EVIDENCE SUMMARY
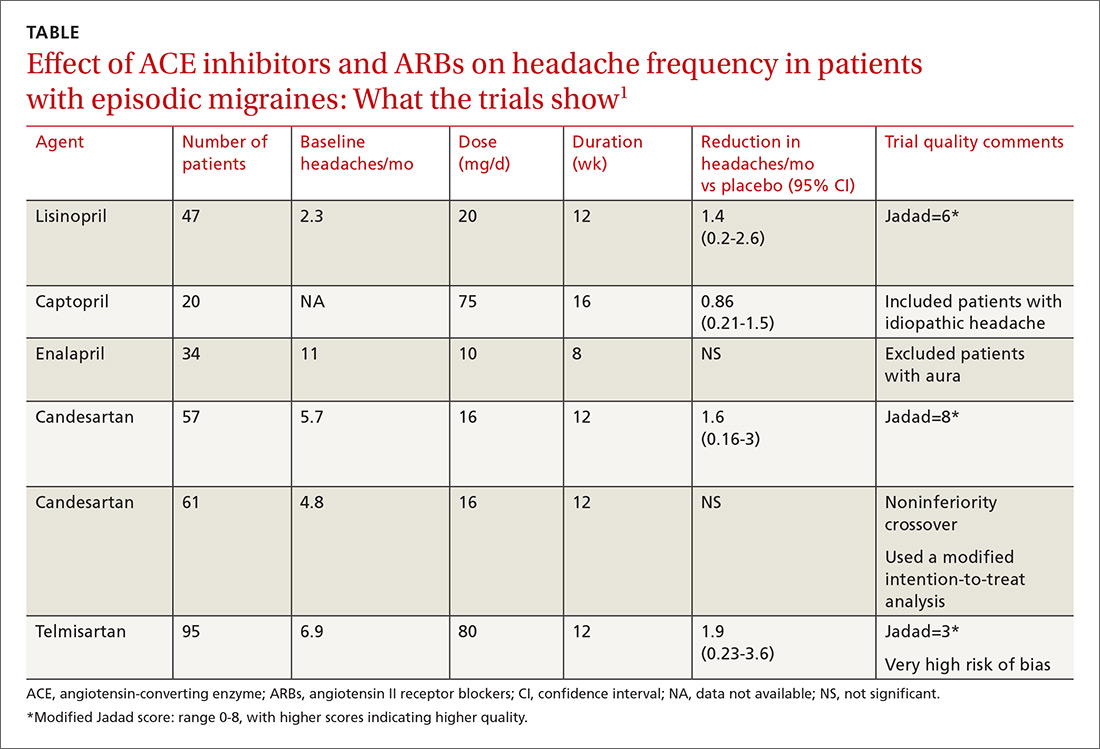
A network meta-analysis of 179 placebo-controlled trials of medications to treat migraine1 headache identified 3 trials involving ACE inhibitors and 3 involving ARBs (TABLE1). The authors of the meta-analysis gave 2 trials (one of lisinopril and one of candesartan) relatively high scores for methodologic quality.
Lisinopril reduces hours, days with headache and days with migraine
The first, a placebo-controlled lisinopril crossover trial, included 60 patients, 19 to 59 years of age, who experienced migraines with or without auras 2 to 6 times per month.2 Thirty patients received lisinopril 10 mg once daily for 1 week followed by 20 mg once daily (using 10-mg tablets) for 11 weeks. The other 30 patients received a similarly titrated placebo for 12 weeks. After a 2-week washout period, the groups were given the other therapy. Patients took triptan medications and analgesics as needed. Primary outcomes, extracted from headache diaries, included the number of hours and days with headache (of any type) and number of days with migraine specifically.
Out of the initial 60 participants, 47 completed the study. Using intention-to-treat analysis, lisinopril therapy resulted in fewer hours with headache (162 vs 138, a 15% difference; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0-30), fewer days with headache (25 vs 21, a 16% difference; 95% CI, 5-27), and fewer days with migraine (19 vs 15, a 22% change; 95% CI, 11-33), compared with placebo. Three patients discontinued lisinopril because of adverse events. Mean blood pressure reduction with lisinopril was 7 mm Hg systolic and 5 mm Hg diastolic more than placebo (P<.0001 for both comparisons).
Candesartan also decreases headaches and migraine
The other study given a high methodologic quality score by the network-meta-analysis authors was a placebo-controlled candesartan crossover trial.3 It enrolled 60 patients, 18 to 65 years of age, who experienced migraines with or without auras 2 to 6 times per month.
Thirty patients received 16 mg candesartan daily for 12 weeks, followed by a 4-week washout period before taking a placebo tablet daily for 12 weeks. The other 30 received placebo followed by candesartan. Patients took triptan medications and analgesics as needed. The primary outcome measure was days with headache, recorded by patients using daily diaries. Three patients didn’t complete the study.
Using intention-to-treat analysis, the mean number of days with headache was 18.5 with placebo and 13.6 with candesartan (P=.001). Secondary end points that also favored candesartan were hours with migraine (92 vs 59; P<.001), hours with headache (139 vs 95; P<.001), days with migraine (13 vs 9; P<.001), and days of sick leave (3.9 vs 1.4; P=.01). Adverse events, including dizziness, were similar with candesartan and placebo. Mean blood pressure reduction with candesartan was 11 mm Hg systolic and 7 mm Hg diastolic over placebo (P<.001 for both comparisons).
Continue to: Overall both drugs have a significant effect on number of headaches