Two reviewers extracted the quantitative data from eligible studies. The 2 primary outcomes of interests were all-cause readmission rates, and reasons for readmission 30 and 90 days after TJA. Other extracted data were evidence level; publication journal, year, and country; data source (academic institution, Medicare); study design; number of patients; patient characteristics; surgical approach; follow-up period; overall readmission rate; anticoagulant use; tourniquet use; and compression stocking use. In addition, all post-TJA readmissions were assumed to be unplanned, except for staged sequential bilateral arthroplasty for osteoarthritis (excluded from analysis).
Readmission reasons were divided into 4 major categories as defined by the literature and the authors: thromboembolic disease, joint-specific reasons, surgical site infection, and surgical sequelae. The diagnoses in these categories are listed in Table 1. Other extracted reasons were cardiac dysrhythmia and pneumonia.
In cases in which there were at least 2 comparable studies, a meta-analysis was performed to obtain pooled estimates of the proportion of patients readmitted at 30 or 90 days. We calculated a Higgins I2 measure for between-study heterogeneity and random-effects analysis, using the method of DerSimonian and Laird23 if I2 was greater than 0.5. Pooled estimates were obtained for both overall and cause-specific reasons for readmission for all reasons reported in at least 3 studies. Small-study or publication bias was assessed using funnel plot asymmetry when at least 5 studies were analyzed as recommended.24 The meta-analytic findings for both overall and cause-specific readmission are presented as pooled proportions with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). All meta-analyses were performed using Stata 10.0.
Results
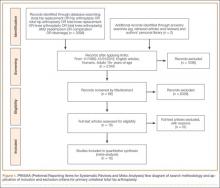
Fifteen unique TJA studies (12 THA, 10 TKA) met the criteria for the meta-analysis.20,25-38Figure 1 depicts the PRISMA flowchart for study identification.22
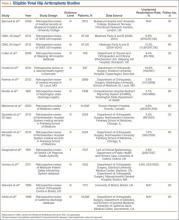
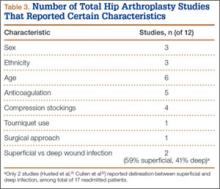
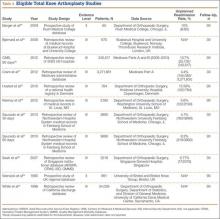
Of the 12 studies eligible for the THA analysis (Table 2), 6 were conducted in the United States,20,26,27,30,33,34 5 in Europe,25,28,29,32,35 and 1 in Canada.31 Seven of the 12 studies reported readmission rates at 30 days, and 7 reported rates at 90 days (2 reported rates at both follow-ups). We analyzed a total of 113,396 patients at the 30-day window and 192,380 patients at the 90-day window. Mean age was 74.2 years. The included studies were variable and sparse in their reporting of specific characteristics (Table 3).
Of the 10 studies (2 prospective, 8 retrospective) eligible for the TKA analysis (Table 4), 6 were conducted in the United States,20,26,27,34,36,37 3 in Europe,25,29,35 and 1 in Asia.38 Four of the 10 studies reported readmission rates at 30 days, and 7 reported rates at 90 days (1 reported rates at both follow-ups).27 We analyzed a total of 3,278,635 patients at the 30-day window and 272,419 patients at the 90-day window. Mean age was 74.3 years. The included studies were quite variable and sparse in their reporting of specific characteristics (Table 5).
We performed random-effects meta-analyses of all unplanned readmissions at both 30 and 90 days (all I2s > 0.5). Among 5 THA studies that reported overall rates at 30 days,20,27,28,32,33 the estimated overall unplanned rate among the 120,272 index surgeries was 5.6% (95% CI, 3.2%-8.0%). Among 5 THA studies that reported overall rates at 90 days,20,25-27,31 the estimated overall unplanned rate among the 192,380 index surgeries was 7.7% (95% CI, 3.2%-12.2%) (I2 = 1.00). Among 3 TKA studies that reported overall rates at 30 days,27,37,38 the estimated overall unplanned rate among the 3,278,635 index surgeries was 3.3% (95% CI, 0.7%-5.9%). Among 5 TKA studies that reported overall rates at 90 days,20,25-27,36 the estimated overall unplanned rate among the 272,419 index surgeries was 9.7% (95% CI, 7.1%-12.4%) (I2 = 0.97).
30-Day Readmission Rates
The most common reason for readmission 30 days after THA discharge was joint-specific. This reason accounted for 39.3% of all unplanned readmissions among studies that reported joint-specific causes, with an estimated pooled rate of 2.2% (95% CI, 0.0%-4.6%; P < .001; I2 = 1.00) among 4 studies. The second and third most common reasons were surgical sequelae (1.6%; 95% CI, 0.8%-2.5%; P < .001; I2 = 0.95) and thromboembolic disease (1.5%; 95% CI, 1.0%-1.9%; P < .001; I2 = 0.95). See Figure 2 for 30-day THA readmission rates. The fourth most common readmission reason was surgical site infection (0.6%; 95% CI, 0.2%-1.1%; P < .001; I2 = 0.94). Only these 4 reasons could be pooled, as cardiac dysrhythmia, pneumonia, and bleeding were reported in only 1 study each.
The most common reason for readmission 30 days after TKA discharge was surgical site infection. This reason accounted for 12.1% of all unplanned readmissions among studies that reported surgical site infections, with an estimated pooled rate of 0.4% (95% CI, 0.3%-0.6%; P < .001; I2 = 0.61) among 3 studies. The second and third most common reasons were joint-specific and thromboembolic disease, both occurring 0.3% of the time. Joint-specific reasons were reported in 2 studies (95% CI, 0.0%-0.8%; P = .259; I2 = 0.94). Thromboembolic disease was reported in 4 studies (95% CI, 0.0%-0.7%; P = .067; I2 = 0.98) (Figure 3). Only these 3 reasons could be pooled, as cardiac dysrhythmia, pneumonia, and “sequelae” were reported in only 1 study each.