The Cox-Maze IV procedure (CMPIV) has become the standard for surgical ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF), yet little information has been available on how late outcomes compare with catheter-based ablation. A recent analysis of 576 procedures found that after 5 years, most people who had the procedure remained free of atrial tachyarrhythmias and anticoagulation.
The study, by investigators from Washington University, Barnes-Jewish Hospital in St. Louis, was published in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;150:1168-78). The researchers first presented the study in April at the American Association for Thoracic Surgery meeting in Seattle.
“The results of the CMPIV remain superior to those reported for catheter ablation and other forms of surgical AF ablation, especially for patients with persistent or long-standing AF,” wrote Dr. Matthew C. Henn and his colleagues.
They set out to evaluate late outcomes after CMPIV using current consensus definitions of treatment failure, noting that such outcomes had yet to be reported. They followed 576 patients with atrial fibrillation who had a CMPIV from 2002 to 2014 and compared long-term freedom from atrial fibrillation on and off antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) across various subgroups. They included the left-sided CMPIV lesion in the analysis because, they said, it had success rates similar to those of biatrial CMPIV.
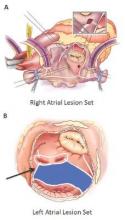
The Cox-Maze procedure was first introduced by Dr. James Cox in 1987 and updated from the original “cut-and-sew” technique in 2002 to combine bipolar radiofrequency and cryothermal ablation lines in place of most surgical incisions. This iteration was called the Cox-Maze IV procedure. In 2005, CMPIV was modified to include a superior connecting lesion, which formed a “box lesion” by completely isolating the entire posterior left atrium. The study included 512 people who underwent the “box lesion” set procedure.
“The modifications of the CMPIV have allowed it to be performed through a right minithoracotomy (RMT) approach, which has further reduced major morbidity, mortality, and hospital stay compared to those who underwent sternotomy while enjoying equivalent outcomes with regards to freedom from AF,” wrote Dr. Henn and his coauthors.
In the entire cohort, the overall freedom from atrial tachyarrhythmias (ATAs) and anticoagulation were 92% at 1 year, 88% at 2 years, 87% at 3 years, 81% at 4 years, and 73% at 5 years. Overall freedom from ATAs off antiarrhythmic drugs for the entire cohort ranged from 81% at 1 year to 61% at 5 years, and freedom from anticoagulation ranged from 65% at 1 year to 55% at 5 years.
“Freedoms from ATAs on or off AADs were significantly higher in those who underwent box lesion sets when compared to those who did not at 5 years,” noted Dr. Henn and his coauthors. Among the box lesion set group, 78% of those on AADs remained free of ATAs vs. 45% in the non–box lesion set group, and for those off AADs, 66% had no ATAs at 5 years while 33% of the non–box lesion set group did.
Of the overall study population, 41% had paroxysmal AF and 58% had nonparoxysmal AF. Among the latter group, 20% had persistent and 80% had long-standing persistent AF. The nonparoxysmal AF group had a longer duration of preoperative AF, larger left atria and more failed catheter ablations, Dr. Henn and coauthors reported. But, the study showed no differences in freedom from atrial fibrillation on or off AADs at 5 years between patients with paroxysmal AF or persistent/long-standing persistent AF, or between those who underwent stand-alone procedure and those who received a concomitant Cox-Maze procedure. Among those who had a concomitant procedure, 50% had a concomitant mitral valve procedure and 23% had coronary artery bypass grafting.
“The CMPIV results in our series were better than what has been achieved with catheter ablation,” the researchers wrote. They cited studies that showed arrhythmia-free survival after a single ablation procedure ranging from 17% to 29% and “equally poor results.” (Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2015;8:18-24; J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:160-166; J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e004549.)
“The CMPIV remains the most successful surgical treatment for AF, even in patients with non-paroxysmal AF and regardless of the complexity of the concomitant procedures,” Dr. Henn and his coauthors concluded.