Mr. C, age 30, with schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type, Cannabis abuse, and nicotine dependence, has been enrolled in a Program of Assertive Community Treatment (PACT) for approximately 5 years. He presents to the PACT clinic for follow-up with his psychiatrist. Mr. C reports dizziness, lightheadedness, blurred vision, and nausea worsening over the last few days, and he appears drowsy and hypoactive. He does not report any chest pain, abdominal pain, swelling, cold extremities, shortness of breath, vomiting, diarrhea, or blood loss. Mr. C admits he has eaten only once daily for several weeks because of delusional ideation that he is responsible for others suffering from anorexia nervosa.
His medical history includes gastroesophageal reflux disease. Mr. C’s medication regimen for the past year included total daily oral doses of benztropine, 2 mg, divalproex extended-release, 1,000 mg, fluphenazine, 15 mg, and gabapentin, 300 mg. He also receives IM fluphenazine decanoate, 50 mg every 2 weeks; lithium, 600 mg/d, was added to his regimen 5 months ago. Vital signs include temperature 97°F, weight 162 lb, height 69 inches, blood pressure 105/64 mm Hg, heart rate (HR) 46 beats per minute (bpm), and respirations 18 breaths per minute.
Because of Mr. C’s complaints, appearance, and low HR, the psychiatrist calls emergency medical services (EMS). Although the paramedics recommend emergency transport to the hospital, Mr. C refuses. The psychiatrist instructs Mr. C to stop taking lithium because of suspected lithium-induced bradycardia and a concern that he may be more susceptible to lithium toxicity with prolonged anorexia nervosa. When nursing staff evaluate Mr. C the next day, his vitals are HR 60 bpm, respirations 20 breaths per minute, and blood pressure 124/81 mm Hg; his dizziness, blurred vision, lightheadedness, and nausea are resolved.
Laboratory tests reveal a low lithium level of 0.3 mEq/L (reference range, 0.6 to 1.2 mEq/L), a low valproic acid level of 29.2 µg/mL (reference range, 50 to 100 µg/mL), hemoglobin A1c 5% (reference range, <5.7%), thyroid-stimulating hormone 0.4 mIU/L (reference range, 0.4 to 4.5 mIU/L), creatinine 1.36 mg/dL (reference range, 0.6 to 1.35 mg/dL), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 11 mg/dL (reference range, 7 to 25 mg/dL), a normal complete blood count, and an otherwise unremarkable chemistry panel. A urine drug screen is positive for marijuana. Other than discontinuation of lithium, no other medication changes are made.Prior to starting lithium, Mr. C’s weight was 165 lb, blood pressure was 129/89 mm Hg, respirations 22 breaths per minute, and HR 80 bpm. Over a 5-month pretreatment period, his HR readings ranged from 60 to 91 bpm, averaging 75 bpm. Over the 5-month period after lithium initiation, his HR readings ranged from 46 to 66 bpm, averaging 56 bpm. Over the 5-month period after discontinuing lithium, his HR readings range from 55 to 84 bpm, averaging 68 bpm. Use of the Naranjo Adverse Drug Reaction Probability Scale1 indicates a possible relationship (4 of 13) between bradycardia and lithium use.Bradycardia is defined as a HR <60 bpm; however, symptoms may not occur until the HR is <50 bpm. Symptoms include fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness, chest pain, shortness of breath, and syncope. The incidence of bradycardia during lithium treatment is unknown; it is considered a rare but serious adverse effect. A literature review reveals several case reports of bradycardia with lithium treatment,2-4 including symptomatic bradycardia after a single dose of lithium.5 Other possible causes of bradycardia include anorexia nervosa, hypothermia, hypothyroidism, hypoxia, infection, stroke, acute myocardial infarction, sedative or opiate use, increased vagal tone with exercise conditioning, and other medications including fluphenazine.6
Mr. C’s symptoms may have been assumed to be secondary to several possible causes, including bradycardia, dehydration from poor oral intake, lithium toxicity, or an undiagnosed medical condition. The combination of nausea, dizziness, anorexia nervosa, blurred vision, and lightheadedness in a patient receiving lithium would certainly trigger a clinician’s concern for lithium toxicity, but he (she) may not be aware of the risk of bradycardia as an adverse effect of lithium. Because Mr. C refused hospital transportation by EMS, discontinuing lithium appears to have been the safest option. Laboratory studies from the day after Mr. C presented to the clinic appeared to lessen the probability that lithium toxicity, hypothyroidism, valproate toxicity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or infection had caused Mr. C’s symptoms.
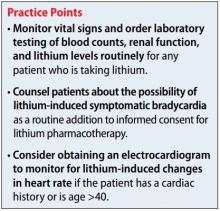
Although psychiatrists may be vigilant about monitoring for signs and symptoms of toxicity with lithium use by utilizing regular laboratory studies, they may not be as vigilant with monitoring vital signs at every patient visit (Table). This case demonstrates the importance of regular vital sign measurements to be able to detect this rare but serious adverse effect.