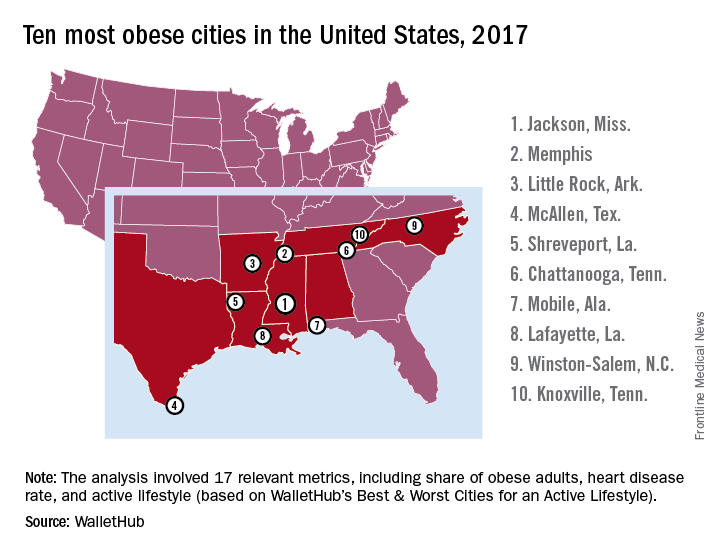
Jackson, Miss., is the most obese city in the United States for 2017, according to the personal finance website WalletHub.
The city topped the ranking of the 100 heaviest metro areas in the country with a score of 84.9 out of a possible 100 points based on 17 key metrics in three broad categories: obese and overweight people (50 points), weight-related health problems (30 points), and health environment (20 points), according to WalletHub.
Among all cities included in the analysis, Jackson had the highest percentage of diabetic adults, the second highest percentage of physically inactive adults and adults eating less than one serving of fruits/vegetables per day, and the fourth highest percentage of adults with high blood pressure, WalletHub reported.The second-most obese city for 2017 is Memphis, with Little Rock, Ark.; McAllen, Tex.; and Shreveport, La., occupying the rest of the top five. All of the cities in the top 10 – all of the cities in the top 20, actually – are located in the South, with the first non–Southern city (Indianapolis) making its appearance at number 21, the WalletHub analysis shows. At number 100 in the rankings is Seattle/Tacoma.
Data for the analysis came from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, County Health Rankings, the Department of Agriculture’s Economic Research Service, the Child and Adolescent Health Measurement Initiative, the Trust for America’s Health, and WalletHub’s own research, including its report Best & Worst Cities for an Active Lifestyle.