TYPES OF THYROID CANCER
Four possible types of thyroid cancer are identified on pathology after FNA: papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic. Differentiated thyroid cancers, which encompass papillary and follicular cancers, are the most commonly diagnosed. Approximately 90% of thyroid cancers fall into this category.2
In most cases of differentiated thyroid cancer, patients can be treated with thyroidectomy alone if the cancer remains confined to the thyroid.2 Just over two-thirds of differentiated thyroid cancer cases are localized in the thyroid. The five-year survival rate for these patients is nearly 100%.1
About 27% of differentiated thyroid cancer is also found in neck lymph nodes; these patients may be treated with thyroidectomy and radioactive iodine.2 The five-year survival rate in these cases is nearly 98%.1 Chemotherapy is generally not needed for differentiated thyroid cancers.
Medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) is diagnosed in up to 4% of thyroid cancer patients. Characterized by high levels of calcitonin, MTC can be genetically mediated or sporadic. MTC is associated with a variety of RET oncogene mutations; genetic testing of family members is recommended, as well as prophylactic thyroidectomy when high-risk RET oncogenes are detected.3
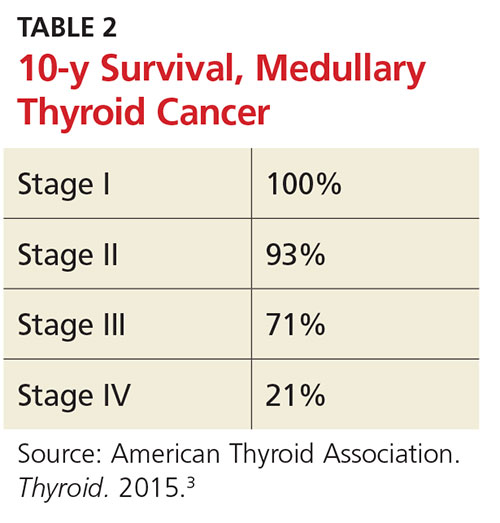
The 10-year survival prognosis for MTC patients varies according to stage at diagnosis (see Table 2). Up to 70% of patients with a palpable MTC nodule present with metastasis consistent with stage III or IV disease.3
Medullary thyroid cancer is treated with total thyroidectomy and cervical lymph node dissection. Radioactive iodine has not been proven effective for MTC patients, unless there is also papillary or follicular thyroid cancer present.3
Anaplastic thyroid cancer has the highest mortality rate of all types of thyroid cancer. Fortunately, it is relatively rare, occurring in only 1.7% of thyroid cancer patients. The one-year survival rate is 20%, with a median postdiagnosis survival prognosis of approximately five months. Anaplastic thyroid cancer is treated with total thyroidectomy and radical neck dissection when it is considered resectable. Metastatic lesions in the brain or spine are often indicators of unresectable disease. In some cases, external beam radiation therapy is used as palliative treatment.4