Perniosis, or chilblain, is characterized by localized, tender, erythematous skin lesions that occur as an abnormal reaction to exposure to cold and damp conditions. Although the lesions favor the distal extremities, perniosis may present anywhere on the body. Lesions can develop within hours to days following exposure to temperature less than 10°C or damp environments with greater than 60% humidity.1 Acute cases may lead to pruritus and tenderness, whereas chronic cases may involve lesions that blister or ulcerate and can take weeks to heal. We report an unusual case of erythematous plaques arising on the buttocks of a 73-year-old woman using ice pack treatments for chronic low back pain.
Case Report
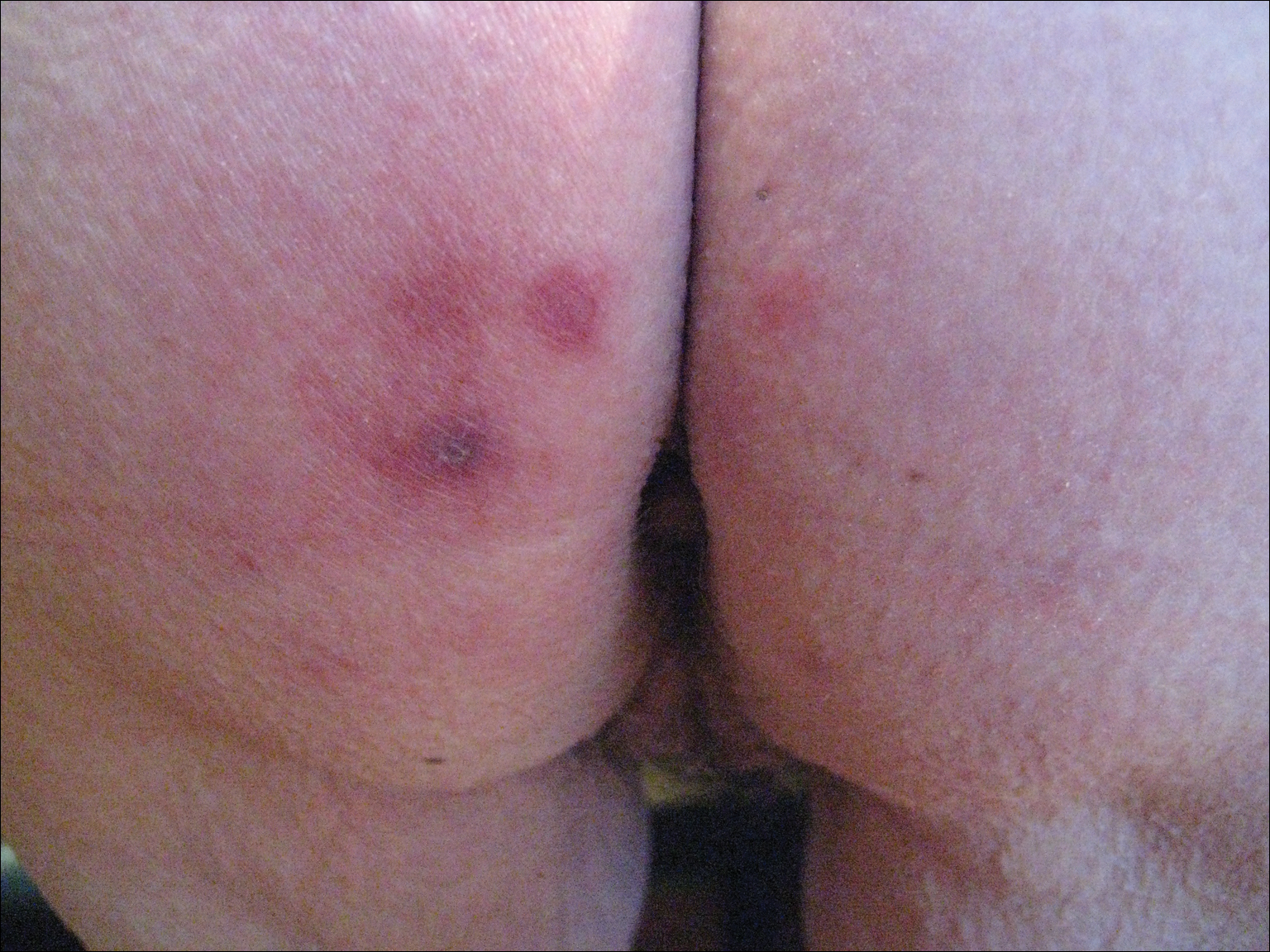
A 73-year-old woman presented with recurrent tender lesions on the buttocks of 5 years’ duration. Her medical history was remarkable for hypertension, hypothyroidism, and lumbar spinal fusion surgery 5 years prior. Physical examination revealed indurated erythematous plaques with areas of erosions on the left buttock with some involvement of the right buttock (Figure 1).
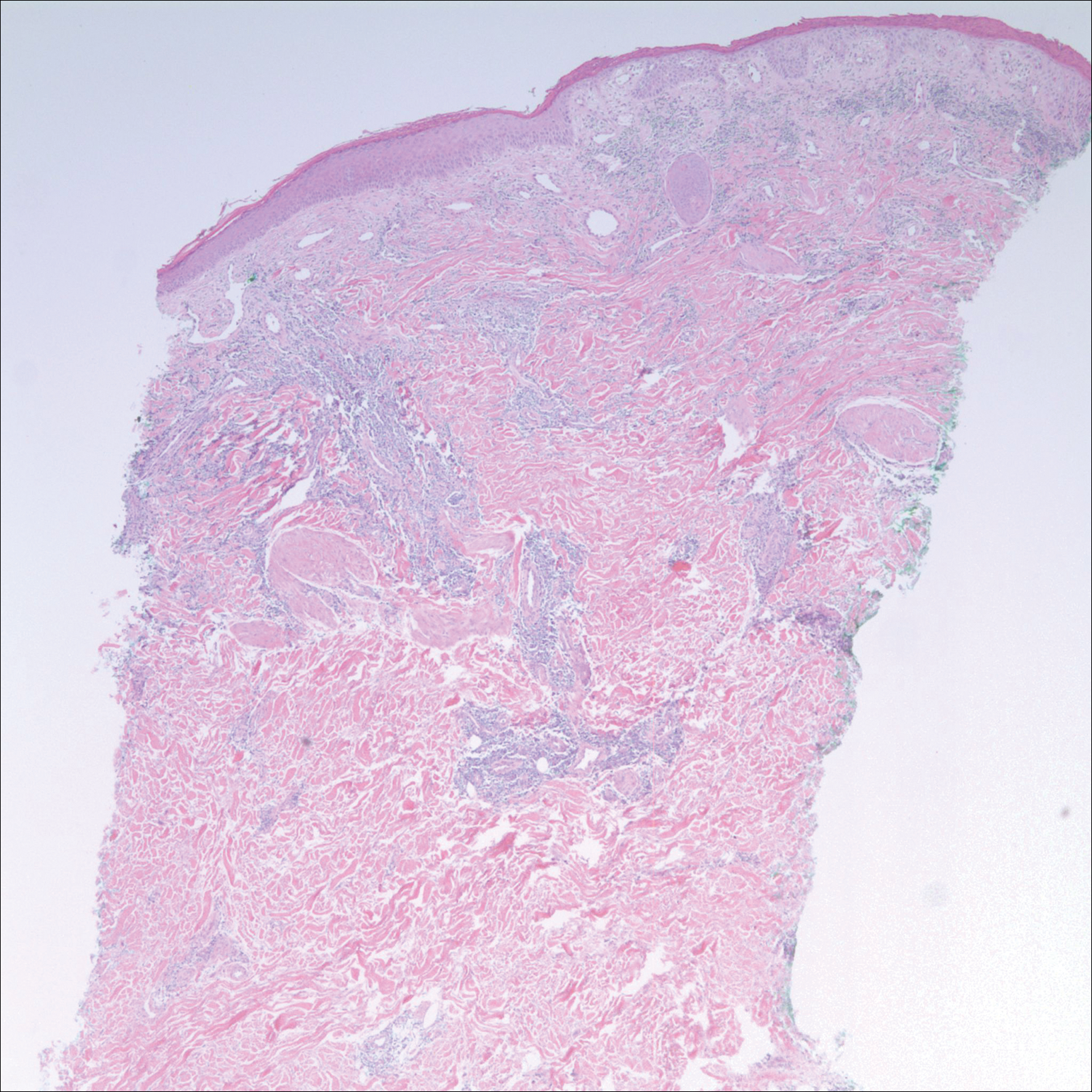
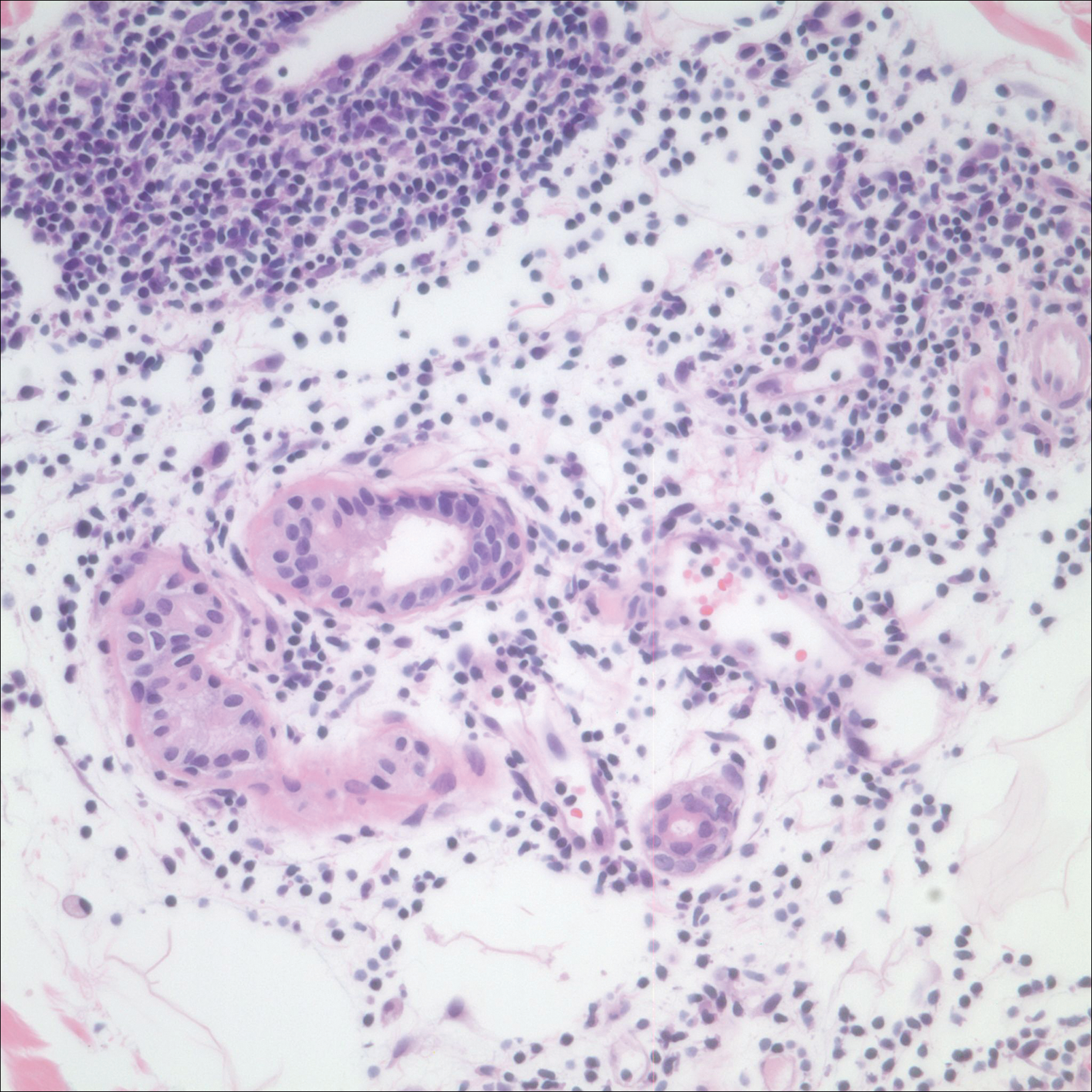
After a trial of oral valacyclovir for presumed herpes simplex infection provided no relief, a punch biopsy of the left buttock was performed, which revealed a cell-poor interface dermatitis with superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic infiltrates (Figure 2). Perieccrine lymphocytes were present in a small portion of the reticular dermis (Figure 3). The patient revealed she had been sitting on ice packs for several hours daily since the lumbar spinal fusion surgery 5 years prior to alleviate chronic low back pain.
Based on the clinicopathologic correlation, a diagnosis of perniosis secondary to ice pack therapy was made. An evaluation for concomitant or underlying connective tissue disease (CTD) including a complete blood cell count with sedimentation rate, antinuclear antibodies (ANAs), serum protein electrophoresis, and serum levels of cryoglobulins and complement components was unremarkable. Our patient was treated with simple analgesia and was encouraged to avoid direct contact with ice packs for extended periods of time. Because of her low back pain, she continued to use ice packs but readjusted them sporadically and decreased frequency of use. She had complete resolution of the lesions at 6-month follow-up.