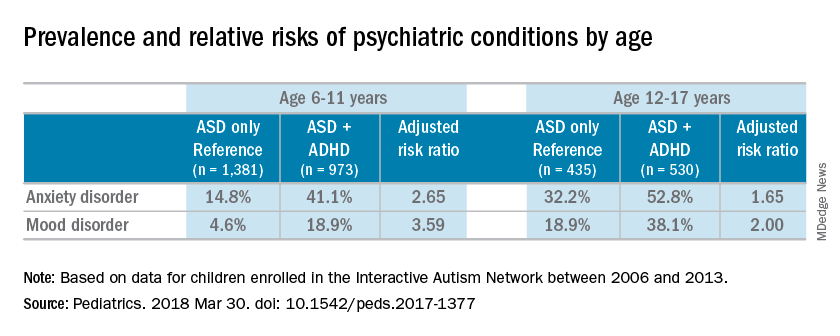
Children with comorbid autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are at an increased risk of anxiety and mood disorders, a cross-sectional analysis has shown.
“Our study supports that anxiety and mood disorders, although highly prevalent in those with ASD alone, are even more prevalent in individuals who have ADHD,” wrote Eliza Gordon-Lipkin, MD, of the Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore, and her associates. ”The identification of psychiatric conditions in children with ASD is important because these disorders are treatable and affect quality of life.”
The study was published in Pediatrics.
Dr. Gordon-Lipkin and her associates conducted a cross-sectional analysis of information on 3,319 children obtained between 2006 and 2013 in the Interactive Autism Network (IAN), an online autism research registry that uses parent report information. Using three questionnaires: the Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Questionnaire, the Social Communication Questionnaire–Lifetime, and the Social Responsiveness Scale, Dr. Gordon-Lipkin and her associates collected information from the parents of children with ASD about their children’s birth, development, medical histories, and the severity of social impairment.Most of the children were male (83%), white (87%), and non-Hispanic (92%); the mean age of the children was 10 years. Almost half of the children in the study had parent-reported ADHD (45%). Almost one-third of patients were diagnosed with an anxiety disorder (31%), and many also were reported to have been diagnosed with a mood disorder (16%). An increased risk of reported anxiety disorder was found in patients with both ADHD and ASD (adjusted relative risk, 2.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.97-2.46).
The researchers also found an increased risk of mood disorders (aRR, 2.72; 95% CI, 2.28-3.24) among children with comorbid conditions. Those risks increased with age (both P less than .001). An increased prevalence of anxiety and mood disorders was found in adolescents, compared with school-aged children with both ASD and ADHD or ASD alone. But higher relative risk ratios were found for the younger children, compared with the adolescents for those in the ADHD/ASD group and the ASD alone group.
“This suggests that or more likely to exhibit detectable symptoms at an earlier age,” reported Dr. Gordon-Lipkin, also with the department of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, in Baltimore.