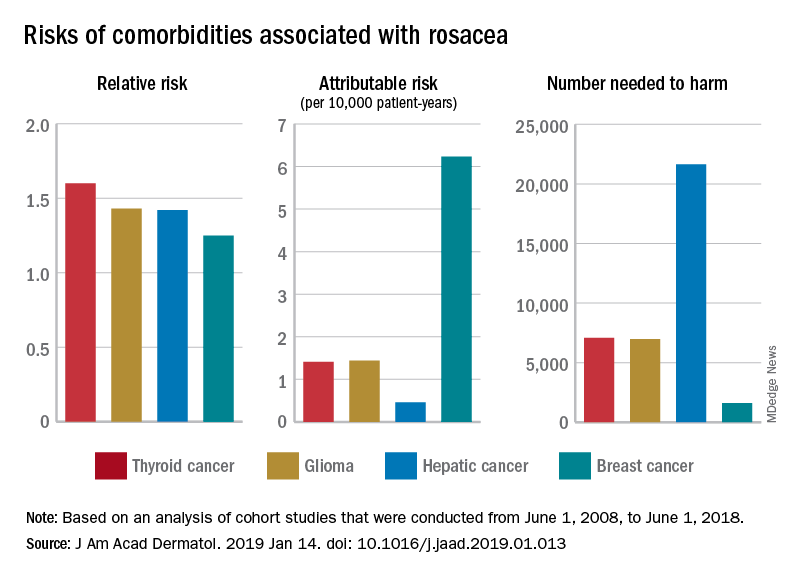
Rosacea has several known comorbidities, but the widespread use of their relative, rather than absolute, risks “may result in overestimation of the clinical importance of exposures,” Leonardo A. Tjahjono and his associates wrote.
For a patient with rosacea, the relative risk of hepatic cancer is 1.42, but the attributable risk and the number needed to harm (NNH), which provide “a clearer, absolute picture regarding the association” with rosacea, are 0.46 per 10,000 patient-years and 21,645, respectively. The relative risk of comorbid breast cancer is 1.25, compared with an attributable risk of 6.23 per 10,000 patient-years and an NNH of 1,606, Mr. Tjahjono of Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C., and his associates reported in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Physician misconceptions based on patients’ relative risks of comorbidities may lead to increased cancer screenings, which “can provide great benefit in a proper context; however, they are not without consequences. For example, 0.7 % of liver biopsies result in severe intraperitoneal hematoma,” the investigators said.
The absolute risks – calculated by the investigators using cohort studies that were conducted from June 1, 2008, to June 1, 2018 – present “a better understanding regarding rosacea’s impact on public health and clinical settings, “ they wrote.
SOURCE: Tjahjono LA et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.013.