adverse outcomes with COVID-19 infection, the authors wrote.
The researchers therefore embarked on a case series looking at 28 HT recipients with COVID-19 infection (median age, 64.0 years; interquartile range, 53.5-70.5; 79% male) to “describe the outcomes of recipients of HT who are chronically immunosuppressed and develop COVID-19 and raise important questions about the role of the immune system in the process.”
The median time from HT to study period was 8.6 (IQR, 4.2-14.5) years. Most patients had numerous comorbidities.
“The presentation of COVID-19 was similar to nontransplant patients with fever, dyspnea, cough, and GI symptoms,” Dr. Uriel reported.
No protective effect
Twenty-two patients (79%) required admission to the hospital, seven of whom (25%) required admission to the ICU and mechanical ventilation.
Despite the presence of immunosuppressive therapy, all patients had significant elevation of inflammatory biomarkers (median peak high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], 11.83 mg/dL; IQR, 7.44-19.26; median peak interleukin [IL]-6, 105 pg/mL; IQR, 38-296).
Three-quarters had myocardial injury, with a median high-sensitivity troponin T of 0.055 (0.0205 - 0.1345) ng/mL.
Treatments of COVID-19 included hydroxychloroquine (18 patients; 78%), high-dose corticosteroids (eight patients; 47%), and IL-6 receptor antagonists (six patients; 26%).
Moreover, during hospitalization, mycophenolate mofetil was discontinued in most (70%) patients, and one-quarter had a reduction in their calcineurin inhibitor dose.
“Heart transplant recipients generally require more intense immunosuppressive therapy than most other solid organ transplant recipients, and this high baseline immunosuppression increases their propensity to develop infections and their likelihood of experiencing severe manifestations of infections,” Dr. Uriel commented.
“With COVID-19, in which the body’s inflammatory reaction appears to play a role in disease severity, there has been a question of whether immunosuppression may offer a protective effect,” he continued.
“This case series suggests that this is not the case, although this would need to be confirmed in larger studies,” he said.
Low threshold
Among the 22 patients who were admitted to the hospital, half were discharged home and four (18%) were still hospitalized at the end of the study.
Of the seven patients who died, two died at the study center, and five died in an outside institution.
“In the HT population, social distancing (or isolation), strict use of masks when in public, proper handwashing, and sanitization of surfaces are of paramount importance in the prevention of COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Uriel stated.
“In addition, we have restricted these patients’ contact with the hospital as much as possible during the pandemic,” he said.
However, “there should be a low threshold to hospitalize heart transplant patients who develop infection with COVID-19. Furthermore, in our series, outcomes were better for patients hospitalized at the transplant center; therefore, strong consideration should be given to transferring HT patients when hospitalized at another hospital,” he added.
The authors emphasized that COVID-19 patients “will require ongoing monitoring in the recovery phase, as an immunosuppression regimen is reintroduced and the consequences to the allograft itself become apparent.”