Dermpath Diagnosis

Clear Cell Fibrous Papule
A fibrous papule is a common benign lesion that usually presents in adults on the face, especially on the lower portion of the nose.
Victoria Vaughan, BA; Tammie Ferringer, MD
Ms. Vaughan is from the Medical College of Georgia, Georgia Regents University, Augusta. Dr. Ferringer is from the Departments of Dermatology and Laboratory Medicine, Geisinger Medical Center, Danville, Pennsylvania.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Victoria Vaughan, BA, Medical College of Georgia, Georgia Regents University, 1004 Chafee Ave, FH-100, Augusta, GA 30904 (viclava@gmail.com).

Granular cell tumors (GCTs) tend to present as solitary nodules, not uncommonly affecting the dorsum of the tongue but also involving the skin, breasts, and internal organs. Cutaneous GCTs typically present as 0.5- to 3-cm firm nodules with a verrucous or eroded surface. They most commonly present in dark-skinned, middle-aged women but have been reported in all age groups and in both sexes. The differential diagnosis includes lepromatous leprosy, mastocytoma, reticulohistiocytoma, and xanthelasma.
Granular cell tumors (GCTs) tend to present as solitary nodules, not uncommonly affecting the dorsum of the tongue but also involving the skin, breasts, and internal organs.1 Cutaneous GCTs typically present as 0.5- to 3-cm firm nodules with a verrucous or eroded surface.2 They most commonly present in dark-skinned, middle-aged women but have been reported in all age groups and in both sexes.3 Multiple GCTs are reported in up to 25% of cases, rarely in association with LEOPARD syndrome (consisting of lentigines, electrocardiographic abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pulmonary stenosis, abnormalities of genitalia, retardation of growth, and deafness).4 Granular cell tumors generally are benign with a metastatic rate of approximately 3%.2
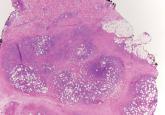
Granular cell tumors are histopathologically characterized by sheets of large polygonal cells with small, round, central nuclei; cytoplasm that is eosinophilic, coarse, and granular, as well as periodic acid–Schiff positive and diastase resistant; and distinct cytoplasmic membranes (Figure 1). Pustulo-ovoid bodies of Milian often generally appear as larger eosinophilic granules surrounded by a clear halo (Figure 2).5 Increased mitotic activity, a high nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, pleomorphism, and necrosis suggest malignancy.6
Figure 1. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia and sheets of polygonal cells with light pink cytoplasm of a granular cell tumor (H&E, original magnification |
Figure 2. Sheets of large polygonal cells with central nuclei; coarse, eosinophilic, granular cytoplasm; and large eosinophilic cytoplasmic pustulo-ovoid bodies of Milian characterize a granular cell tumor (H&E, original magnification ×600). |
Lepromatous leprosy is characterized by sheets of histiocytes with vacuolated cytoplasm, some with clumped amphophilic bacilli known as globi (Figure 3). Mastocytoma can be distinguished from GCTs by the “fried egg” appearance of the mast cells (Figure 4). Although mast cells have a pale granular cytoplasm, they are smaller and lack pustulo-ovoid bodies and the polygonal shape of GCT cells. Reticulohistiocytoma, on the other hand, has two-toned dusty rose ground glass histiocytes (Figure 5), and xanthelasma can be distinguished histologically from GCT by the presence of a foamy rather than granular cytoplasm (Figure 6).
Figure 3. Lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with amphophilic collections of mycobacteria (globi) in lepromatous leprosy (H&E, original magnification ×600). |
|
|
|

A fibrous papule is a common benign lesion that usually presents in adults on the face, especially on the lower portion of the nose.

Lipidized dermatofibromas most commonly are found on the ankles, which has led some authors to refer to these lesions as ankle-type fibrous...
Subcutaneous panniculitislike T-cell lymphoma is a cutaneous lymphoma of α and β phenotype cytotoxic T cells in which the neoplastic cells are...
