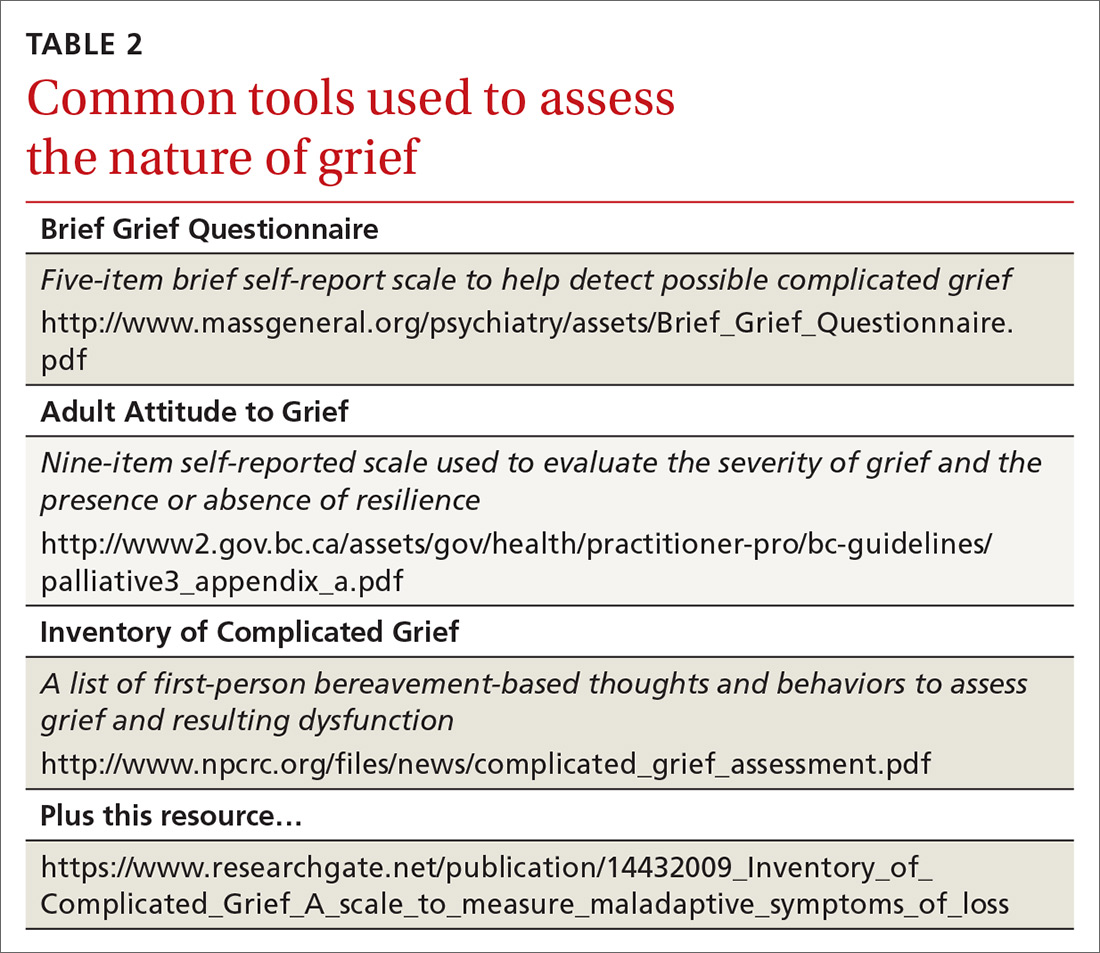
While no clinical measure is perfect, there are tools that can help in assessing patients for the possibility of complicated grief (TABLE 2). Also keep in mind that no measure can make a diagnosis of PCBD, as it is a clinical judgment, not a score on a scale. Furthermore, there is no measure that can accurately predict future complicated grief.6 In most busy practices, the Brief Grief Questionnaire (http://www.massgeneral.org/psychiatry/assets/Brief_Grief_Questionnaire.pdf ) would be the easiest tool to administer, but a case could be made for any of the measures.
Treatment hallmarks
The literature base emphasizes that PCBD treatment requires a different focus than that applied to uncomplicated grief. And while most people with major depression will respond to medication and psychotherapy, there are provisos to keep in mind when depression is associated with complicated grief.
Complicated grief treatment (CGT) has been studied extensively.6 This treatment combines some of the tenets of evidence-based PTSD treatments, interpersonal therapy for grief, and cognitive behavioral therapy. CGT is generally an individual treatment, although group therapy using some of its tenets can also be effective. According to complicated grief researchers, tasks to accomplish in CGT include establishing a “new normal” following the loss, promoting self-regulation in the grieving, building social connections, and setting aspirational goals for the future.6 Other goals are to revisit the world, tell stories of the past, and relive old memories in a more positive light. Common suggestions in CGT that run parallel to conventional thoughts on dealing with grief include increasing time outside the home, getting more involved interpersonally, and increasing mindfulness-based practices.
A second-line evidence-based treatment for PCBD is the use of selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).6 Some studies have found benefit from SSRI treatment, although the findings are preliminary and modest.12 One observational study examined patients who had recently experienced loss and were receiving CGT with or without medication. Researchers found that CGT with medication (citalopram) led to a 61% positive response rate while CGT alone led to a 41% response rate.13 Thus, findings revealed some benefit to combining an antidepressant with CGT, indicating that SSRIs may be helpful as an adjunct treatment.
THE CASE
Al was treated for complicated grief by his family physician and a psychologist for approximately a year. He responded well to an SSRI and received psychotherapy that focused on the tenets of CGT. Prior to his last psychotherapy visit, he reported leaving the house regularly to dine at restaurants and meet up with co-workers after hours. He said, “I still miss Vera quite a bit, but I know that I feel better.”
CORRESPONDENCE
Scott A. Fields, PhD, 3200 MacCorkle Avenue Southeast, 5th Floor, Robert C. Byrd Clinical Teaching Center, Department of Family Medicine, Charleston, WV 25304; sfields@hsc.wvu.edu