PHOENIX – A team of cardiac surgeons has developed the first clinical risk score for predicting the risk that patients face for operative mortality and postsurgical major morbidity when undergoing isolated tricuspid valve repair or replacement.
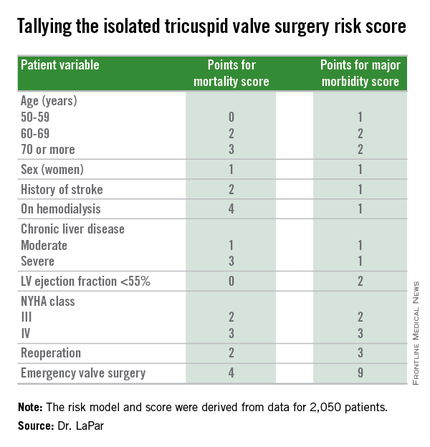
The risk score uses nine easily collected variables, and the derived model discriminates outcomes based on patients who score from 0-10 or more points on both a mortality and a morbidity risk scale, Dr. Damien J. LaPar said at the annual meeting of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons.
The risk scores allow surgeons to better describe and quantify to patients considering isolated tricuspid valve surgery the risks they face from the operation, and they have already been incorporated into practice at the University of Virginia, in Charlottesville, where Dr. LaPar practices.
“Patients love to better understand their risks. We can provide them with empirical data from a large, heterogeneous population that are better than a surgeon’s gut feeling” about the risks they face, said Dr. LaPar, a cardiothoracic surgeon at the University.
Another consequence of having the new risk model and score is that it identified certain key risk factors that are controllable, and thereby, “makes the case for early referrals” for isolated tricuspid valve surgery, Dr. LaPar said in an interview. For example, the risk score shows that patients who are older, on hemodialysis, have a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, or require emergency intervention all contribute to worse outcomes, compared with patients who are younger, have better renal function, better cardiac output, or can be treated on a more routine basis.
Many physicians have viewed isolated tricuspid valve surgery as posing similar risks to all patients, with an overall average operative mortality rate of about 10%, he noted. The new risk score model shows that some patients who are younger and healthier have operative mortality rates below 5%, while older and sicker patients have rates that can surpass 20%.
“Our data show a spectrum of risk, and that it is better to operate sooner than later. That is the huge clinical message of these data,” Dr. LaPar said.
Designated discussant Dr. Michael A. Acker noted that the risk score for tricuspid-valve surgery “is a first of its kind and a major contribution.” Dr. Acker is professor of surgery and chief of cardiovascular surgery at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. He is a consultant to Thoratec and HeartWare.
Dr. LaPar and his associates derived the risk model and score from data collected on 2,050 patients who underwent isolated tricuspid valve repair or replacement at 49 hospitals in Virginia or Michigan during 2002-2014. The data came from databases maintained by the Virginia Cardiac Surgery Quality Initiative and by the Michigan Society of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgeons, and reported to the Adult Cardiac Surgery Database of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. The model they developed showed operative mortality rates that ranged from 2%, for patients with a mortality score of zero, to 34% for patients with a score of 10 or more. It further showed major morbidity rates of 13%, for patients with a morbidity score of zero, to 71% for those with a score of 10 or more. Scoring for mortality uses a slightly different system than the scoring for morbidity, so the scores must be calculated individually, and the score totals for a patient can differ for each endpoint. The maximum score is 22 for mortality and 23 for morbidity.
Only 5%-15% of patients undergoing tricuspid valve surgery have an isolated procedure, so a relatively limited number of patients fall into this category, a fact that has in the past limited collection of data from large numbers of patients. The dataset used for this analysis, with 2,050 patients “is one of the largest series collected,” and made possible derivation of a robust risk model and scoring system. Future analysis of even more patients should further improve the model and scoring system.
“These data set the stage for looking at national-level data to further refine the model and make it even more generalizable,” Dr. LaPar said.
On Twitter @mitchelzoler