A concerted a lethal disease affecting one-quarter of the world’s population by the year 2030.
On September 26 the United Nations General Assembly will convene a high-level meeting of global stakeholders to solidify the eradication plan, addressing the global crisis of tuberculosis (TB), the world’s most deadly infectious disease.
“We must seize the moment,” said Tereza Kasaeva, MD, director of the World Health Organization’s global TB program, speaking at a telebriefing and press conference accompanying the release of the World Health Organization’s annual global tuberculosis report. “It’s unacceptable in the 21st century that millions lose their lives to this preventable and curable disease.”
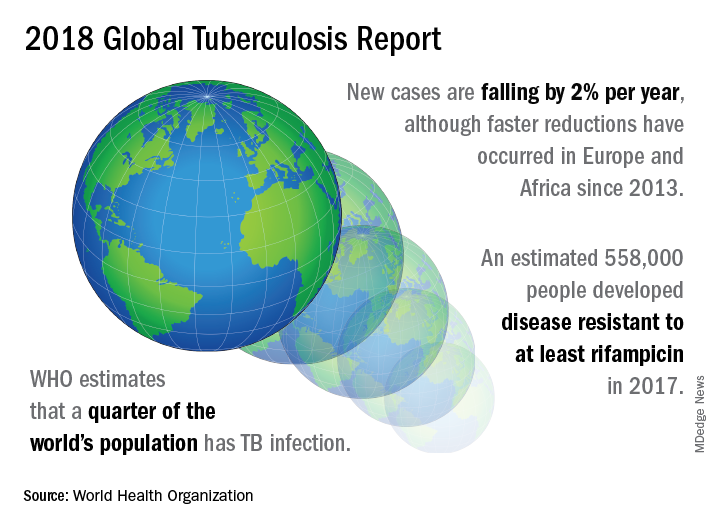
TB caused 1.6 million deaths globally in 2017, and the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that of the 10 million new cases of TB last year, 558,000 are multi-drug resistant (MDR) infections.
Though death rates and new cases are falling globally each year, significantly more resources are needed to boost access to preventive treatment for latent TB infection; “Most people needing it are not yet accessing care,” according to the press briefing accompanying the report.
A review and commentary on TB incubation and latency published in BMJ (2018;362:k2738 doi: 10.1136/bmj.k2738; e-pub 23 Aug 2018) has called into question the focus preventive treatment of latent cases at the expense of reaching those most likely to die from TB (e.g., HIV patients, children of individuals living with active TB). The authors state that “latent” TB is identified by indirect evidence of present or past infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis as inferred by a detectable adaptive immune response to M tuberculosis antigens. Active TB infection is overwhelmingly the result of a primary infection and almost always occurs within two years.
In order to meet the ambitious goal of TB eradication by the year 2030, treatment coverage must rise to 90% globally from the current 64%, according to the report.
Progress in southern Africa and in the Russian Federation, where efforts have led to a 30% reduction in TB mortality and a decrease in incidence of 5% per year, show that steep reductions in TB are possible when resources are brought to bear on the problem, said Dr. Kasaeva. “We should acknowledge that actions in some countries and regions show that progress can accelerate,” she said. Still, she noted, “Four thousand lives per day are lost to TB. Tuberculosis is the leading killer of people living with HIV, and the major cause of deaths related to antimicrobial resistance” at a global level.
Two thirds of all TB cases occur in eight countries, with India, China, and Indonesia leading this group. About half of the cases of MDR TB occur in India, China, and Russia, said Dr. Kasaeva, and globally only one in four individuals with MDR TB who need access to treatment have received it. “We need to urgently tackle the multidrug resistant TB public health crisis,” she said.
Major impediments to successful public health efforts against TB are underdiagnosis and underreporting: It is estimated that 3.6 million of 2017’s 10 million new cases were not officially recorded or reported. Countries where these problems are most serious include India, Indonesia, and Nigeria. Fewer than half of the children with TB are reported globally, according to the report.
People living with HIV/AIDS who are also infected with TB number nearly 1,000,000, but only about half of these were officially reported in 2017.
In terms of prevention priorities, WHO has recommended targeting treatment of latent TB in two groups: People living with HIV/AIDS, and children under the age of 5 years who live in households with TB-infected individuals.
“To enable these actions,” said Dr. Kasaeva, “we need strengthened commitments not just for TB care, but for overall health services. So the aim for universal coverage is real.” Underreporting is particularly prevalent in lower income countries with large unregulated private sectors, she said, though India and Indonesia have taken corrective steps to increase reporting.
A meaningful global initiative will not come cheap: The current annual shortfall in funding for TB prevention, diagnosis, and treatment is about $3.5 billion. By the year 2022, the gap between funding and what’s needed to stay on track for the 2030 target will be over $6 billion, said Dr. Kasaeva.
The best use of increased resources for TB eradication will be in locally focused efforts, said Irene Koek, MD, the United States Agency for International Development’s deputy administrator for global health. “It is likely that each region requires a tailored response.” Further, “to improve quality of care we need to ensure that services are patient centered,” she said at the press conference.
To that end, Dr. Koek expects that at the upcoming high-level meeting, the United Nations member states will be called on to develop an open framework, with clear accountability for monitoring and reviewing progress. The road forward should “celebrate accomplishments and acknowledge shortcomings,” she said. Some recent studies have shown that treatment success rates above 80% for patients with MDR TB can be achieved.
“Lessons learned from these experiences should be documented and shared in order to replicate success globally,” said Dr. Koek.
The United States, said Dr. Koek, is the leading global investor in TB research and treatment. “We welcome increased partnerships, especially with countries with the highest burden, to end global suffering from this disease.”
Eric Goosby, MD, the United Nations special envoy on TB, used his speaking time to lend some perspective to the social framework around TB’s longtime lethality.
There are aspects of TB infection that differentiate it from HIV/AIDS, said Dr. Goosby, who has spent most of his clinical and public health career on HIV/AIDS treatment and prevention. In contrast to an infection that at present requires a lifetime of treatment, TB can ordinarily be treated in 6 months, making it an unpleasant episode that an individual may be eager to move past. Additionally, the fact that TB has had a “hold on the world since the time of the ancient Egyptians” may paradoxically have served to lessen urgency in research and treatment efforts, he noted.
Dr. Goosby also spoke of the stigma surrounding TB, whose sufferers are likely to be facing dire poverty, malnutrition, and other infectious disease burdens. Civil society concerned with TB, he said, has spoken up “for those without a voice, for those who have difficulty advocating for themselves.”
Dr. Kasaeva agreed, noting that TB “affects the poorest of the poor, which makes it extraordinarily difficult for activism to come from that population.”
However, others have spoken for those affected, said Dr. Goosby. “The TB civil society has put its heart and soul this last year into gathering political will from leaders around the world…. It’s not a passive effort; it involves a lot of work.” During the past year of concerted effort, he said, “All of us have known the difficulty of pushing a political leader up that learning curve.”
As the upcoming high-level meeting approaches, those who have been working on the effort can feel the momentum, said Dr. Goosby. Still, he noted, “While there’s a significant step forward, this is not the time for a victory dance. This is really the time for a reflection...Do we understand the burden in our respective countries, and has the response been adequate?”
The goal for the meeting is to have leaders “step up to commit, not for one day, or for one meeting, but for the duration of the effort,” said Dr. Goosby. “We must make sure that the words that we hear next week from our leaders translate into action...Next week the world will say, ‘No more. No longer. No one is immune to TB. Tuberculosis is preventable; tuberculosis is treatable; tuberculosis is curable.’”
The BMJ commentary, by Marcel A. Behr, MD, of McGill International TB Centre, Infectious Diseases and Immunity in Global Health Program, McGill University Health Centre Research Institute, and his colleagues, recommend caution when building a prevention strategy around treating many millions of individuals with “latent” TB. They wrote, “Immunoreactivity to TB does not necessarily indicate the presence of live bacteria, as reactivity can persist after infection has been cleared. Classifying two billion people with evidence of immunoreactivity as having latent TB infection may divert fundamental research and public health interventions away from transmissible active TB disease and newly infected people at highest risk of progression to disease.”
This story was updated on 09/24/2018