Lanadelumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits kallikrein, reduced attacks of hereditary angioedema with C1 inhibitor deficiency by 88%-100% in a small, phase I trial.
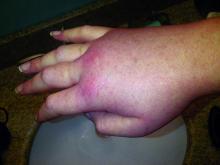
Hereditary angioedema with C1 inhibitor deficiency is a rare disorder characterized by unpredictable, recurrent, and potentially life-threatening episodes of subcutaneous or submucosal swelling, typically affecting the hands and feet, abdomen, face, larynx, or genitourinary tract. It is caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of the C1 inhibitor, which regulates the complement, coagulation, and kallikrein-kinin cascades.
In affected patients, “activation of the kallikrein-kinin cascade leads to uncontrolled generation of plasma kallikrein and consequent proteolysis of high-molecular-weight kininogen. This results in excessive bradykinin production, which causes vasodilation, vascular leakage, and subsequent angioedema and pain,” said Aleena Banerji, MD, of the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and her associates (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 23;376[8]:717-728).They performed a multicenter, double-blind, randomized study to assess the safety and adverse-effect profile of four doses of this new agent or placebo in 37 adults (aged 18-71 years, mean age, 39.9 years) who received two injections, 2 weeks apart, and were followed for 6 weeks. Given their histories, all the study participants had “a reasonable probability of having one or more attacks” during the study period, the researchers noted.
Four participants received a 30-mg dose, 4 received a 100-mg dose, 5 received a 300-mg dose, 11 received a 400-mg dose, and 13 received placebo.
There were no serious adverse events, no deaths, and no discontinuations of the study medication because of an adverse effect. One patient each developed severe adverse events: pain at the injection site that lasted for 1 minute and headache plus night sweats.
Pharmacodynamic assessments showed that lanadelumab inhibited kallikrein in a linear, dose-dependent manner, and the two higher doses reduced levels of cleaved high-molecular-weight kininogen to those reported in healthy control subjects. At the same time, the two higher doses decreased the number of attacks by 88% and 100%, respectively, compared with placebo.
All the patients in the 300-mg group and 9 of the 11 in the 400-mg group had no attacks during the study period, the investigators said.
These findings “provide proof of concept that lanadelumab has the potential to correct the pathophysiological abnormality underlying attacks of angioedema and may be a new therapeutic option for hereditary angioedema with C1 inhibitor deficiency,” Dr. Banerji and her associates said.
The HELP Study, a phase III trial assessing the safety and efficacy of 6 months of lanadelumab treatment, is now underway, they added.
The trial was sponsored by Dyax, which also participated in the study design, data collection and interpretation, and writing of the results. Dr. Banerji reported ties to Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, CSL Behring, Dyax, and Shire; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
dermnews@frontlinemedcom.com