Article
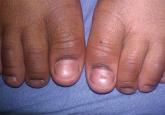
Bilateral Onychodystrophy in a Boy With a History of Isolated Lichen Striatus
Lichen striatus (LS) is a relatively rare and self-limited linear dermatosis of unknown etiology. It primarily affects children, with more than 50...
From the Faculty of Medicine, Ege University, Izmir, Turkey. Drs. Ceylan, Tuna, Ertam, and Günaydın are from the Department of Dermatology and Venereology. Drs. Kantar, Aksoylar, and Çetingül are from the Department of Pediatric Oncology.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: llgen Ertam, MD, Ege University, Department of Dermatology and Venereology, 35040 Bornova, Izmir, Turkey (ilgen.ertam@ege.edu.tr).

Of 65 patients, 62 completed the study and were included in the analysis. Three patients were excluded from the results, as 2 patients died during treatment and 1 patient withdrew from the study prior to completion. Twenty-seven (43.5%) patients were female and 35 (56.5%) were male ranging in age from 1 to 17 years (mean age, 8.14 years; median age [standard deviation], 7.25 [5.42] years). There were 31 (50%) patients in the hematological malignancies group, 11 (17.7%) in the solid organ tumors group, 10 (16.1%) in the bone and soft tissue tumors group, and 9 (14.5%) in the central nervous system tumors group; Langerhans cell histiocytosis was diagnosed in 1 (1.6%) patient. Hodgkin lymphoma made up 29.0% (n=9) of hematological malignancies. Other hematological malignancies included acute myeloblastic leukemia (n=7 [22.5%]), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (n=7 [22.5%]), T-cell lymphoma (n=5 [16.1%]), non-Hodgkin lym-phoma (n=1 [3.2%]), anaplastic giant cell lymphoma (n=1 [3.2%]), and diffuse giant cell lymphoma (n=1 [3.2%]).
In addition to chemotherapeutic agents, 7 (11.3%) patients in this study also received antibiotics and 3 (4.8%) received antivirals. The most frequently employed chemotherapeutic agents were vincristine, methotrexate, cytarabine, etoposide, and dexamethasone. Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, ifosfamide, asparaginase, carboplatin, procarbazine, daunorubicin, actinomycin D, vinblastine, cisplatin, bleomycin, idarubicin, 6-mercaptopurine, temozolamide, and cyclosporine also were administered. The most commonly encountered dermatological side effects were alopecia, xeroderma, inflammatory skin lesions, infectious lesions, and mucositis, respectively (Table 1). Cutaneous side effects were frequently seen at months 1 and 3 of treatment.
The most commonly encountered dermatologic side effect was alopecia (31/62 [50%]). Anagen effluvium (Figure 1) was detected in half of the cases, while complete scalp hair loss was noted in the rest. Alopecia was encountered more commonly in cases with central nervous system tumors (5/9 [55.6%]) and hematological malignancies (16/31 [51.6%])(Table 2).
The second most commonly encountered side effect was xeroderma (29/62 [46.8%])(Figure 2). This side effect was most commonly encountered in patients with solid organ tumors (6/11 [54.5%]) and central nervous system tumors (4/9 [44.4%]), and occurred less frequently with bone and soft tissue tumors (4/10 [40.0%]).
Findings of eczema accounted for the majority of inflammatory lesions, which were the third most commonly encountered side effects. Among 24 cases of inflammatory skin lesions, 8 patients (33.3%) had diaper dermatitis, 7 (29.2%) had asteatotic eczema, 6 (25.0%) had contact dermatitis, and 3 (12.5%) had seborrheic dermatitis. Although inflammatory skin lesions were commonly encountered in patients with hematological malignancies (14/31 [45.2%]), the difference was not statistically significant.
Mucositis and oral aphthous lesions were observed in 15 (24.2%) and 3 (4.8%) patients, respectively. Nail signs were noted in 10 (16.1%) patients; 4 patients had transverse streaks on the nail plates, 3 had linear streaks, 2 had nail plate fragility, and 1 had increased pigmentation at the nail bed and periungual area. Figure 3 shows linear streaks on the nail plate. These side effects were most commonly encountered in patients with solid organ tumors (5/11 [45.5%]); however, the difference was not statistically significant when compared with the other diagnostic groups.
Dermatologic signs with infectious origins were detected in 15 (24.2%) patients; 2 patients had herpes labialis, 2 had verruca vulgaris, 3 had bacterial folliculitis, 1 had acute paronychia, 1 had soft tissue infection, 2 had tinea versicolor, and 4 had mucocutaneous candidiasis. Dermatologic side effects due to infectious causes were more commonly encountered in patients with bone and soft tissue tumors (4/11 [36.4%]), and the difference was statistically significant when compared with the other diagnostic groups (P=.04).
Petechiae and ecchymotic lesions were present in 13 (21.0%) patients. These side effects occurred mainly in the first month of chemotherapy, namely when patients were in the pancytopenic phase.

Lichen striatus (LS) is a relatively rare and self-limited linear dermatosis of unknown etiology. It primarily affects children, with more than 50...

Dr. Nanette Silverberg discusses melanoma screening in children.
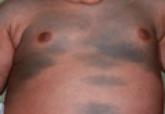
Dermal melanocytosis is thought to be the result of a defect in melanoblast migration during embryogenesis and is characterized by the presence of...
