CHALLENGE 3: Difficult IUD removal
CASE Strings not palpated in a patient with history of LEEP
A 37-year-old woman (G3P2) presents to your office for IUD removal. She underwent a loop electrosurgical excision procedure 2 years ago for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 2 and since then has not been able to feel the IUD strings. On pelvic examination, you do not palpate or visualize the IUD strings after speculum placement.
How can you achieve IUD removal for your patient?
When a patient requests that her IUD be removed, but the strings are not visible and the woman is not pregnant, employ ultrasonography to confirm the IUD remains intrauterine and to rule out expulsion or perforation.
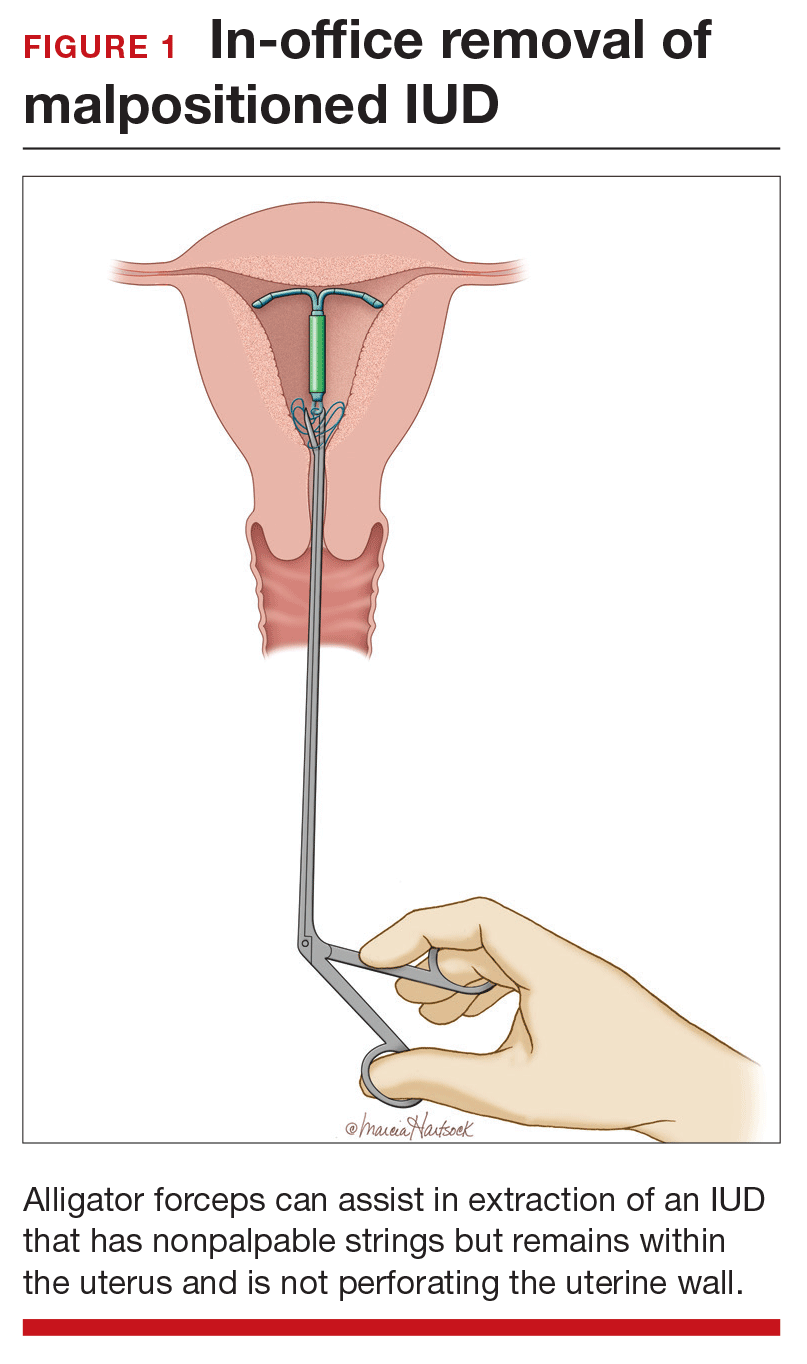
Employ alligator forceps or an IUD hook. Once intrauterine position is confirmed, use an alligator forceps of suitable length and with a small diameter to extract the device (FIGURE 1). It is useful to utilize ultrasonography for guidance during the removal procedure. The alligator forceps will grasp both the IUD device itself and IUD strings well, so either can be targeted during removal.
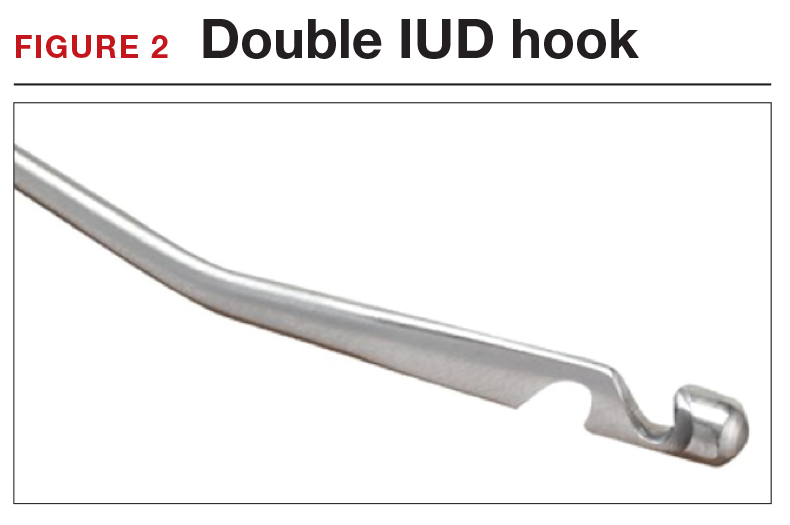
A second useful tool for IUD removal is an IUD hook (FIGURE 2). In a similar way that a curette is used for endometrial sampling, IUD hooks can be used to drag the IUD from the uterus.
Anesthesia is not usually necessary for IUD removal with alligator forceps or an IUD hook, although it may be appropriate in select patients. Data are limited with regard to the utility of paracervical blocks in this situation.
Related article:
Surgical removal of malpositioned IUDs
Hysteroscopy is an option. If removal with an alligator forceps or IUD hook is unsuccessful, or if preferred by the clinician, hysteroscopic-guided removal is a management option. Hysteroscopic removal may be required if the IUD has become embedded in the uterine wall.