Cancer survivors have significantly higher out-of-pocket medical costs than those with no history of cancer, and a quarter of those survivors have some type of material hardship related to their diagnosis, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Along with those material financial hardships – the need to borrow money, go into debt, or declare bankruptcy – more than 34% of cancer survivors aged 18-64 years experienced psychological financial hardship, defined as worry about large medical bills, in 2011 and 2016, Donatus U. Ekwueme, PhD, and his associates reported in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
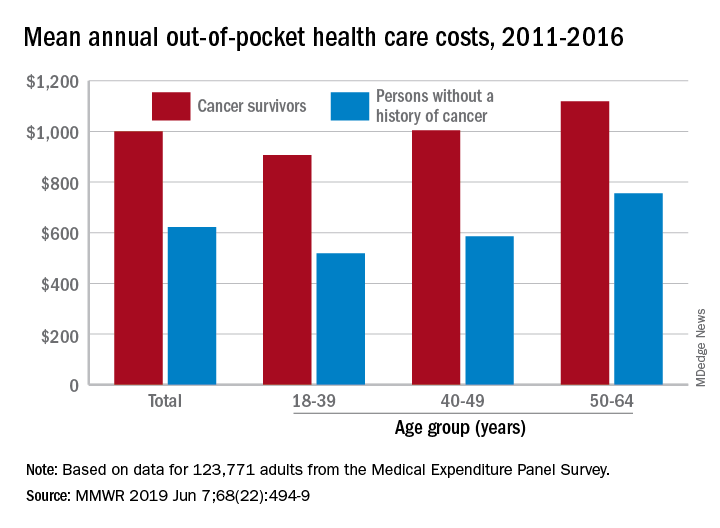
Cancer survivors spend 60% more out of pocket than those with no cancer history: $1,000 a year from 2011 to 2016, compared with $622 for adults without a history of cancer. Spending was lowest among younger people (18-39 years) and increased with age, but the prevalence of both material and psychological hardships was highest in the middle age group (40-49 years) and lowest in the oldest group (50-64 years), they said.
Women had higher out-of-pocket costs than men, although the difference was smaller for those with cancer ($1,023 vs. $976) than for those without ($721 vs. $519). Material and psychological hardships were both more common among women, said Dr. Ekwueme of the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Atlanta, and his associates.
Mean out-of-pocket spending was much higher for cancer survivors with private health insurance ($1,114) than for survivors with public insurance ($471), but material hardship was much more prevalent among those with public insurance (33.1% vs. 21.9%). Rates of psychological hardship, however, were much closer: 35.9% for those with public insurance and 32.5% for those with private insurance, the investigators said.
“The number of Americans with a history of cancer is projected to increase in the next decade, and the economic burden associated with living with a cancer diagnosis will likely increase as well,” they wrote, and interventions such as “systematic screening for financial hardship at cancer diagnosis and throughout the cancer care trajectory [are needed] to minimize financial hardship for cancer survivors.”
The analysis was based on data for 123,771 adults aged 18-64 years from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Out-of-pocket costs were calculated using data from 2011 to 2016, with all costs adjusted to 2016 dollars, but the hardship calculations involved data from only 2011 and 2016.
SOURCE: Ekwueme DU et al. MMWR 2019 Jun 7;68(22):494-9.