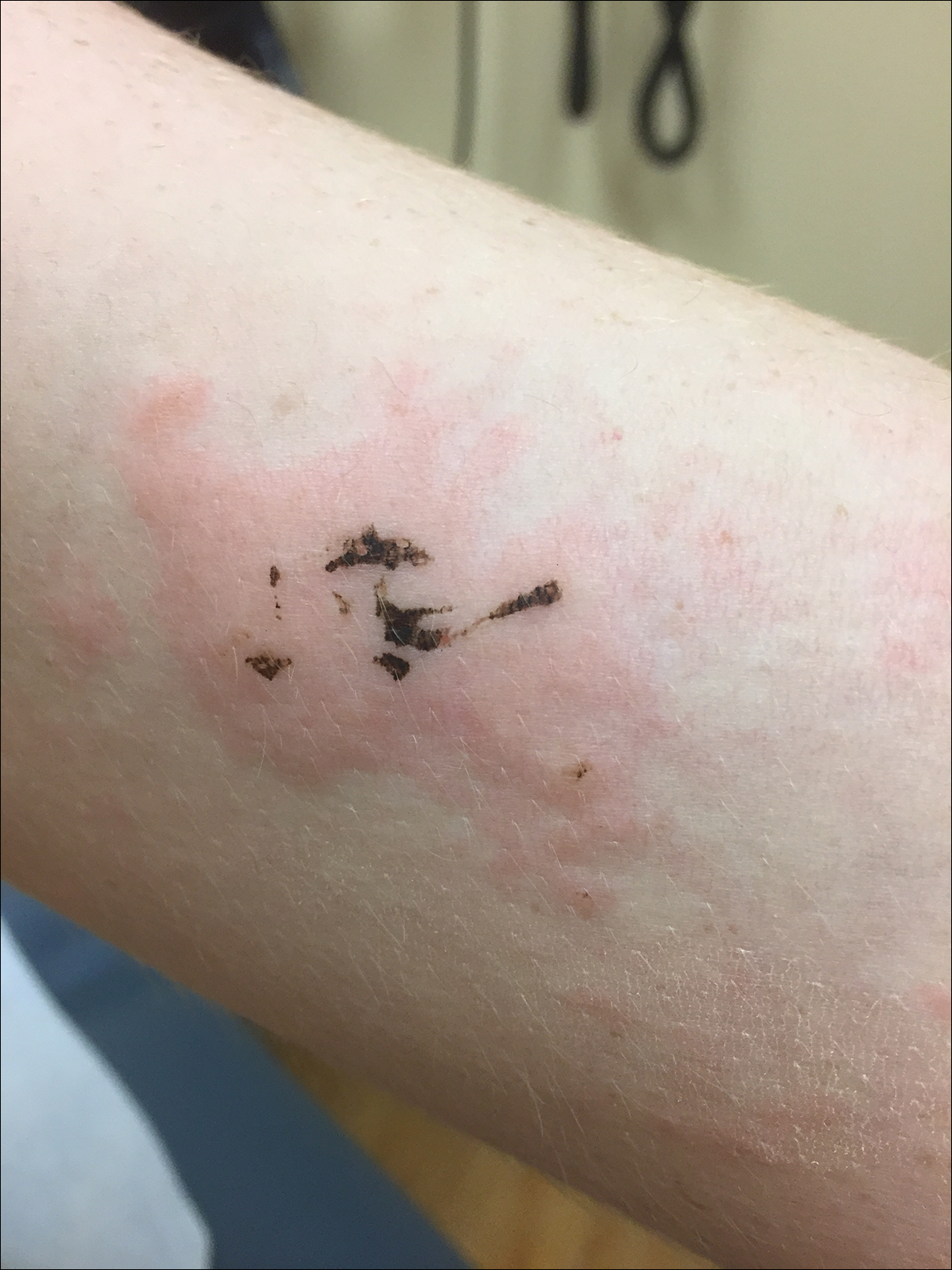
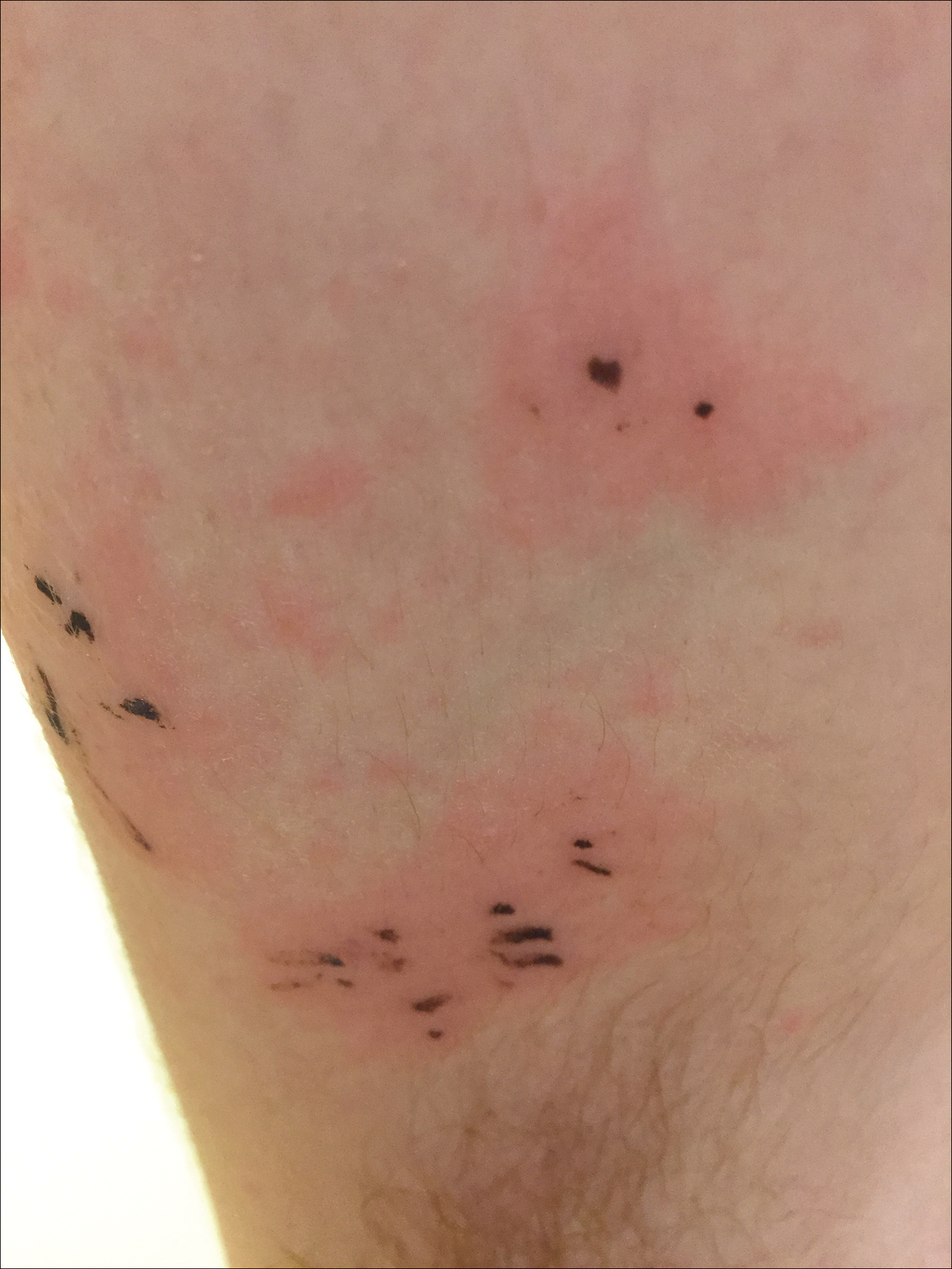
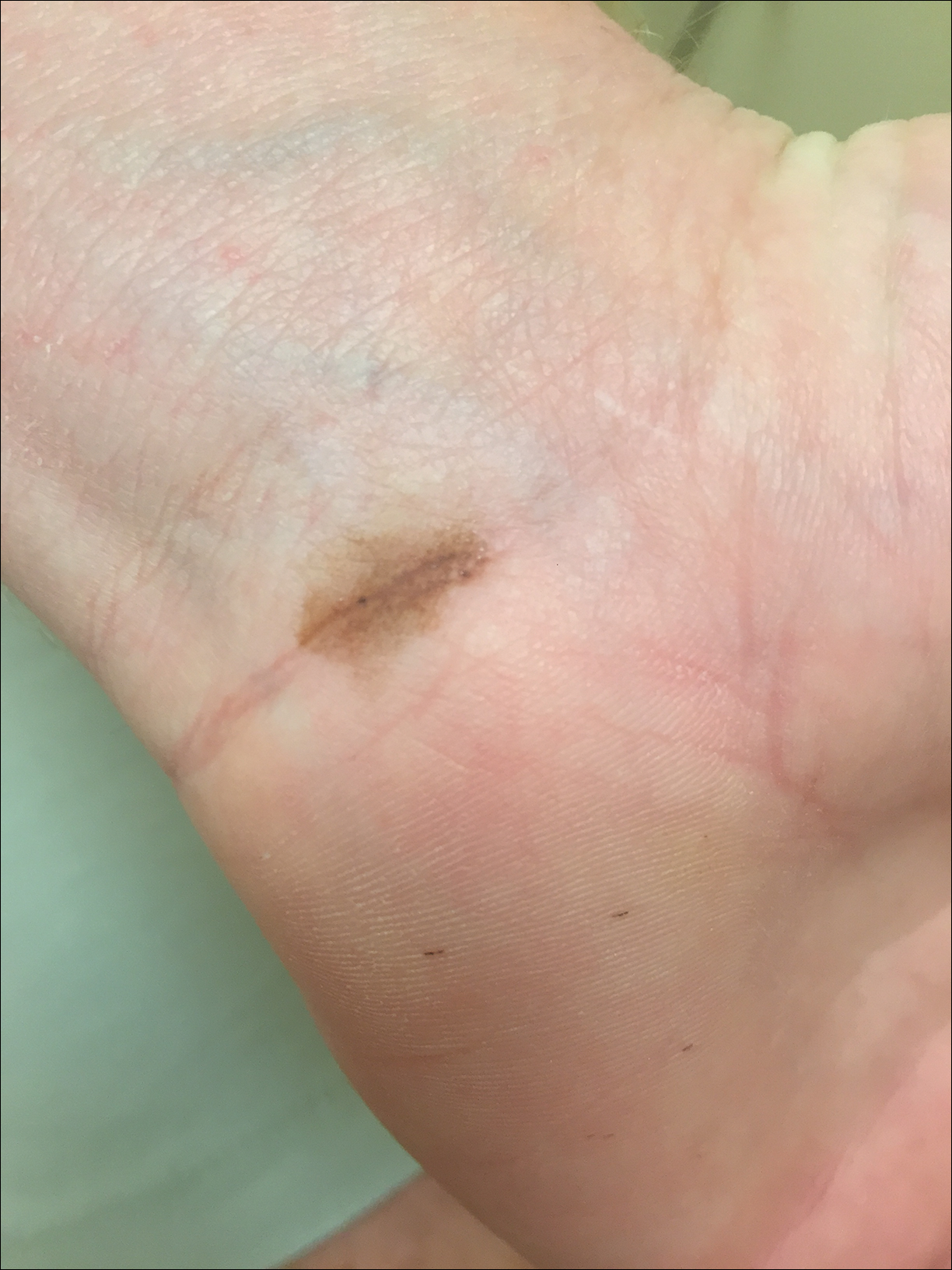
The Diagnosis: Black-Spot Poison Ivy
Due to the detailed account of the patient's history including acuity of current presentation, history of recent activities, travel history, and recent exposures, as well as a thorough skin examination, a diagnosis of black-spot poison ivy was made. In this case, the linear distribution of the lesions with overlying black pigment that could not be removed (Figures 1 and 2) provided important clues to diagnosis.
Poison ivy is an allergic contact dermatitis that affects an estimated 25 to 40 million Americans annually who are exposed to its resin. Poison ivy is a plant from the Toxicodendron genus, and an estimated 85% of the North American population report sensitivity to these plants, of which poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans) is the most common.1 Other related plants include poison sumac and poison oak. Poison ivy and other Toxicodendron plants produce urushiol, the oleoresin responsible for one of the most common allergic contact dermatitides in the United States.2 Black-spot poison ivy is an uncommon presentation following exposure to urushiol or oleoresin,3 as sufficient concentration of urushiol on the skin rarely is achieved.3,4 This plant's resin oxidizes and turns coal black when exposed to air.5 Contact with enough of this oleoresin will produce black-spot poison ivy.6 Patients with sufficient concentrations of oleoresin on their skin to cause this black oxidation usually have similar black spots on their clothing.7 Interestingly, some Toxicodendron species, such as the Japanese lacquer tree, Toxicodendron vernicifluum, have a black lacquer sap that was historically used as ink.8 This ink was used on Chinese and Japanese jars and has caused contact dermatitis hundreds of years after they were created.7
Poison ivy is characterized by a generalized, pruritic, erythematous rash with vesicles and papules in a linear distribution.9 Black-spot poison ivy presents the same with the addition of black lacquer-like macules with surrounding erythema.10 The skin lesions usually appear on exposed areas 24 to 48 hours after contact.11 Histology of black-spot poison ivy lesions should reveal yellow material in the stratum corneum with epidermal necrosis, in addition to classic features of acute allergic contact dermatitis.3 Interestingly, because these lesions occur with the first exposure to poison ivy, a patient may not develop the typical itchy eczematous eruption characteristic of poison ivy dermatitis. Differential diagnosis includes superficial purpura; exogenous pigment such as marker, ink, or tattoo pigment; tinea nigra; purpuric allergic contact dermatitis to resins or dyes; arthropod assault; irritant contact dermatitis; and infectious and noninfectious vasculitis.11
Similar to poison ivy, treatment of black-spot poison ivy involves oral and topical steroids combined with antihistamines if the patient continues to experience pruritus.6,12 It was recommended to our patient to apply cool compresses with water or Burow solution to alleviate itching and promote drying of the lesions. Calamine lotion can provide similar outcomes.13 Once the oleoresin is oxidized and bound to skin, the black spots cannot be removed with soap, water, or alcohol. The black spots gradually desquamate 1 to 2 weeks after formation without scarring,11 and patients do not require further monitoring.1 Patients should clean or discard clothing and evaluate for possible sources of poison ivy exposure. Because this type of poison ivy dermatitis is rare, most health care workers likely have never seen black-spot poison ivy, and it is an important diagnosis to consider.13