Contraindications
Allergic reactions. Patients who are hypersensitive to oral aripiprazole should not receive aripiprazole lauroxil. Hypersensitivity reactions have ranged from pruritus and urticaria to anaphylaxis.2
Drug−drug interactions. Reduce aripiprazole lauroxil dosage to the next lower dosage when used in combination with strong cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 inhibitors (eg, itraconazole, clarithromycin) or strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (eg, quinidine, fluoxetine, paroxetine) for more than 2 weeks or if the patient is known to be a poor metabolizer of CYP2D6, because concentration of aripiprazole lauroxil could increase. No dose adjustment is required if the patient is already taking 441 mg/month or if CYP450 modulators are added for less than 2 weeks.2 Similarly, a dosage increase is recommended when aripiprazole lauroxil is used in combination with strong CYP3A4 inducers (eg, carbamazepine, rifampin).2
Overdose
No data are available on aripiprazole lauroxil overdose. However, there is one known case of oral aripiprazole overdose in a patient who ingested 1,260 mg of oral aripiprazole (42 times the maximum recommended daily dosage) but recovered completely.2 Common side effects reported in at least 5% of all overdose cases include vomiting, somnolence, and tremor. If an overdose occurs, call a poison control center immediately.
‘Black-box’ warning for patients with dementia
Aripiprazole lauroxil, similar to all other atypical antipsychotics, has a “black-box” warning stating that (1) it is not approved for treating dementia-related psychosis, and (2) it is associated with an increased risk of death with off-label use to treat behavioral problems in older adults with dementia-related psychosis.2 Meta-analysis of 17 placebo-controlled trials in patients taking an atypical antipsychotic (olanzapine, aripiprazole, risperidone, or quetiapine) revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients 1.6 to 1.7 times that of placebo-treated patients.6
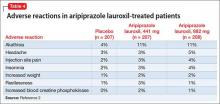
Adverse reactions
The overall safety profile of aripiprazole lauroxil is similar to that of oral aripiprazole. Most commonly observed adverse reaction during clinical trials of aripiprazole lauroxil was akathisia (incidence ≥5% and at least twice rate seen with placebo).2 Other common adverse reactions are shown in Table 4.2 Recently, the FDA issued a warning that compulsive or uncontrollable urges to gamble, binge eat, shop, and have sex have been reported with all formulations of aripiprazole.7 According to reports, these urges stopped when the drug was discontinued or the dosage reduced. Although rare, these impulse-control problems could result in harm if they are not recognized. See the full prescribing information for a complete set of adverse reactions.
BOTTOM LINE
Aripiprazole lauroxil is a novel, long-acting second-generation antipsychotic that offers flexibility in terms of safe and effective dosing and can be administered in the deltoid (441 mg) or gluteal muscle (626 mg and 882 mg) and at dosing intervals of 4 to 6 weeks. Safety and tolerability profile of aripiprazole lauroxil are similar to that of oral aripiprazole. Aripiprazole lauroxil represents a new treatment option for patients with schizophrenia.
Related Resources
- Kennedy WK. When and how to use long-acting injectable antipsychotics. Current Psychiatry. 2012;11(8):40-43.
- Citrome L, Du Y, Risinger R, et al. Effect of aripiprazole lauroxil on agitation and hostility in patients with schizophrenia. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2016;31(2):69-75.
Drug Brand Names
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Aripiprazole extended-release • Abilify Maintena
Aripiprazole lauroxil • Aristada
Carbamazepine • Tegretol
Clarithromycin • Biaxin
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Itraconazole • Sporanox
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
Paroxetine • Paxil
Quetiapine • Seroquel
Quinidine • Quinidex
Rifampin • Rifadin
Risperidone • Risperdal
Acknowledgement
Maaz A. Khan, a student at the University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, contributed to this article.