according to newly released data from the 2019 Youth Risk Behavior Survey.
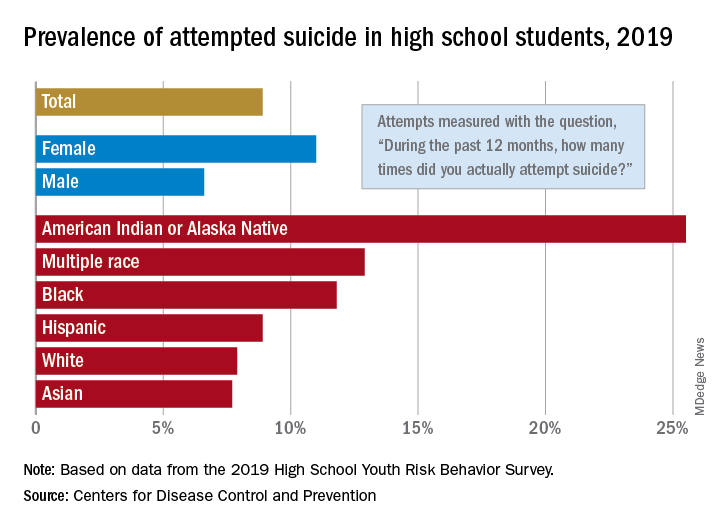
The prevalence of attempted suicide during the previous 12 months was 8.9% among the 13,677 students in grades 9-12 who took the survey last year, but the rate was 25.5% for American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) respondents, almost 2.9 times higher, the YRBS data show.
Respondents with multiple races in their backgrounds, at 12.9%, and African Americans, with a prevalence of 11.8%, also were above the high school average for suicide attempts, while Whites (7.9%) and Asians (7.7%) were under it and Hispanics equaled it, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported.
The number of AI/AN students was insufficient to examine differences by sex, but females in all of the other racial/ethnic groups were more likely than males to have attempted suicide: multiple race (17.8% vs. 7.3%), African American (15.2% vs. 8.5%), Hispanic (11.9% vs. 5.5%), White (9.4% vs. 6.4%), and Asian (8.4% vs. 7.1%), the CDC’s Division of Adolescent and School Health said.
Among all respondents, 11.0% of females had attempted suicide in the 12 months before the survey, a figure that is significantly higher than the 6.6% prevalence in males. Females also were significantly more likely than males to make a plan about how they would attempt suicide (19.9% vs. 11.3%) and to seriously consider an attempt (24.1% vs. 13.3%), CDC investigators said in a separate report.
Significant differences also were seen when looking at sexual identity. Suicide attempts were reported by 6.4% of heterosexuals, 16.1% of those who weren’t sure, and 23.4% of lesbians/gays/bisexuals (LGBs). For serious consideration of suicide, the respective numbers were 14.5%, 30.4%, and 46.8%, they reported (MMWR Supp. 2020 Aug 21;69[1]:47-55).
For nonheterosexuals, however, males were slightly more likely (23.8%) than females (23.6%) to have attempted suicide, but females were more likely to seriously consider it (49.0% vs. 40.4%) and to make a plan (42.4% vs. 33.0%), according to the YRBS data.
“Adolescence … represents a time for expanded identity development, with sexual identity development representing a complex, multidimensional, and often stressful process for youths,” the CDC investigators said in the MMWR. “To address the health differences in suicidal ideation and behaviors observed by student demographics and to decrease these outcomes overall, a comprehensive approach to suicide prevention, including programs, practices, and policies based on the best available evidence, is needed.”