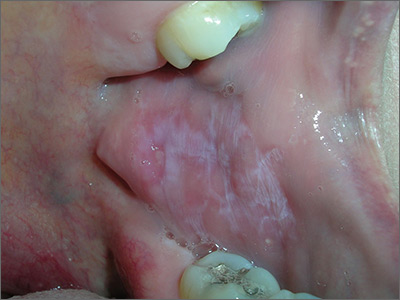
Based on the presence of bilateral Wickham striae, the FP diagnosed oral lichen planus in this patient. If the pattern were unilateral or the patient had a history of tobacco or alcohol use, the FP’s suspicion would have turned to a diagnosis of oral leukoplakia—a precursor to squamous cell carcinoma.
A mid-potency topical steroid is a good initial treatment for oral lichen planus. Triamcinolone can be prescribed in an oral base, but because it is very thick and sticky, it is better for local application to small areas around the teeth. Other treatment options include a gel or ointment, but these are not necessarily better inside the mouth. Most patients will find the cream easier to apply, even if it doesn’t taste good. If a mid-potency steroid doesn’t work, it is possible to use a high-potency steroid and change the vehicle according to the patient’s preference.
The FP in this case prescribed topical triamcinolone 0.1% cream to be applied twice daily to the buccal mucosa. At follow-up one month later, the patient’s cheeks no longer hurt, and the white Wickham striae were less visible. The FP instructed the patient to continue using the topical steroid twice daily as needed, and to return if her condition worsened.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Kraft RL, Usatine R. Lichen planus. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013: 901-909.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com