A clinical diagnosis with a large differential
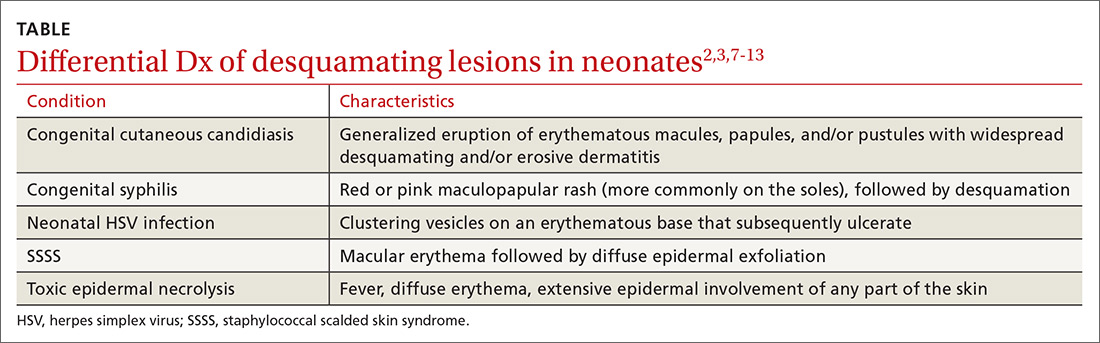
While biopsy rarely is required, it may be helpful to distinguish SSSS from other entities in the differential diagnosis (TABLE2,3,7-13).
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is a rare and life-threatening desquamating disease nearly always caused by a reaction to medications, including antibiotics. TEN can occur at any age. Fever, diffuse erythema, and extensive epidermal involvement (>30% of skin) differentiate TEN from Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), which affects less than 10% of the epidermis. It is worth mentioning that TEN and SJS are now considered to be a spectrum of one disease, and an overlap syndrome has been described with 10% to 30% of skin affected.8 Diagnosis is made clinically, although skin biopsy routinely is performed.7,9
Congenital syphilis features a red or pink maculopapular rash followed by desquamation. Lesions are more common on the soles.10 Desquamation or ulcerative skin lesions should be examined for spirochetes.11 A quantitative, nontreponemal test such as the rapid plasma reagin (RPR) or the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) will be positive in most infants if exposed through the placenta, but antibodies will disappear in uninfected infants by 6 months of age.8
Congenital cutaneous candidiasis presents with a generalized eruption of erythematous macules, papules, and/or pustules with widespread desquamating and/or erosive dermatitis. Premature neonates with extremely low birth weight are at higher risk.13 Diagnosis is confirmed on microscopy by the presence of Candida albicans spores in skin scrapings.13
Neonatal herpes simplex virus (HSV) symptoms typically appear between 1 and 3 weeks of life, with 60% to 70% of cases presenting with classic clustering vesicles on an erythematous base.14 Diagnosis is made with HSV viral culture or polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Continue to: SSSS should be considered a pediatrics emergency