Discuss this article at www.facebook.com/CurrentPsychiatry
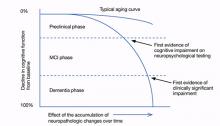
In 2011, a workgroup of experts from the Alzheimer’s Association and the National Institute on Aging published new criteria and guidelines for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the first new AD guidelines since 1984.1-4 These criteria reflect data that suggest AD is not synonymous with dementia of the Alzheimer’s type (DAT) but is a disease that slowly develops over many years as a result of accumulated neuropathologic changes, with dementia representing only the final phase of the disease (Figure).1-4
Figure: Cognitive decline in AD over time
AD: Alzheimer’s disease; MCI: mild cognitive impairment
Source: Adapted from reference 2
This article highlights the similarities and differences of the 1984 and 2011 AD diagnosis guidelines. We also discuss the new guidelines’ limitations and clinical implications.
The 1984 AD criteria
Both the 1984 AD criteria5 and DSM-IV-TR criteria6 rely on the concept that AD is a clinical diagnosis made after a patient develops dementia. That is, diagnosis rests on the physician’s clinical judgment about the etiology of the patient’s symptoms, taking into account reports from the patient, family, and friends, as well as results of neurocognitive testing and mental status evaluation. The 1984 criteria were developed with the expectation that if a patient who met clinical criteria for AD were to undergo an autopsy, he or she likely would have evidence of AD pathology as the underlying etiology. These criteria were developed before researchers discovered that in AD, pathologic changes occur over many years and clinical dementia is the end product of accumulated pathology. The 1984 criteria did not address important phases that precede clinical dementia—such as mild cognitive impairment (MCI). See the Table for a summary of the 1984 AD criteria.
Table
The 1984 NINCDS-ADRDA criteria for clinical diagnosis of AD
|
| AD: Alzheimer’s disease; NINCDS-ADRDA: National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Diseases and Stroke/Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders Association Source: McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, et al. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology. 1984;34(7):939-944 |
The 2011 AD criteria
The new AD criteria differ from the 1984 criteria in 2 major ways:
- expansion of AD into 3 phases, only 1 of which is characterized by dementia
- incorporation of biomarkers to provide information regarding pathophysiologic changes underlying the disease state (Table 1).1-5
The 3 phases. The 2011 criteria expand the definition of AD to include an asymptomatic, preclinical phase; a symptomatic, pre-dementia phase; and a dementia phase. In the initial phase, neuronal toxins such as beta-amyloid (Aβ) plaques and elevated tau first become detectable. Patients in this phase are asymptomatic or have subtle symptoms. This phase should be viewed as part of a continuum and includes patients who may, for instance, develop Aβ plaques but do not progress to further neurodegeneration.2 The diagnostic criteria of this phase are intended for research purposes only.1,2
Patients in the symptomatic, pre-dementia phase—also known as the MCI phase—exhibit mild decline in memory, attention, and thinking. Although this decline is more than what is expected for the patient’s age and education, it does not compromise everyday activity and functioning.
A patient who develops cognitive or behavioral problems that interfere with his or her ability to function at work or in everyday activities has entered the dementia phase. Similar to the 1984 guidelines, the 2011 criteria classify patients into probable and possible AD dementia. All patients who would have satisfied criteria for probable AD under the 1984 guidelines will satisfy criteria for probable AD dementia under the 2011 criteria.4 The same is not true for possible AD dementia. The 2011 criteria include 2 other major categories for patients with AD dementia: probable and possible AD dementia with evidence of the AD pathophysiological process. These categories are intended for research purposes only, whereas the criteria for the MCI and dementia phases are intended to guide diagnosis in the clinical setting.