Details of the trial
Women were eligible to participate if they reported 10 or more episodes of UI over 7 days, were at least 30 years old, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25 to 50 at baseline (normal is 19 to 24). In addition, they had to agree not to initiate any new treatments for UI or weight loss during the 6-month study period.
Subjects were randomized in a 2:1 ratio, with 226 women assigned to the intensive weight loss program and 112 assigned to the structured educational program. Baseline characteristics were similar in both groups, with a mean age of 53±11 years, mean BMI of 36±6 kg/m3, and total mean number of UI episodes of 24±18 per week.
Strengths and limitations
Strengths of this study include the large and varied study population. One important limitation, however, is the fact that the primary outcome measure was based on self-reported UI episodes. Because participants were not blinded to their treatment assignment, bias in self-reporting may have been present. In addition, subjects were selected because of their potential to adhere to the rigorous study protocol.
As the prevalence of obesity reaches pandemic level, it’s imperative that medical science continue to develop novel methods with which we can help patients achieve ideal body weight.
The findings of this study contribute to the growing body of medical literature—across specialties—demonstrating that weight loss can significantly improve the general health of patients, and that it should be part of the first-line treatment for overweight and obese women who complain of UI.
TVT is more effective than TOT
for intrinsic sphincter deficiency
Schierlitz L, Dwyer PL, Rosamilia A, et al. Effectiveness of tension-free vaginal tape compared with transobturator tape in women with stress urinary incontinence and intrinsic sphincter deficiency: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112:1253–1261.
Many experts consider intrinsic sphincter deficiency (ISD) to be a severe form of stress incontinence. Earlier studies suggested that women who had stress incontinence complicated by ISD had a lower success rate after certain surgical procedures than did women who had stress incontinence alone.
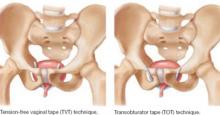
This randomized trial compared tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) with transobturator tape (TOT) in the treatment of stress incontinence with ISD ( FIGURE 1 ). The primary outcome measure was the presence of urodynamically confirmed stress incontinence 6 months after surgery.
At that 6-month mark, stress incontinence was present in 14 of 67 subjects (21%) in the TVT group, compared with 32 of 71 subjects (45%) in the TOT group (P=.004). Nine patients in the TOT group requested a repeat surgical procedure, compared with none in the TVT group.
Although the study was not powered to detect a difference in postoperative complications, there were six bladder perforations in the TVT group and none in the TOT group.
FIGURE 1 TVT and TOT trace different routes
Details of the trial
Women were selected for the trial on the basis of urodynamic parameters and recruited from two academic centers. ISD was defined as maximal urethral closure pressure below 20 cm H2O or Valsalva leak-point pressure less than 60 cm H2O. Subjects in the two groups had similar baseline characteristics.
Surgeons were required to have independently performed at least 15 surgical midurethral sling procedures before the study began.
In addition to placement of TVT or TOT, approximately one third of subjects underwent concomitant prolapse surgery. Postoperatively, subjects were assessed at 6 weeks, 6 months, and 12 months, with repeat urodynamic testing performed at 6 months. Analysis of data was based on intention to treat.
Only 138 of 164 women completed repeat urodynamic testing 6 months after surgery. Seventeen women declined testing, claiming to be “cured,” and nine women withdrew from the study or were lost to follow-up.
Short follow-up was a limitation
The definition of treatment failure as persistent, urodynamically confirmed stress incontinence was another shortcoming of the trial. In addition, the 17 subjects who declined repeat postoperative testing were classified as “cured,” potentially biasing the results.
TVT may be the preferred surgical option for women who have urodynamically confirmed stress incontinence complicated by intrinsic sphincter deficiency (ISD)—on the basis of the data gathered by these researchers. Longer follow-up is needed, however, to determine the long-term, clinical efficacy of midurethral slings in women who have ISD.
Accumulation of more data from future studies will better equip ObGyns to customize surgical treatment options to individual clinical parameters and reduce the risk of surgical failure.
Is Botox a panacea for refractory urge incontinence?